The Importance of Promoting Digital Citizenship for Students

With school closures and isolation from their peers, many students depend now more than ever on mobile devices and computers for learning and socializing. Digital technology may offer many advantages, but it also poses risks. That’s why educators support digital citizenship for students.

Topics Related to Digital Citizenship for Students
As digital technology grows more sophisticated, so do cyberthreats. To keep up, students need to learn about digital citizenship: the use of digital devices and the internet in responsible and productive ways.
Digital Literacy
Today, people use technology to manage their bank accounts, stay in touch with friends, and keep up with work obligations. To succeed in a world dominated by technology, students must become digitally literate: They must be able to efficiently and securely use technology, interactive digital tools, and search networks.
For example, when students read online, they access embedded hyperlinks and videos. When they write a paper, they use search engines. Digitally literate students know how to not only find digital content but also distinguish it so that they can use it appropriately. This can mean, for example, differentiating sponsored content from a legitimate news article.
Almost every career involves using digital technology, so teaching students digital literacy prepares them for their future as well.
Digital Etiquette
Digital etiquette, sometimes called netiquette, refers to treating others online with respect. Thus, cyberbullying is never appropriate. Students should learn basic rules that guide their behavior and help make the online world a decent place for themselves and others.
Netiquette rules vary according to the online environment. For example, in an online classroom, students learn to carefully review their writing before posting it. They also learn to avoid abbreviations they may use when texting and stay on topic during discussions, just as they would in a physical classroom.
On social media platforms, students should follow the same rules of decorum and politeness expected of them in face-to-face encounters. This includes avoiding offensive language, as well as respecting people’s privacy by not forwarding information they don’t have permission to share. Educators must remind students that their use of technology affects others—a living, breathing person is at the receiving end of their texts, posts, and tweets.
Digital Health
Technology has changed how many people communicate and spend their time. Tweens spend almost five hours a day looking at screens, and teens spend more than seven, according to a report from Common Sense. That time doesn’t include screen time for school.
Balancing one’s use of technology with other aspects of life requires thoughtful consideration. How much time should students spend using digital devices? What should they use technology for? What do healthy interactions with technology look like?
Digital health means making choices about how to best interact with technology, so it doesn’t negatively affect important aspects of people’s lives, such as their physical activity, mental health, and sleep.
Students need support in building healthy relationships with technology. Educators can teach students about healthy digital technology habits and help them recognize how technology can potentially negatively affect their well-being. For example, teachers can engage their students in discussions about how to use digital tools to pursue personal goals, such as fitness. They may also discuss the dangers of excessive screen time and techniques students can use to limit the distractions that technology can create.
Digital Security
The digital world poses many types of dangers to students. In addition to learning about security issues related to identity theft, hacking, scams, and viruses, students need to learn about their digital footprints. Digital footprints can leave students vulnerable if they don’t have a clear set of guidelines about what to share.
Students may give out their locations, birthdates, telephone numbers, or other personal information that can put them in danger. They may also overshare about the daily activities of their lives, their private feelings, or inappropriate photos without fully appreciating the potential consequences of doing so.
Teaching digital citizenship to students involves helping them understand the permanence of their digital footprints and how to avoid harming themselves or others with what they post online. They can be encouraged to selectively share on social media. Teaching digital citizenship also involves training students to look out for online scams and malware.
This means educating students about:
- Effective internet safety practices, such as creating strong passwords and not opening files from unknown senders
- How to use privacy settings (controls that allow them to determine the use and storage of their information)
Examples of Lessons on Digital Citizenship for Students
Lessons about digital citizenship vary according to grade level. Educators must consider which topics to address and how to approach them based on a student’s age. For example, lessons for younger students in elementary school may start with a focus on safety. Teachers may introduce topics such as cyberbullying to older elementary students.
In higher grade levels, educators tackle more complex topics.
Digital Security for First Graders
Young students need to understand that just like in the real world, they need to stay safe online. Educators can teach young students how to choose age-appropriate websites and apps by using the familiar concept of a stoplight.
First, teachers can help students divide websites and apps into three categories:
- Green (safe websites and apps)
- Yellow (websites and apps they’re unsure of)
- Red (websites and apps not meant for children their age)
For each type of website, educators should give students examples of what they might find there. For example, on green websites and apps, students might find fun pictures and activities for kids, while on red websites and apps students may see pictures that look like they’re for adults or places to chat with strangers.
After identifying types of websites and apps, educators can invite students to share green and yellow websites and apps that they’ve visited with the class and each other. Educators can also ask students if they’ve visited a red website and how they knew it was red. Then, students should learn how to respond to yellow and red websites and apps.
To reinforce the lesson’s concepts, educators can introduce a game in which students are given descriptions of websites, and they have to determine if they classify as green, yellow, or red. Finally, to wrap up, educators can invite students to reflect on what they should do if they find themselves at a red website by writing and drawing a picture.
Digital Health for Eleventh Graders
High school students need nuanced lessons that ask them to think deeply about their relationship to technology. Teaching these students to recognize how technology is designed to “lock in” their attention—making some people feel “addicted”—gives students a chance to better understand the role technology plays in their lives. This offers a solid starting point for making intentional choices about technology use.
Educators can begin by having students consider if they’re addicted to their devices. Using a T-chart headed “Addicted/Not Addicted,” students list behaviors and share them with the class.
Next, students can read and analyze articles that argue for and against the idea that people are addicted to their devices. Using graphic organizers, students track the evidence presented in each article. Then, they share their own opinions on the issue in small groups before joining a larger class discussion exploring the issue.
Explore How Educators Prepare Students to Become Good Digital Citizens
Today, educators must consider how to prepare their students to function in a world increasingly dominated by technology. A curriculum focused on digital citizenship provides students with invaluable knowledge about how to stay safe and thrive.
Learn more about how today’s digital landscape is impacting communities and culture by watching Dr. Cynthia Miller-Idriss’ interview for American University’s Big Ideas in Education speaker series.
Explore how American University’s online Master of Education in Education Policy and Leadership trains educators to promote digital citizenship for students.
LGBTQ Cyberbullying: How to Combat Online Attacks Against Youth
Understanding the Digital Divide in Education
Why Is School Attendance Important? The Effects of Chronic Absenteeism
Common Sense, Can Media Be Addictive?
Common Sense, “Everything You Need to Teach Digital Citizenship”
Common Sense, Internet Traffic Light
Common Sense, The Common Sense Census: Media Use by Tweens and Teens, 2019
CORDIS, Exploring the Effect of Digital Technologies on Youth
EdSurge, “Kids Are Spending More of Their Lives Online. Teachers Can Help Them Understand Why.”
ISTE, “Digital Citizenship Is More Important Than Ever”
Microsoft, “Microsoft Report Shows Increasing Sophistication of Cyber Threats”
NEO Blog, “4 Steps Towards Digital Wellness for Students”
Renaissance, What Is Digital Literacy and Why Does It Matter?
Verywell Family, “5 Things to Teach Your Kids About Digital Etiquette”
Waterford.org, How to Teach Your Students the 9 Elements of Digital Citizenship
Request Information

AU Program Helper
This AI chatbot provides automated responses, which may not always be accurate. By continuing with this conversation, you agree that the contents of this chat session may be transcribed and retained. You also consent that this chat session and your interactions, including cookie usage, are subject to our privacy policy .

Essay on Digital Citizenship
Students are often asked to write an essay on Digital Citizenship in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Digital Citizenship
What is digital citizenship.
Digital Citizenship is about using the internet and digital devices in a responsible and respectful manner. It’s like being a good citizen in the digital world. We should use technology in a way that doesn’t harm others and helps us learn and grow.
Why is Digital Citizenship Important?
Digital Citizenship is important because we spend a lot of time online. We learn, play, and talk with friends on the internet. Being a good digital citizen helps us use the internet safely and respectfully. It also helps us understand the impact of our actions online.
Elements of Digital Citizenship
There are several parts to being a good digital citizen. These include understanding digital etiquette, knowing how to stay safe online, respecting other people’s digital rights, and being aware of your digital footprint. All these elements help us use technology in a positive and responsible way.
Role of Schools in Digital Citizenship
Schools play a big role in teaching digital citizenship. They help students understand how to use technology responsibly. Schools also teach us about the dangers of the internet and how to avoid them. This helps us become better digital citizens.
In conclusion, digital citizenship is about being responsible and respectful online. It’s an important skill for everyone who uses the internet. By understanding digital citizenship, we can make the digital world a better place for everyone.
250 Words Essay on Digital Citizenship
Understanding digital citizenship.
Digital Citizenship is about how we behave online. It’s like being a good citizen in the real world, but in the digital world. We need to know how to use the internet and digital tools safely, respectfully, and responsibly.
Importance of Digital Citizenship
The digital world is a big part of our lives. We use it to learn, play, and talk with friends. But just like in the real world, there are rules we need to follow. Being a good digital citizen means following these rules. This will keep us safe and help us use the internet in a good way.
Aspects of Digital Citizenship
There are many parts to being a good digital citizen. One part is online safety. This means keeping personal information private and not sharing passwords. Another part is being respectful online. This means not bullying or hurting others with words or actions. A third part is using the internet responsibly. This means not stealing or copying other people’s work.
Schools play a big role in teaching digital citizenship. They can teach us about online safety, respect, and responsibility. They can also help us learn how to use digital tools in a good way. This will prepare us for a world where the internet is a big part of work and life.
Being a good digital citizen is important. It helps us stay safe, respect others, and use the internet in a good way. Schools can help us learn about digital citizenship. This will prepare us for a world that is more and more digital.
500 Words Essay on Digital Citizenship
Digital Citizenship is all about using the internet and digital devices in a responsible and respectful way. It’s like being a good citizen in the real world, but online! It includes understanding how to stay safe online, respecting others’ rights and privacy, and using digital tools in a positive way.
In today’s world, we spend a lot of time online. We use the internet for school, to talk to friends, and even to play games. But just like in the real world, there are rules we need to follow. These rules help to keep us safe and make sure we are being kind to others. That’s why understanding digital citizenship is so important.
Staying Safe Online
One of the key parts of digital citizenship is knowing how to stay safe online. This means not sharing personal information like your address or phone number with people you don’t know. It also means being careful about clicking on links or downloading things from the internet. These could be tricks to get your information or harm your computer.
Respecting Others
Just like in the real world, it’s important to respect others online. This means not saying mean things or sharing someone else’s information without their permission. It also means understanding that not everything you read online is true. So, before you share something, make sure it’s accurate.
Positive Use of Digital Tools
Digital citizenship also includes using digital tools in a positive way. This could mean using the internet to learn new things or to help others. It could also mean creating things like art or music using digital tools. The key is to use these tools to make the world a better place, not to harm others or break the rules.
In conclusion, digital citizenship is a very important part of our lives. It helps us to stay safe online, respect others, and use digital tools in a positive way. By understanding and following the rules of digital citizenship, we can make the internet a better place for everyone.
Remember, being a good digital citizen is like being a good citizen in the real world. It’s all about respecting others, staying safe, and using tools in a positive way. So, the next time you go online, think about how you can be a good digital citizen!
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Digital Addiction
- Essay on Digestive System
- Essay on Different Religions
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Board And Staff
- Founder Isabelle Vladoiu
- Regional Directors
- All Courses
- Accreditation
- Digital Batch & Certification
- Professional Consultant
- Edu For Every Child
- Let Her Lead Program
- HRB Academy
- Nobody Left Behind
- Religious Freedom
- Rebuilding Ukraine Forum
- Disability Rights Summit 2022
- Youth Summit 2022
- Diplomacy And Human Rights2021
- Diplomacy And Human Rights2020
- Business Etiquette Secrets
- Human Rights Book
- Human Rights Coloring Book
- Blog Articles
- Volunteering
- Affiliate Program
- Religious Freedom Program

What is Digital Citizenship and Why is it Important?
May 26, 2022 by usidhr.org
The Covid-19 pandemic led to business and school closures which increased technology use for telework and online learning. Technology use is continuing to rise and it is increasingly important to be knowledgeable about how to use it correctly. Digital Citizenship is a way for business leaders, educators, governmental workers, and advocates to understand how we should use technology appropriately. Dr. Mike Ribble believes it’s “more than just a teaching tool, it is a way to prepare students for a society full of technology”[9]. With the correct use of the internet, students and adults can be more aware of human rights violations and how to protect themselves from fraud and disinformation. This article will cover the topics of technology, the importance of digital citizenship, and its implementation in society.
What is the impact of technology on youth?
Technology has had an enormous impact on a student’s learning. For example, it allowed them to have easy access to a larger amount of resources, it encouraged self-paced learning, it prepared them for careers in the tech industry, it improved their multitasking and problem-solving skills, and it can be used as a classroom tool to help students learn in new ways. With the rise of technology, children have started to use it from a very young age. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, children between the ages of 8-10 years old spend 8 hours per day on technology, while teenagers spend more than 11 hours per day[1]. Many kids have computers and tablets at home before they start school, but elementary schools also have the option of online learning because it provides more independence and flexibility to a student’s learning. Recently, due to school closures, many students reverted to online learning and that led to an increase in technology use. According to Pew Research Center, 93% of parents with children from kindergarten to 12th grade said their children had online learning during the pandemic[13]. Among these parents, 62% report that the online learning was very successful[13]. While young people have increased their use of technology in schools, they also spend a lot of their time on social media. According to the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 51% of teens between the ages of 13-17 use social media daily[15]. Social media platforms are often used as a news source by young people, so it is important to consider social media in Digital Citizenship Education. Concurrently, education also affects people's motivation to participate online. As students become more familiar with technology through their educational experiences, they are more likely to engage with digital platforms beyond just academic purposes. This increased engagement can lead to greater participation in online communities, discussions, and even activism, shaping not only their social interactions but also their role as informed digital citizens.
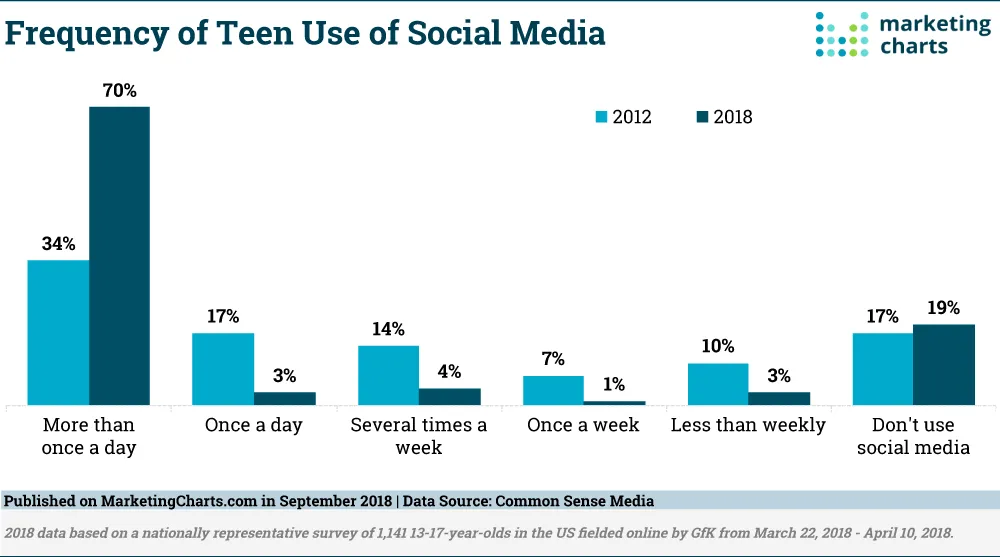
Source: Marketing Charts

Source: Pew Research Center
Digital citizenship.
What is Digital Citizenship? Digital Citizenship teaches individuals how to engage and participate in responsible ways of using technology, in order to protect themselves from internet dangers and respect each other’s human rights. According to the Council of Europe, digital citizenship can be defined as:
“The competent and positive engagement with digital technologies (creating, working, sharing, socializing, investigating, playing, communicating, and learning); participating actively and responsibly (values, skills, attitudes, knowledge) in communities (local, national, global) at all levels (political, economic, social, cultural, and intercultural); being involved in a double process of lifelong learning (in formal, informal, and non-formal settings) and continuously defending human dignity”[4].
It is important to note that Digital Citizenship allows citizens to use technology and humanity in a thoughtful and empathetic manner. In 2017, the Alaska Department of Education and Early Development (DEED) organized the first “Alaska Digital Citizenship Week” where they encouraged schools to implement education technology. It was held again the following year and it became a very popular program throughout the state, thus encouraging teachers to be the main guide for students and their families into developing their safety awareness in the digital world[8].
Why is digital citizenship important?
In 2021, The Federal Trade Commission received 2.8 million fraud reports[10]. With the large number of news and media sources, there is a rise in fraud, misinformation, and disinformation. This is why it is important that people choose credible and valid sources. According to a Research led by Stanford History Education Group director Joel Breakstone, PhD, and co-authored by Wineburg, out of a sample of 3,446 students from 14 different states, less than 10% verified an online source’s credentials with a quick web search[11]. Fraudsters and sources spreading misinformation and disinformation take advantage of people without technological knowledge. Digital Citizenship Education is necessary because it protects others from being vulnerable to these issues.
Digital Citizenship Education
Digital Citizenship Education encourages individuals to use their knowledge, skills, and understanding to protect and promote human rights online, such as freedom, privacy, and security. In this way, people become more aware of internet safety. This is because digital citizenship education teaches us how to use the internet responsibly and safely, and how to protect ourselves from fraudsters and predators.
In Canada, 99% of students from 4th to 11th grade use the internet at home[9]. With the rise of technology users, this shows the importance of being knowledgeable about fraud, misinformation,
and disinformation. As a result, Digital Citizenship Education was implemented in Saskatchewan Schools, in order to support the appropriate and responsible online activity of Kindergarten to 12th Grade students. As seen with the evidence above, fraud, misinformation, and disinformation are on the rise and it is vital to be taught how to protect yourself from these common online problems.
Conclusion:
With the rise of technology use, Digital Citizenship Education is very important because it teaches citizens to use technology in order to engage respectfully online, to find reliable online sources and to avoid the violation of human rights. This can be achieved with schools and businesses implementing programs which will encourage people to expand their technological knowledge and promote human rights online.
Reference list:
[1] Strasburger, Victor C., Marjorie J. Hogan, Deborah Ann Mulligan, Nusheen Ameenuddin, Dimitri A. Christakis, Corinn Cross, Daniel B. Fagbuyi, et al. “Children, Adolescents, and the Media.” American Academy of Pediatrics. American Academy of Pediatrics, November 1, 2013. https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/132/5/958/31699/Children-Adolescents-and-the-Media .
[2] “How Technology in the Classroom Can Impact Student Learning.” Top Hat, May 10, 2022. https://tophat.com/blog/how-does-technology-impact-student-learning/ .
[3] Western Governors University. “Impact of Technology on Kids Today and Tomorrow.” Western Governors University. Western Governors University, August 25, 2020. https://www.wgu.edu/blog/impact-technology-kids-today-tomorrow1910.html#close .
[4] “Digital Citizenship and Digital Citizenship Education.” Digital Citizenship Education (DCE). Accessed May 19, 2022.
[5] “Digital Citizenship in Education.” ISTE. Accessed May 19, 2022. https://www.iste.org/areas-of-focus/digital-citizenship .
[6] “The State of Privacy in Post-Snowden America.” Pew Research Center. Pew Research Center, August 17, 2020. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/09/21/the-state-of-privacy-in-america/ .
[7] Schoology. “4 Benefits of Digital Citizenship for Internet Safety.” Schoology. Schoology, April 2, 2019. https://www.schoology.com/blog/4-benefits-digital-citizenship-internet-safety .
[8] Jordan, Sam. “Empowering Communities through Teaching Digital Citizenship.” Association of Alaska School Boards, November 18, 2018. https://aasb.org/empowering-communities-through-teaching-digital-citizenship/ .
[9] Couros, Alec, Hildebrandt, Katia. “Digital Citizenship Education in Saskatchewan Schools.” Accessed May 19, 2022. http://iamstronger.ca/userdata/files/244/DC%20Guide%20-%20ENGLISH%20WEB.pdf .
[10] Staff, the Premerger Notification Office, and This blog is a collaboration between CTO and DPIP staff and the AI Strategy team. “New Data Shows FTC Received 2.8 Million Fraud Reports from Consumers in 2021.” Federal Trade Commission, February 22, 2022. https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/news/press-releases/2022/02/new-data-shows-ftc-received-28-million-fraud-reports-consumers-2021-0 .
[11] Pappas, Stephanie. “Fighting Fake News in the Classroom.” Monitor on Psychology. American Psychological Association. Accessed May 19, 2022. https://www.apa.org/monitor/2022/01/career-fake-news .
[12] “Educational Researcher – Volume 50, Number 8, Nov 01, 2021.” Accessed May 19, 2022. https://journals.sagepub.com/toc/edr/50/8 .
[13] McClain, Colleen, Emily A. Vogels, Andrew Perrin, Stella Sechopoulos, and Lee Rainie. “The Internet and the Pandemic.” Pew Research Center: Internet, Science & Tech. Pew Research Center, April 28, 2022. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2021/09/01/the-internet-and-the-pandemic/ .
[14] “What Is Digital Citizenship?” Avast. Accessed May 20, 2022. https://blog.avast.com/what-is-digital-citizenship-avast .
[15] Aacap. Social Media and teens. Accessed May 23, 2022. https://www.aacap.org/AACAP/Families_and_Youth/Facts_for_Families/FFF-Guide/Social-Media-and-Teens-100.aspx .
Join One of Our Certificate Trainings:

Human Rights Education Certification Training

Human Trafficking Certification

International Business and Diplomatic Protocol Certification

Capacitación En Derechos Humanos

Business Consulting Certification Training

Digital Citizenship Certification
Other blogs you may like:.

What is meant by Open Diplomacy?


Youth-Led Diplomacy in International Organizations

How Can Youth Get Involved In Diplomacy?

The US Institute of Diplomacy and Human Rights (USIDHR) is an International Continuing Professional Development (CPD) Accredited Organization. Accredited CPD training means the learning activity has reached the required Continuing Professional Development standards and benchmarks. The learning value has been scrutinized to ensure integrity and quality. The CPD Certification Service provides recognized independent CPD accreditation compatible with global CPD requirements

US Institute Of Diplomacy And Human Rights
1250 Connecticut Ave NW Ste 700, Washington, DC 20036
Email support at: [email protected]
USA Phone: +1(202)-505-7707

Six Ways to Promote Digital Citizenship and Device Ownership

Digital citizenship refers to the responsible and ethical use of technology and the internet. It encompasses the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that individuals need to navigate the digital world safely, responsibly, and respectfully. The purpose of promoting digital citizenship is to empower students to become responsible digital citizens who can make informed decisions, engage in positive online behavior, understand how to protect their privacy and security, and contribute positively to the digital community.
Let’s explore six strategies for promoting digital citizenship and device ownership among students in the classroom.
1. Teach responsible device use.
Educating students on the proper use of devices extends beyond technical skills; it encompasses fostering a strong foundation of digital ethics. This involves teaching guidelines for appropriate online behavior, emphasizing the importance of respecting others’ privacy, and addressing the critical issue of cyberbullying. Adopt a proactive approach and introduce these concepts when students are still in their formative years. Doing so will empower them with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the digital landscape responsibly and ethically throughout their lives.
One effective method to achieve this is by employing an engagement kit . An engagement kit can consist of age-appropriate resources, interactive activities, and engaging content tailored to the specific needs of young learners. These kits not only make learning about responsible device use fun and interactive but also help create a positive association with digital citizenship from an early age. By instilling these values in our little tech users, we lay a strong foundation for a future generation of responsible digital citizens who will contribute positively to the digital world.

2. Establish clear expectations.

Setting clear rules and expectations for device usage in the classroom is fundamental to fostering responsible digital citizenship. These guidelines not only outline when and how devices should be used but also establish consequences for any misuse. Maintain consistency with your district’s universal device usage guidelines, ensuring that the information you share with your students aligns seamlessly with broader policies.
To further reinforce these expectations, consider incorporating visuals around the classroom or near areas where student devices are stored. Visual cues, such as posters or reminders, can serve as constant reminders of responsible device use, increasing the likelihood that students will hold themselves and their peers accountable for handling devices appropriately.
Resources:
- Classroom Management Tips for Teachers (Google Docs)
- iPad, Chromebook, and Teacher Expectation Visuals (Canva)
- iPad Visual Cues (Canva)
- Classroom Signs (Google Slides)
3. Encourage collaboration and communication.
Fostering a collaborative learning environment enriched by digital tools is not only conducive to academic growth but also a powerful vehicle for promoting responsible digital citizenship. When students work together using these tools, they not only learn subject matter but also valuable life skills.
In this environment, they acquire the ability to communicate effectively, collaborate seamlessly, and respect the ideas and perspectives of others. These skills are not only essential in the classroom but also in the broader digital world where they will increasingly interact as they grow. Encouraging such collaboration also helps students develop a sense of digital responsibility as they engage with their peers online.

4. Provide resources and support.
Offer resources and support to both students and educators to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge to navigate the digital world safely. This can include workshops, online courses, or access to digital literacy resources. Bear in mind that digital citizenship content may not be suitable for all age groups. It’s important to customize the information to align with the specific requirements of your audience. Consider hosting device camps for students and their teachers to learn more about their device and how to properly use it.
- Digital Citizenship Week Resources (Common Sense Media)
- Maintaining Classroom Devices for Effective Learning (Edutopia)
5. Involve parents and guardians.

Engage parents and guardians in the conversation about digital citizenship and device ownership. Provide them with a wealth of resources and information to help reinforce responsible device use at home. These materials can empower them with the knowledge and tools needed to reinforce responsible digital practices within the home environment. Such resources might include informative pamphlets, educational workshops, or online guides that cover topics ranging from online safety to managing screen time.
Additionally, fostering open lines of communication with parents and guardians is crucial. Encourage them to share their concerns and experiences, allowing for a more collaborative approach to addressing digital citizenship issues. This dialogue not only strengthens the educational effort but also helps create a supportive home environment where responsible device use becomes a shared family value.
6. Celebrate responsible device use.
Additionally, remember that positive reinforcement can be a powerful tool. Recognizing and celebrating instances of responsible device usage can motivate students to maintain these behaviors. Consider implementing a system of rewards or acknowledgments for students who consistently exhibit exemplary digital citizenship, creating a culture where responsible device use is not only expected but also celebrated
Fostering digital citizenship among students is a paramount endeavor in today’s technology-driven world. By instilling responsible and ethical practices in the use of devices and the internet, we equip our students with the tools they need to thrive in the digital realm. These five strategies form a comprehensive approach to promoting digital citizenship and device ownership in the classroom. As educators, it’s our duty to empower our students to become responsible digital citizens who make informed decisions, contribute positively to the online community, protect their privacy and security, and practice respectful online behavior. Together, we can ensure that they navigate the digital world with confidence, competence, and compassion, both in the classroom and beyond.
Candice, the author of this article, is presenting two sessions at the upcoming 2024 TCEA Convention & Exposition in Austin, Texas, February 3-7! Don’t miss the chance to see her in action for Becoming a Culture Unicorn: Mastering Blended Learning and Sipping Success: Set Up Blended Learning Like a Pro Barista . Early bird pricing ends on November 3, so hurry and register!
What is TCEA’s Convention & Exposition?
TCEA is a nonprofit association that gathers thousands of educators from around the world every year at the TCEA Convention & Exposition? Why? To connect, learn, and build skills and knowledge in the areas of good teaching, good leading, and good learning through ed tech! With top-notch speakers , on-trend sessions , an exhibit hall full of first-rate vendors, and lots of networking, TCEA sets educators up to dig into curiosity and discover.

Candice Adcock
Candice Adcock has been in education since 2014, working in Mesquite ISD. Prior to becoming an instructional technology coach, she taught 5th and 7th grade reading. She has a master’s degree in curriculum and instruction from Texas A&M University- Commerce. Throughout the school year, Candance presents within her school district, for the City of Mesquite, and has presented for Lead4ward for the last six years. Candice is also a Certified Google Trainer. Outside of work, she enjoys attending her son’s soccer games, karaoke, and spending time camping with her family.
NaNoWriMo’s Young Writer’s Program (YWP)
13 security browser extensions and sites you may not know, you may also like, supercharge your tech plans with the ai plan..., celebrate digital citizenship week october 14-18, 2024, digital citizenship week 2024 , responsible ai adoption, cipa compliance made easy with learning.com, integrate the 2024 ta teks into your third..., encrypt and protect sensitive, confidential data, hacktivate: cybersecurity for grades 6 and up, digital citizenship week: prioritize students’ mental health and..., seven picture books with digital citizenship themes, leave a comment cancel reply, you've made it this far.
Like what you're reading? Sign up to stay connected with us.
*By downloading, you are subscribing to our email list which includes our daily blog straight to your inbox and marketing emails. It can take up to 7 days for you to be added. You can change your preferences at any time.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
By subscribing, you will receive our daily blog, newsletter, and marketing emails.

Digital Citizenship 101: Educating Students for a Better Digital World
In an era defined by technology and connectivity, educators face the challenge of preparing students for a digital world that is constantly evolving. As teachers, we strive to equip our students with academic knowledge and the skills and competencies necessary to thrive in the digital age. One of the most critical skills we must impart upon them is digital citizenship.
What is Digital Citizenship?
Digital citizenship encompasses the values, knowledge, and behaviors individuals need to navigate the digital landscape responsibly and ethically. It goes beyond technical proficiency and delves into the realm of digital ethics, online safety, privacy, and responsible digital engagement. In an increasingly interconnected world, understanding and practising digital citizenship is of paramount importance for our students.
But why is digital citizenship such a crucial skill for our students to possess? The answer lies in the transformative power of technology and its pervasive influence on their lives. From social media platforms to online collaboration tools, technology has become an integral part of our students’ daily routines. While this digital realm presents immense opportunities for learning, creativity, and global connections, it also exposes them to various risks and challenges that are magnified when passed on to our youth.
Digital citizenship equips students with the tools and knowledge to navigate these challenges effectively. By fostering critical thinking, empathy, and responsible decision-making, it empowers them to be informed and engaged participants in the digital world. Digital citizens understand the importance of respect, kindness, and ethical behavior in online interactions, creating a positive digital culture.
Teaching digital citizenship helps students develop the skills they need for today and prepares them for their future careers. As technology continues to shape the workforce, employers will desire individuals who can demonstrate digital responsibility, effective communication, and collaboration in online environments. By imparting digital citizenship skills, we enable our students to become responsible and ethical professionals with the competencies required in the digital age.
Moreover, incorporating digital citizenship education into our classrooms is crucial for creating a safe and inclusive learning environment. By teaching students about online safety, digital footprint management, cyberbullying prevention, and critical evaluation of online content, we empower them to navigate the digital landscape confidently while protecting their well-being. Digital citizenship education ensures our students are aware of their rights, responsibilities, and the potential consequences of their online actions.
In the following sections of this article, we will delve deeper into the key components of digital citizenship and explore practical strategies for integrating digital citizenship education into our classrooms.
What digital ethics do our students require?
It is essential for individuals to adhere to a set of principles and values in the digital realm, which are commonly known to teachers and students as digital ethics. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, students must gain a solid understanding of digital ethics to responsibly navigate the complexities of the digital world. There are several key digital ethics that students must understand, including:
Respect and Kindness: Students should comprehend the importance of treating others with respect and kindness in all online interactions. This means avoiding cyberbullying, harassment, and hate speech. Encouraging empathy and fostering positive communication is crucial to creating a healthy and inclusive digital environment.
Privacy and Security: Students must understand the importance of safeguarding their personal information and respecting the privacy of others. They should know the potential risks of sharing sensitive data online and learn how to protect their privacy through strong passwords, privacy settings, and responsible data-sharing practices.
Digital Footprint Management: Students should be educated about the concept of a digital footprint—the traces they leave behind through their online activities. They must recognize that their digital footprints can have long-lasting consequences that they have little to no control or ownership of, impacting their reputation, education, and future opportunities. Students should learn to curate a positive digital footprint by thoughtfully considering what they share online.
Copyright and Intellectual Property: Students should develop an understanding of intellectual property rights and respect copyright laws. They need to learn to attribute and cite sources properly when using digital content and understand the implications of plagiarism. Encouraging creativity while respecting the intellectual property of others is vital.
Critical Evaluation of Information: In the age of abundant information, students must develop critical thinking skills to evaluate the reliability, credibility, and bias of online sources. They should learn to discern accurate information from misinformation or fake news . Instilling a sense of media literacy empowers students to make informed decisions and engage in responsible digital citizenship.
Digital Balance and Well-being: Students must be aware of the potential impact of excessive screen time and digital addiction on their well-being. Balancing online and offline activities, such as physical activity, face-to-face interactions, and self-care, is essential for maintaining a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
Digital Citizenship Rights and Responsibilities: Students should understand their rights and responsibilities as digital citizens. This includes respecting the terms of service of online platforms, adhering to appropriate online behavior guidelines, and understanding the consequences of their actions online. Encouraging responsible digital engagement and fostering a sense of civic responsibility is crucial.
There is now another aspect of dealing with digital rights and responsibilities, which has become apparent with the rise of automation and artificial intelligence. And that is, when a machine makes a decision that excludes or impacts your life in a meaningful way are there any rights you have to challenge or contest the efficacy and legality of the process?
By integrating these digital ethics into their mindset and behavior, students can become ethical digital citizens who contribute positively to the digital world while protecting their own well-being and respecting the rights of others.
COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON INTERNET RESEARCH SKILLS USING GOOGLE SEARCH

Teach your students ESSENTIAL SKILLS OF THE INFORMATION ERA to become expert DIGITAL RESEARCHERS.
⭐How to correctly ask questions to search engines on all devices.
⭐ How to filter and refine your results to find exactly what you want every time.
⭐ Essential Research and critical thinking skills for students.
⭐ Plagiarism, Citing and acknowledging other people’s work.
⭐ How to query, synthesize and record your findings logically.
Strategies for Teaching Digital Citizenship
In this section, we have curated some proven strategies that, whilst not dedicated lessons, can be easily integrated into your teacher planner with minimal fuss.
Incorporate Digital Citizenship into the Curriculum: Integrate digital citizenship lessons and activities into your curriculum across various subjects and grade levels. Find opportunities to discuss responsible online behavior, critical evaluation of online sources, digital footprint management, and ethical use of technology within the context of different subjects. This approach helps students understand the relevance of digital citizenship in their academic pursuits and daily lives.
Interactive Discussions and Case Studies: Engage students in interactive discussions and case studies that prompt critical thinking about real-world digital citizenship scenarios. Present them with dilemmas and ethical challenges related to privacy, cyberbullying, intellectual property, or online etiquette. Encourage students to analyze and discuss possible solutions, consider different perspectives, and evaluate the consequences of their actions. These discussions help students develop their decision-making skills and ethical reasoning.
Digital Citizenship Pledges and Agreements: Collaboratively create digital citizenship pledges or agreements with your students. These documents outline the rights and responsibilities of digital citizens and establish shared expectations for online behavior within the classroom and beyond. Involve students in discussing and drafting the guidelines, allowing them to take ownership of their digital citizenship commitments. Display the pledges prominently in the classroom and revisit them periodically to reinforce the importance of responsible digital conduct.
Example of a student digital citizenship pledge
Note: This is just an example, and students can personalize their digital citizenship pledge based on their understanding and commitment to responsible and respectful digital behavior.
Digital Citizenship Lessons and Resources: Utilize various age-appropriate resources and lesson plans specifically designed to teach digital citizenship. Websites like Common Sense Education, Digital Citizenship Institute, and iKeepSafe offer a wealth of resources, including videos, interactive games, and lesson plans that cover different aspects of digital citizenship. These resources can provide structured guidance and engaging activities to supplement your teaching.
5 Digital Citizenship resources we can highly recommend
Common Sense Education ( https://www.commonsense.org/education/ ): Common Sense Education offers a wide range of resources, lesson plans, and interactive activities for teaching digital citizenship. The website provides engaging videos, games, and interactive lessons that cover various aspects of digital citizenship, including internet safety, privacy, online communication, and digital footprints.
Digital Passport ( https://www.digitalpassport.org/ ): Digital Passport, developed by Common Sense Education, is an interactive game-based website that allows students to explore different aspects of digital citizenship. Through engaging scenarios, students learn about internet safety, privacy, cyberbullying, and responsible online behavior. The website provides teachers with resources, including lesson plans and discussion guides.
Be Internet Awesome ( https://beinternetawesome.withgoogle.com/ ): Developed by Google in partnership with experts in online safety, Be Internet Awesome offers interactive games and resources to teach students about critical digital citizenship skills. The website covers topics such as online privacy, security, responsible communication, and identifying fake news . It also includes a curriculum for educators to use in the classroom.
iKeepSafe ( https://ikeepsafe.org/ ): iKeepSafe is a nonprofit organization dedicated to promoting digital citizenship, privacy, and internet safety. Their website provides a range of resources for educators, parents, and students. It includes lesson plans, videos, and interactive games that cover topics like online safety, cyberbullying prevention, information literacy, and responsible digital behavior.
Digital Citizenship Institute ( https://www.digitalcitizenship.net/ ): The Digital Citizenship Institute offers a wealth of resources and tools to teach students about responsible digital citizenship. The website provides educators with lesson plans, webinars, and research-based strategies for integrating digital citizenship into the curriculum. It covers topics such as digital footprints, online privacy, critical thinking, and global digital citizenship.
These websites offer valuable resources and engaging activities to help students develop essential digital citizenship skills. Remember to review the content on these websites to ensure they align with your specific educational goals and requirements.

Authentic Practice and Digital Projects: Provide students with opportunities to apply digital citizenship skills and principles through authentic projects. Assign projects that require online research , collaboration, and the responsible use of digital tools. Emphasize the importance of citing sources, evaluating information critically, and respecting intellectual property. Encourage students to reflect on their digital choices and the impact of their online contributions. Students can internalize digital citizenship principles and apply them in real-world contexts by engaging in meaningful, hands-on activities.
Remember to adapt these strategies to the specific needs and age group of your students.
Assessing Digital Citizenship
As educators, we must assess our students’ digital citizenship skills to ensure they can navigate the digital world responsibly and ethically. While traditional assessment methods may not fully capture the nuances of digital citizenship, there are various strategies and tools that can help evaluate students’ understanding and application of these vital skills. In this article, we will explore practical approaches to assess students’ digital citizenship and promote their growth in this essential area.
Observation and Reflection: Observation is a powerful tool for assessing students’ digital citizenship. Take note of students’ online behavior, such as how they communicate, collaborate, and engage with others in digital spaces. Look for respectful and inclusive online interactions, responsible use of technology, and ethical decision-making. Reflect on these observations, considering the context and impact of their actions. Provide constructive feedback and engage students in reflective discussions to help them understand the consequences of their online behavior and how they can improve.
Self-Assessment and Digital Portfolios: Encourage students to assess their own digital citizenship skills through self-reflection. Provide them with rubrics or checklists that outline the key components of digital citizenship, such as privacy, respectful communication, critical evaluation of information, and responsible technology use. Ask students to evaluate their performance and identify areas for growth. Digital portfolios can also serve as a means for students to showcase their responsible online behavior, ethical contributions, and reflections on their digital citizenship journey.
Projects and Assignments: Assign projects and assignments that require students to apply their digital citizenship skills. For example, task students with creating multimedia presentations on responsible online behavior, or have them collaborate on a digital project while adhering to ethical guidelines. Assess their ability to cite sources, respect intellectual property, and engage in positive digital interactions. Rubrics can be created to evaluate their performance based on criteria related to digital citizenship, providing specific feedback on their strengths and areas that require improvement.
Digital Citizenship Quizzes and Assessments: Design short quizzes or assessments to gauge students’ understanding of digital citizenship concepts. Include questions that assess their knowledge of online safety, privacy settings, cyberbullying prevention, and responsible digital communication. These assessments can be administered in class or through digital platforms, providing immediate feedback to students. Use the results to identify areas where students need additional support or clarification, and adapt your teaching accordingly.
Peer Feedback and Evaluation: Promote peer assessment and feedback as a valuable tool for evaluating digital citizenship. Encourage students to review and provide constructive feedback on their peers’ online contributions, such as blog posts, digital presentations, or collaborative projects. Develop clear criteria for evaluation, emphasizing the importance of respectful and constructive feedback. This gives students a deeper understanding of digital citizenship and fosters a sense of collective responsibility for maintaining a positive digital culture.
Assessing students’ digital citizenship is a multifaceted process that requires a combination of observation, self-assessment, project-based evaluation, quizzes, and peer feedback. By implementing these strategies, we can gain valuable insights into students’ digital citizenship skills and guide their growth in this vital area.
As teachers, our role goes beyond imparting knowledge; we nurture responsible and ethical digital citizens. By employing these assessment strategies, we can evaluate students’ digital citizenship skills, provide targeted feedback, and support their development as responsible and confident participants in the digital world.
As technology continues to penetrate so much of our lives, many of these teaching ideas and strategies mentioned above will become less about teaching students to be upstanding digital citizens and more about becoming respectful, informed and active citizens, which can’t be a bad outcome.
- Assembly Questionnaire
- Photo Gallery

Nurturing Responsible Digital Citizens: A Comprehensive Guide to Digital Citizenship

What is Digital Citizenship? Digital Citizenship refers to the responsible and ethical use of technology, encompassing various aspects of online life such as social media, digital communication, and internet safety. It emphasizes the development of skills that enable individuals to navigate the digital landscape safely, respectfully, and responsibly.
The Pillars of Digital Citizenship:
- Digital Literacy : Developing the necessary skills to critically evaluate information online, understanding digital tools, and using them effectively.
- Online Safety : Implementing strategies to protect personal information, recognizing online threats, and fostering a secure digital environment.
- Respectful Communication : Cultivating positive online interactions by promoting empathy, kindness, and respectful behavior towards others.
- Cyberbullying Prevention : Understanding the signs of cyberbullying, promoting a culture of kindness, and taking measures to prevent and address online harassment.
- Privacy Awareness : Educating individuals about the importance of protecting their online privacy, including the responsible use of personal information and digital footprints.
Implementing Digital Citizenship Programs: To instill these principles in the younger generation, educational institutions play a pivotal role. Elementary schools, in particular, can integrate Digital Citizenship programs into their curriculum. These programs can include interactive workshops, engaging activities, and discussions focused on responsible online behavior.
Internet Safety Program for Elementary Schools: One effective way to promote Digital Citizenship is through dedicated Internet Safety Programs tailored for elementary schools. These programs can cover topics such as:
- Safe Internet Practices: Teaching students how to navigate the internet safely, discerning between reliable and unreliable sources, and understanding the consequences of sharing personal information online.
- Online Etiquette: Instilling the importance of respectful communication in digital spaces, emphasizing the impact of words and actions online.
- Cyberbullying Awareness: Educating students about the signs of cyberbullying, the importance of reporting such incidents, and fostering a supportive online community.
- Digital Responsibility: Encouraging responsible use of digital devices, balancing screen time, and understanding the long-term implications of online actions.
Conclusion: In a world where technology is an integral part of daily life, instilling Digital Citizenship values from a young age is essential. By embracing the pillars of Digital Citizenship and implementing dedicated Internet Safety Programs in elementary schools, we can empower the next generation to navigate the digital landscape responsibly, respectfully, and safely. This proactive approach not only ensures the well-being of individuals online but also contributes to the creation of a positive and inclusive digital society.
Share this post
Empowering Young Minds

The Importance of Digital Citizenship in Education
by Lcom Team | May 9, 2023 | Blogs

Share this article!
In 2019, 95% percent of 3- to 18-year-olds were reported to have home internet access, according to the American Community Survey (ACS) . In a separate survey , researchers found that 55% of children own a tablet or smartphone, while only 30% of parents reported feeling confident enough to discuss internet safety issues.
Despite the prevalence of technology and internet access in today’s digital world, the burden of educating students on how to engage with this technology safely and effectively has remained somewhat ambiguous.
What is Digital Citizenship?
Digital citizenship includes knowledge, skills and practices to engage safely and responsibly in a digital environment. This is considered an important skill for students to protect them from harmful content, cyberbullying, privacy risks, scams, viruses and more.
Why is Digital Citizenship Important?
Digital citizenship in education is an important way to ensure students, regardless of their level of access or knowledge at home, have the ability to learn how to use technology safely and effectively. Cyberthreats abound , with an online attack happening every 39 seconds. 59% of U.S. teens have been cyberbullied or threatened online, one in seven children is contacted online by someone with sexual intentions, and most children are likely to have seen pornographic content online by the age of 15.
Digital citizenship provides skills to avoid, mitigate and communicate about these threats in a safe and responsible way. Below are some of the important skills digital citizenship teaches:
Improves Digital Safety
One of the most important reasons to teach digital citizenship to students is to help them understand and engage in practices that help improve their digital safety. The world is becoming increasingly interconnected, with 85% of Americans reporting going online daily, over 50% going online multiple times a day and 31% being online “almost constantly.”
The number is even larger for younger adults, with 48% of Americans ages 18-29 reporting being online almost constantly. This means students are entering a world where they can expect to be regularly exposed to situations that can compromise their personal information and put them at risk for innumerable threats.
Digital citizenship teaches students what information is safe to share and in what situations and how to protect their information in unsafe situations. It also teaches students how to interact safely with others and with content online and how to identify threats if and when they arise.
Prevents and Manages Cyberbullying
More than half of teens have experienced online bullying, with 60% of girls and 59% of boys experiencing at least one abusive online behavior, according to teenager internet safety data in a recent Pew Research Center survey.
Cyberbullying refers to the intentional harassment, mistreatment or making fun of another person online. According to the Cyberbullying Research Center , rumors being spread online and mean or hurtful comments are reported as the most common types of cyberbullying, with 22.5% of children ages 12-17 reporting being physically threatened through text messaging, and 22.1% being physically threatened online. Other forms of cyberbullying include posting mean or hurtful photos or videos, pretending to be another person online, posting mean or hurtful comments regarding someone’s race or religion, and more.
Digital citizenship helps students learn about cyberbullying, how to prevent it, why they shouldn’t engage in it, and what to do if they are cyberbullied.
Reduces Exposure to Unsafe Content
Children ages 8-12 are often targeted by predators. Online child exploitation statistics show that 17% have received an email or online message with either words or photos that made them uncomfortable. Internet safety statistics, however, show that only 7% of parents became aware of this.
With increased interconnectedness comes increased exposure to unsafe or uncomfortable content or interactions. Digital citizenship education in students helps them learn how to avoid these situations and teaches them how to handle these situations if they arise.
Digital Citizenship Curriculum
It can be difficult for schools to find the right way to teach digital citizenship to students when digital threats are ever-evolving. EasyTech is a great, easy-to-implement solution that includes a well-rounded, adaptable digital citizenship curriculum in an engaging online platform. Learn more by clicking the button below.

Learning.com Team
Staff Writers
Founded in 1999, Learning.com provides educators with solutions to prepare their students with critical digital skills. Our web-based curriculum for grades K-12 engages students as they learn keyboarding, online safety, applied productivity tools, computational thinking, coding and more.
Further Reading

- 5 Useful AI Tools for Teachers in 2024
by Lcom Team | Nov 6, 2024
Looking for the best AI for teachers? Check out these 5 top AI tools in 2024 that can transform your teaching experience and save you time

- Improve Student Performance on Online Assessments with Digital Literacy
by Lcom Team | Nov 5, 2024
Online assessments have become increasingly prevalent in education, especially with the rise of digital learning environments and the need for...

- Overlooked Digital Skills Students Need to Thrive in a Digital World
by Lcom Team | Oct 29, 2024
As the digital landscape continues to evolve at a rapid pace, educators, parents and policymakers are increasingly focused on preparing students for...
Quick Links
- Request More Info
Recent news & Articles
- Teaching AI: Ethical Considerations for High School Students
- Creating a Classroom Guide to “Netiquette”: Promoting Respectful Online Behavior

IMAGES
COMMENTS
That's why educators support digital citizenship for students. Topics Related to Digital Citizenship for Students. As digital technology grows more sophisticated, so do cyberthreats. To keep up, students need to learn about digital citizenship: the use of digital devices and the internet in responsible and productive ways. Digital Literacy
250 Words Essay on Digital Citizenship Understanding Digital Citizenship. Digital Citizenship is about how we behave online. It's like being a good citizen in the real world, but in the digital world. We need to know how to use the internet and digital tools safely, respectfully, and responsibly. Importance of Digital Citizenship
Digital Citizenship Education is necessary because it protects others from being vulnerable to these issues. Digital Citizenship Education. Digital Citizenship Education encourages individuals to use their knowledge, skills, and understanding to protect and promote human rights online, such as freedom, privacy, and security.
8 Ideas for Promoting Digital Citizenship in Students. Implementing digital citizenship into your school's technology curriculum is an important step to promoting digital literacy in students. However, it is not the only step. Teachers and administrators should also implement tools and processes to promote digital citizenship skills in the ...
Let's explore six strategies for promoting digital citizenship and device ownership among students in the classroom. 1. Teach responsible device use. Educating students on the proper use of devices extends beyond technical skills; it encompasses fostering a strong foundation of digital ethics. This involves teaching guidelines for appropriate ...
Understanding Digital Citizenship. Digital citizenship refers to the responsible use of technology by anyone who uses computers, the internet, and digital devices to engage with society on any level. It's about understanding the rights, responsibilities, and opportunities that come with digital participation, and using technology in ways that ...
This gives students a deeper understanding of digital citizenship and fosters a sense of collective responsibility for maintaining a positive digital culture. Assessing students' digital citizenship is a multifaceted process that requires a combination of observation, self-assessment, project-based evaluation, quizzes, and peer feedback.
In today's rapidly advancing digital age, fostering a sense of responsibility and ethical behavior online is crucial for individuals of all ages. This is where the concept of Digital Citizenship comes into play. This article will delve into the importance of Digital Citizenship and offer valuable insights into promoting responsible online behavior.
Choose to promote a positive and professional image of self online. On social networking Web sites, students can share information about themselves globally (Dewall, Buffardi, Bonser, and Campbell, 2011). ... Digital citizenship: Developing an ethical and responsible online culture. ACCESS, 25 (3), 5-9.
One of the most important reasons to teach digital citizenship to students is to help them understand and engage in practices that help improve their digital safety. The world is becoming increasingly interconnected, with 85% of Americans reporting going online daily, over 50% going online multiple times a day and 31% being online "almost ...