JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
PPT Bundles
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Top 10 Operating Systems PowerPoint Presentation Templates in 2024
Operating systems (OS) serve as the backbone of computer functionality, managing hardware and software resources to ensure seamless operation. They act as intermediaries between users and the computer hardware, enabling users to interact with the system through a user friendly interface. Various types of operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile OS like Android and iOS, cater to different user needs and device capabilities. In the realm of presentations, a PowerPoint (PPT) template focused on operating systems can significantly enhance understanding and engagement. Such a presentation can cover the fundamental roles of an OS, including process management, memory management, file systems, and device management. It can also explore the evolution of operating systems, highlighting key milestones and innovations that have shaped modern computing. Use cases for this PPT template include educational settings, where instructors can effectively teach students about the complexities of operating systems, or corporate environments, where IT professionals can present system upgrades or new software implementations. Additionally, it can serve as a valuable resource for tech enthusiasts looking to deepen their knowledge or for businesses aiming to streamline their operations by understanding the underlying systems that support their software applications. Through visually appealing slides and customizable content, this PPT template can facilitate impactful presentations that resonate with diverse audiences.

Operating System Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles
Deliver a lucid presentation by utilizing this Operating System Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles. Use it to present an overview of the topic with the right visuals, themes, shapes, and graphics. This is an expertly designed complete deck that reinforces positive thoughts and actions. Use it to provide visual cues to your audience and help them make informed decisions. A wide variety of discussion topics can be covered with this creative bundle such as Kernel,User Interface,File System,Memory Management,Process Management. All the twenty slides are available for immediate download and use. They can be edited and modified to add a personal touch to the presentation. This helps in creating a unique presentation every time. Not only that, with a host of editable features, this presentation can be used by any industry or business vertical depending on their needs and requirements. The compatibility with Google Slides is another feature to look out for in the PPT slideshow.
An operating system OS is a fundamental software component that serves as the intermediary between computer hardware and user applications. It manages system resources, including memory, processors, and peripheral devices, to facilitate efficient and secure execution of software. The OS provides essential services such as process management, file storage, and user interface, enabling users to interact with the computer. Key functions of an OS include memory allocation, task scheduling, and input or output management. Common examples include Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux. The operating system plays a critical role in ensuring the stability, security, and overall functionality of computer systems across various devices, from personal computers to servers and embedded systems.
- user interface
- File System
- Memory Management
- process management
Related Products
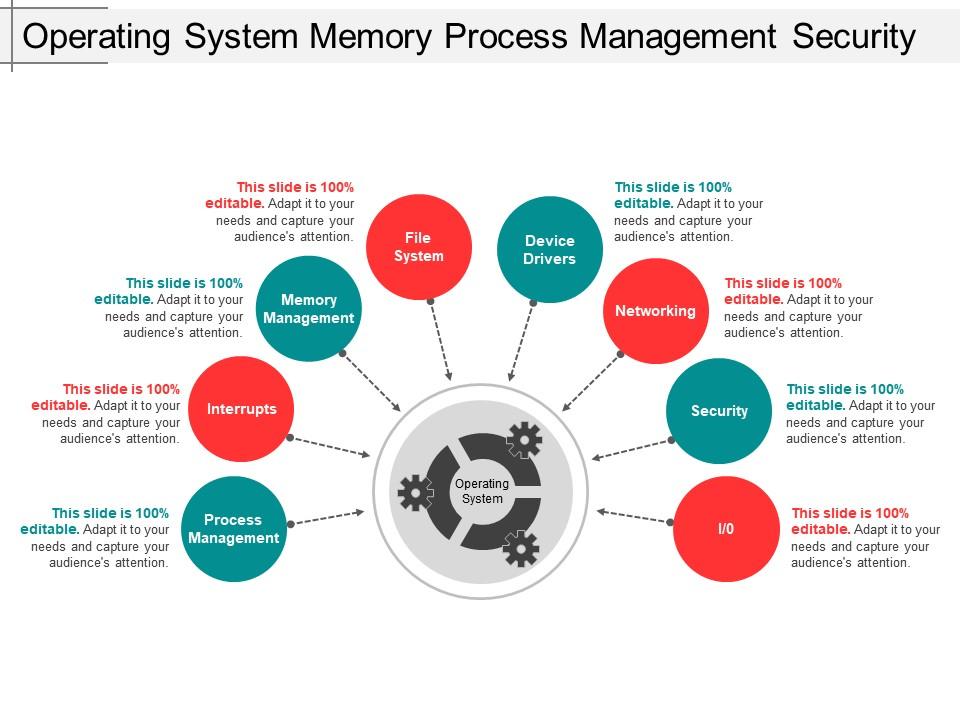
Operating system memory process management security
Presenting this Operating System Memory Process Management Security PowerPoint presentation. Add charts and graphs for a wonderful representation of information. The PPT also supports the standard (4:3) and widescreen (16:9) aspect ratios. It is compatible with Google Slides. Convert this into popular images or document formats such as JPEG, PNG or PDF. High-quality graphics ensure that graphics quality is maintained at every stage of presentation.
Enhance the safety of your organizational information using this Operating System Memory Process Management Security PowerPoint presentation. Take advantage of this OS PPT slide to show numerous security approaches including regular patch updates, scrutinizing network traffic. Take the assistance of this computer system PPT slideshow to depict the primary as well as secondary memory including RAM and ROM. Portray the kinds of memory management such as fragmentation, swapping, paging, memory allocation, etc. with this system software PPT template. Utilize this OS PPT layout to present the types of memory allocation like fixed-size blocks, buddy blocks, slab allocation, and stack allocation. Reveal the numerous security violations like the breach of confidentiality, theft of service, denial of service attacks, replay attacks amongst others using this system security PPT visual. Download this amazing memory management PPT infographic to implement advance techniques to manage memory and counter various cyber threats.
- System Software
- Operating System
- software development

Ethical Operating System Os Risk Mitigation Checklist Ethical Tech Governance Playbook
This slide provides information regarding ethical operating system OS risk mitigation checklist that helps to track various risk zones such as trust, disinformation and propaganda, economic and asset inequalities, addiction and dopamine economy, etc. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Ethical Operating System Os Risk Mitigation Checklist Ethical Tech Governance Playbook. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Disinformation, Dopamine Economy, Economic Asset Inequalities using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
This slide provides information regarding ethical operating system OS risk mitigation checklist that helps to track various risk zones such as trust, disinformation and propaganda, economic and asset inequalities, addiction and dopamine economy, etc.
- Disinformation
- Dopamine Economy
- Economic Asset Inequalities
Notification hub recovery manager operating system bitbucket code ppt icons graphics
Presenting notification hub recovery manager operating system bitbucket code ppt icons graphics. This Power Point icon template has been crafted with graphic of notification, recovering manager and operation system icons. This PPT diagram contains the concept of analyzing operating system and Bit bucket code. Use this icon template for web and graphics related presentations.
Get your foot that bit ahead with our Notification Hub Recovery Manager Operating System Bitbucket Code Ppt Icons Graphics. You will be the first among equals.
- notification
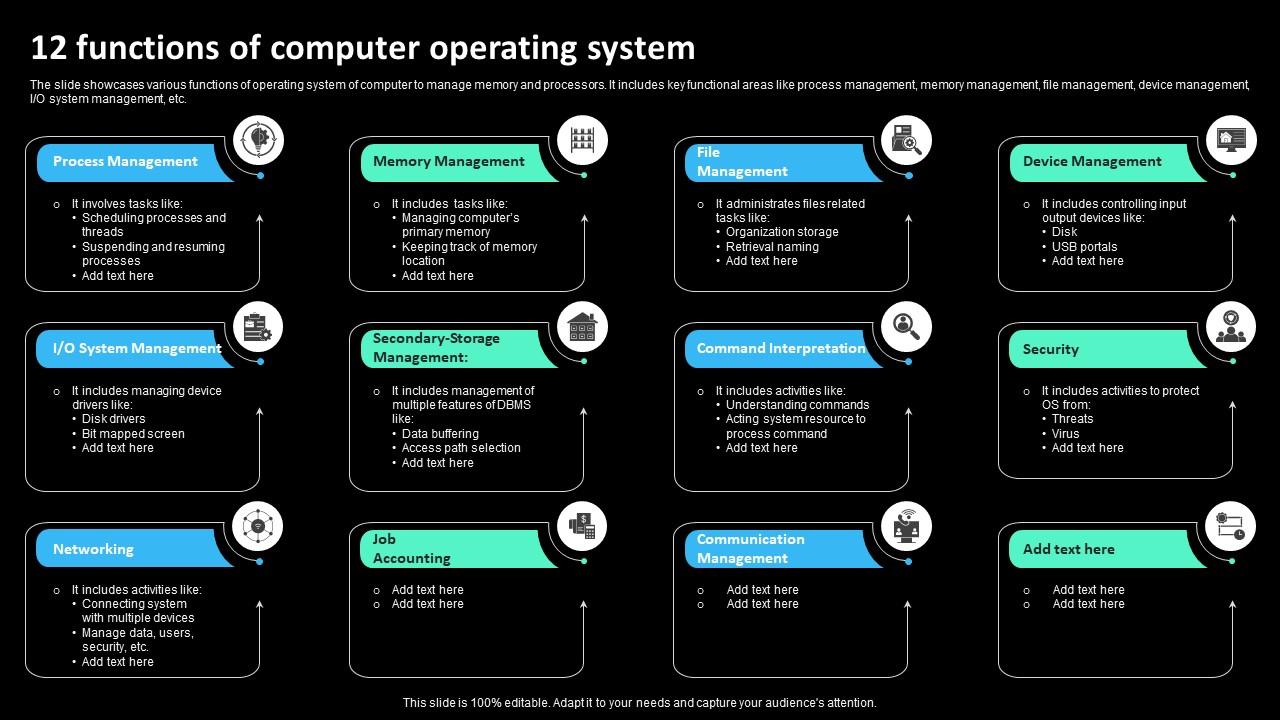
12 Functions Of Computer Operating System
The slide showcases various functions of operating system of computer to manage memory and processors. It includes key functional areas like process management, memory management, file management, device management, I O system management, etc. Introducing our premium set of slides with 12 Functions Of Computer Operating System. Ellicudate the one stages and present information using this PPT slide. This is a completely adaptable PowerPoint template design that can be used to interpret topics like Computer, Management, Storage. So download instantly and tailor it with your information.
The slide showcases various functions of operating system of computer to manage memory and processors. It includes key functional areas like process management, memory management, file management, device management, I O system management, etc.
Roadmap business process and achievement linear timeline flat powerpoint design
Presenting roadmap business process and achievement linear timeline flat PowerPoint design. High-resolution images and the slide icons. Easy to download and save in the variety of formats. Access to open on a wide screen preview. Compatible with the Google Slides and the PowerPoint Software’s. Access to edit the style, size and the background of the slide icons as per your needs. Useful for the business owners, marketing executives and the students.
Are you looking for some presentation design to clearly outlay your business plans and its achievements? Presenting, Business Process and Achievement Linear Timeline Flat PowerPoint Design to help you do it efficiently. Preparing a business structure is one thing and mapping if those targets have been achieved or not is another. This business process and achievement presentation design measures trade processes while displaying complete picture of the design vividly. With this roadmap timeline presentation a user, business presenter as well as the audience will get to know what the determined plans were and how far those have been achieved. On one side it will clearly display the entire business picture and on other hand this business process and achievement linear timeline design will serve as a base to craft the next business structure and increase the level of achievement. Thus, these business structure and achievement presentation designs can be used for various business and technology related presentations. Add some glamour with our Business Process and Achievement Linear Timeline Flat PowerPoint Design. Be the cynosure of every eye around.
- achievement
- Linear Timeline
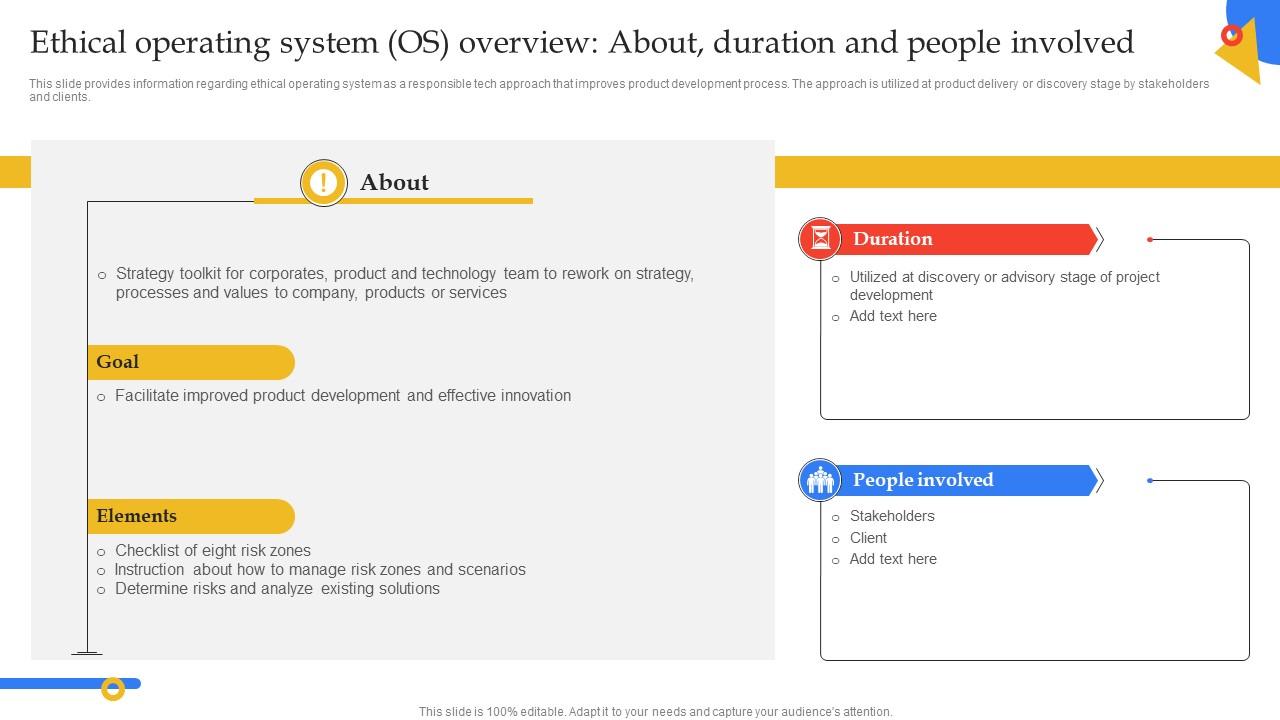
F1419 Ethical Operating System Os Overview About Guide To Manage Responsible Technology Playbook
This slide provides information regarding ethical operating system as a responsible tech approach that improves product development process. The approach is utilized at product delivery or discovery stage by stakeholders and clients. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this F1419 Ethical Operating System Os Overview About Guide To Manage Responsible Technology Playbook. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Overview, Duration, Stakeholders using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
This slide provides information regarding ethical operating system as a responsible tech approach that improves product development process. The approach is utilized at product delivery or discovery stage by stakeholders and clients.
- stakeholders
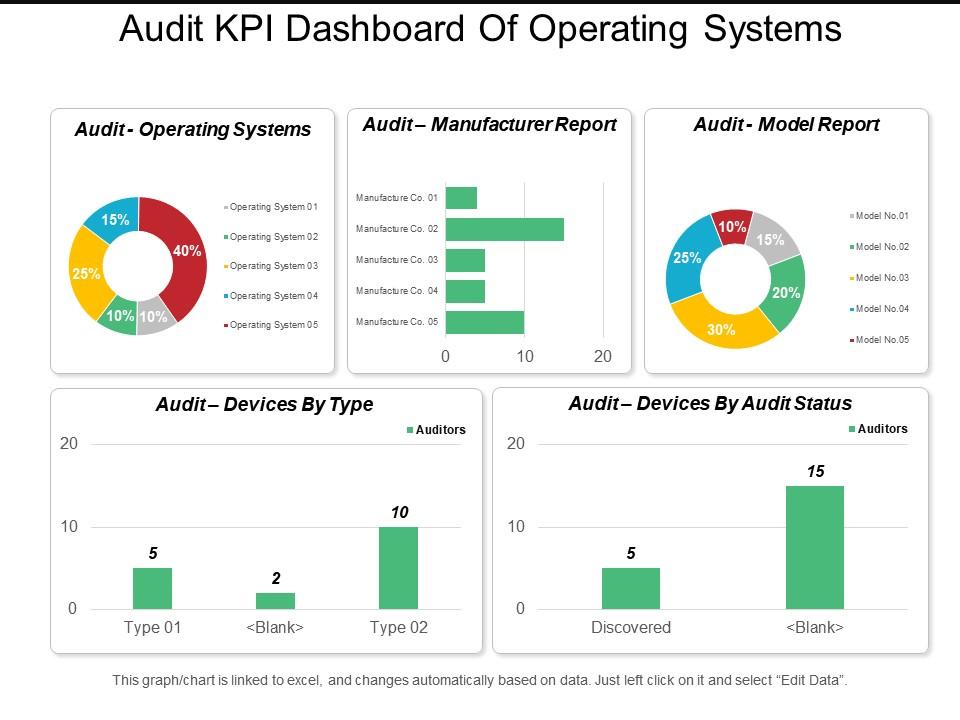
Audit kpi dashboard of operating systems manufacturer report and model report
Presenting this set of slides with name - Audit Kpi Dashboard Of Operating Systems Manufacturer Report And Model Report. This is a five stage process. The stages in this process are Audit, Examine, Survey.
Ensure folks fell entertained in between with our Audit Kpi Dashboard Of Operating Systems Manufacturer Report And Model Report. They will have a good interval.
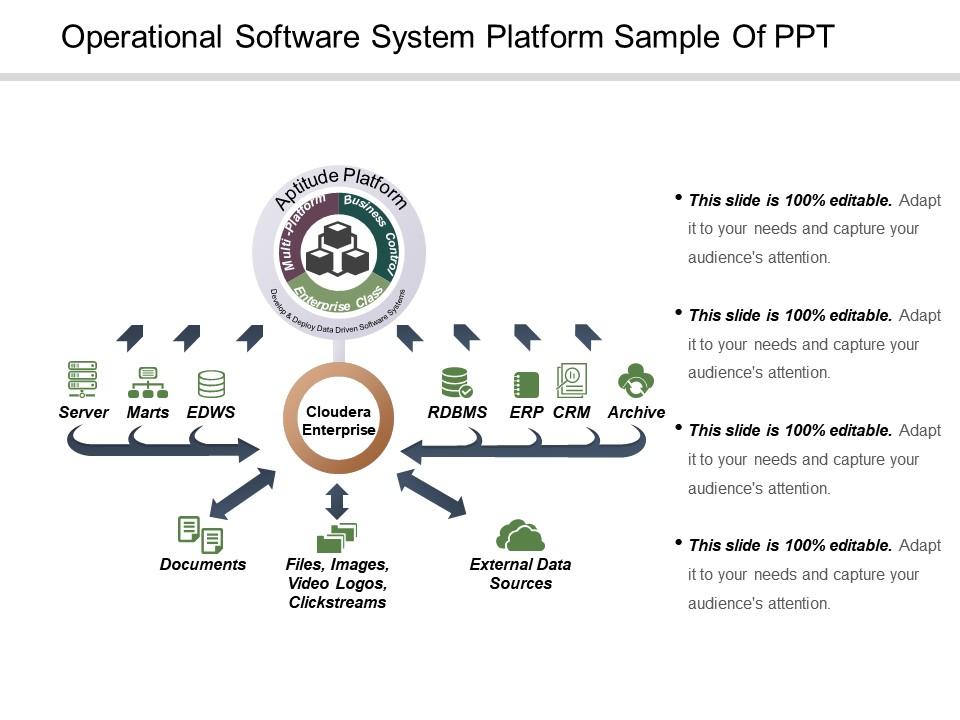
Operational Software System Platform Sample Of Ppt
Presenting, our operational software system platform sample of PPT. All the icons shown here can be adjusted as per your requirement. Alter the text boxes to include your company data and change the color schemes, icons, font. This predesigned format can be downloaded in a snap and can be easily converted into pdf or jpeg format as per your need. Project this layout on to widescreen without any degradation in the quality. This operational software system platform is available in both standard 4:3 and widescreen format 16:9 after downloading. Include your company logo here just by following a few steps.
Give your thoughts greater bandwidth, air them on our operational software system platform sample of PPT. This presentation is ideal to provide an insight into this operational software system. Include this PPT layout in your business meetings to highlight various concerns like software platform, software architecture, software stack. This PowerPoint image depicts the various components that are crucial to the cloudera enterprise. It also highlights the aspects of the aptitude problem which are as follows: multi-platform, business control and enterprise class. Various steps show here covers up all keys aspects of the software system platform. You can include your company data to personalize. Advised to be presented to showcase to provide thought a higher bandwidth, each of the stages included here include a business icon corresponding to it, that helps the viewer analyze the concept with ease and gives an overview of the basics of an operational software system platform. Captivate your audience with our, operational software system platform PPT deck. Give your thoughts greater bandwidth. Air them on our Operational Software System Platform Sample Of Ppt.
- Software Platform
- Software Architecture
- Software Stack
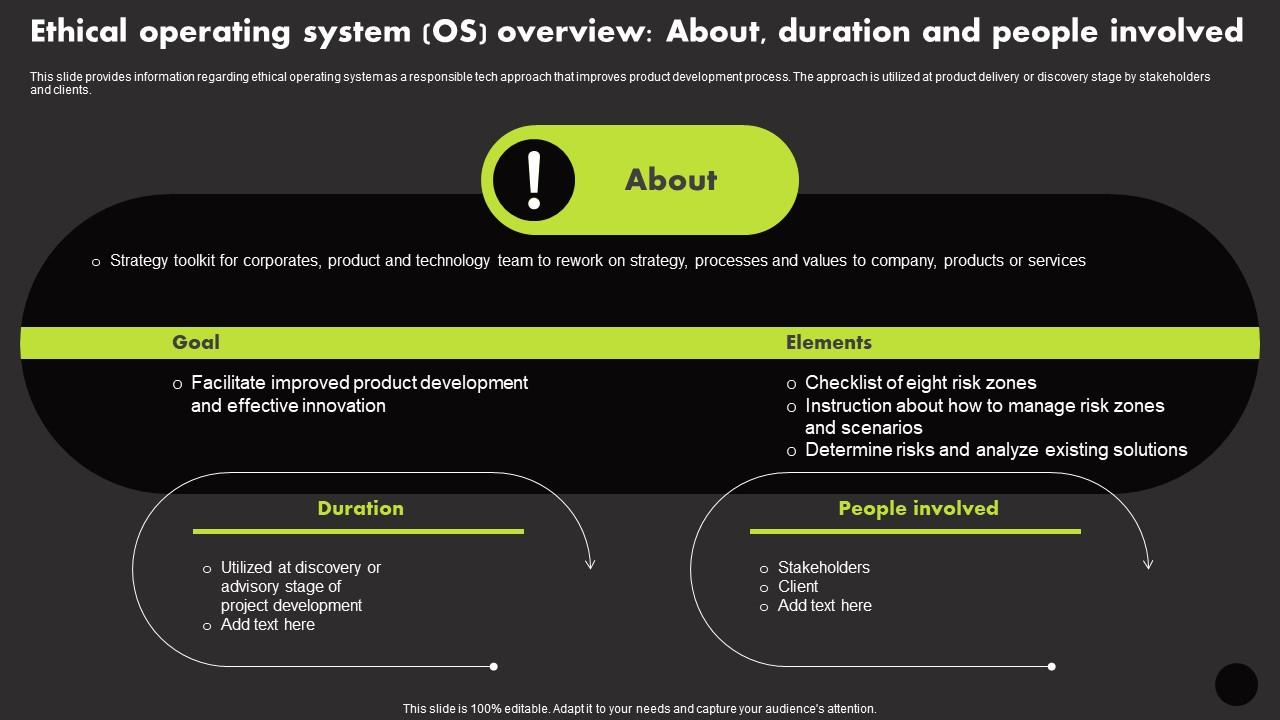
Ethical Operating System Os Overview About Duration Manage Technology Interaction With Society Playbook
This slide provides information regarding ethical operating system as a responsible tech approach that improves product development process. The approach is utilized at product delivery or discovery stage by stakeholders and clients. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Ethical Operating System Os Overview About Duration Manage Technology Interaction With Society Playbook. This template helps you present information on Two stages. You can also present information on Duration, People Involved using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.
- People Involved

1.858.217.5144
Start your project

How can I create a PowerPoint presentation on an operating system?
To create a PowerPoint presentation on an operating system, you will need to follow a series of steps designed to ensure a comprehensive, informative, and engaging presentation. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Research: Start by conducting thorough research on the operating system you plan to discuss. Make sure to understand its key features, benefits, and potential drawbacks. Look for recent updates or changes that may be relevant to your audience.
- Outline: Create an outline to guide the creation of your slides. The outline should include your main points and the order in which you plan to present them. This may include the introduction of the operating system, key features, benefits, drawbacks, comparisons with other operating systems (if relevant), and a conclusion.
- Design: Begin designing your slides in PowerPoint. Keep in mind that visual aids are crucial in maintaining audience engagement. Use graphs, charts, images, and animations to illustrate your points. Try to stick to a consistent theme and color scheme throughout your presentation.
- Content: Populate your slides with content. Make use of bullet points, short sentences, and clear headings. Remember, the slides are there to support your speech, not to replace it. The audience should be able to understand your presentation even without reading the slides word for word.
- Review: Review your presentation to make sure that it’s accurate, comprehensive, and engaging. Check for spelling and grammatical errors. Practice delivering your presentation to ensure that it flows well and that you’re able to explain each slide clearly.
At SlideGenius, we understand that creating a professional PowerPoint presentation can be time-consuming and challenging. That’s why we offer top-quality presentation design services to help you create a compelling and effective PowerPoint presentation. Our team of design experts can help you with everything from slide design to content creation, ensuring that your presentation stands out and achieves its objectives.
View Our Presentation Portfolio

View our presentation portfolio

Manufacturing

Finance & Investments
Business Solutions

Technology & Software
Business Software-B2B

Household Products & Services

Film & Television

Ready to kick off your project?
Fill out the form below to speak with a SlideGenius representative.
Company size None 1 2-10 10-100 100-1000 1000+
Copyright Note

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Computer Operating System.
Published by Paul Dugdale Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Chapter 1 Introduction to Computer Operating System."— Presentation transcript:

Objectives Overview Define an operating system

Chapter 8 Operating Systems and Utility Programs

Discovering Computers Fundamentals, Third Edition CGS 1000 Introduction to Computers and Technology Fall 2006.

Chapter 8 Operating Systems and Utility Programs.

What You Will Learn Components of a computer’s system software The importance of an operating system Functions of an operating system Types of user interfaces.

Professor Michael J. Losacco CIS 1110 – Using Computers Operating Systems & Utility Programs Chapter 7.

Operating Systems: Software in the Background

1 Pertemuan 6 Understanding Operating Systems Matakuliah: J0282 / Pengantar Teknologi Informasi Tahun: 2005 Versi: 02/02.

Chapter 1. What is computer fluency? The knowledge possessed by people who are able to navigate the digital world successfully NOT THIS.

Operating Systems BTEC IT Practitioners.

Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne Operating System Concepts Chapter 1: Introduction What is an Operating System? Mainframe Systems Desktop Systems.

1/16/2008CSCI 315 Operating Systems Design1 Introduction Notice: The slides for this lecture have been largely based on those accompanying the textbook.

Operating Systems.

LECTURE 14 Operating Systems and Utility Programs

Chapter 8 Operating Systems and Utility Programs By: James Granahan.
Lesson 4 Computer Software

Section 2.1 Identify hardware Describe processing components Compare and contrast input and output devices Compare and contrast storage devices Section.

About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Operating System
Mar 29, 2019
3.21k likes | 3.78k Views
Operating System. What is an operating system?. An operating system is a layer of software which takes care of technical aspects of a computer's operation. It shields the user of the machine from the low-level details of the machine's operation and provides frequently needed facilities.
Share Presentation
- first program
- different users
- digital equipment corporation
- level problems
- multiple users

Presentation Transcript
What is an operating system? • An operating system is a layer of software which takes care of technical aspects of a computer's operation. • It shields the user of the machine from the low-level details of the machine's operation and provides frequently needed facilities. • You can think of it as being the software which is already installed on a machine, before you add anything of your own.
What is an operating system? • Normally the operating system has a number of key elements: (i) a technical layer of software for driving the hardware of the computer, like disk drives, the keyboard and the screen; (ii) a filesystem which provides a way of organizing files logically, and (iii) a simple command language which enables users to run their own programs and to manipulate their files in a simple way. • Some operating systems also provide text editors, compilers, debuggers and a variety of other tools.
What is an operating system? • Since the operating system (OS) is in charge of a computer, all requests to use its resources and devices need to go through the OS. • An OS therefore provides (iv) legal entry points into its code for performing basic operations like writing to devices.
What is an operating system? • Operating systems may be classified by both how many tasks they can perform `simultaneously' and by how many users can be using the system `simultaneously'. • That is: single-user or multi-user and single-task or multi-tasking. A multi-user system must clearly be multi-tasking.
What is an operating system? • The first of these (MS/PC DOS/Windows 3x) are single user, single-task systems which build on a ROM based library of basic functions called the BIOS. • These are system calls which write to the screen or to disk etc. • Although all the operating systems can service interrupts, and therefore simulate the appearance of multitasking in some situations, the older PC environments cannot be thought of as a multi-tasking systems in any sense.
What is an operating system? • Only a single user application could be open at any time. • Windows 95 replaced the old coroutine approach of quasi-multitasking with a true context switching approach, but only a single user system, without proper memory protection.
What is an operating system? • The Macintosh system 7 can be classified as single-user quasi-multitasking1.1. That means that it is possible to use several user applications simultaneously. • A window manager can simulate the appearance of several programs running simultaneously, but this relies on each program obeying specific rules in order to achieve the illusion. • The MacIntosh not a true multitasking system in the sense that, if one program crashes, the whole system crashes.
What is an operating system? • Windows is purported to be preemptive multitasking but most program crashes also crash the entire system. • This might be due to the lack of proper memory protection. The claim is somewhat confusing.
What is an operating system? • AmigaDOS is an operating system for the Commodore Amiga computer. • It is based on the UNIX model and is a fully multi-tasking, single-user system. • Several programs may be actively running at any time. • The operating system includes a window environment which means that each independent program has a `screen' of its own and does not therefore have to compete for the screen with other programs. • This has been a major limitation on multi-tasking operating systems in the past.
What is an operating system? • MTS (Michigan timesharing system) was the first time-sharing multi-user system. • It supports only simple single-screen terminal based input/output and has no hierarchical file system.
What is an operating system? • Unix is arguably the most important operating system today, and one which we shall frequently refer to below. • It comes in many forms, developed by different manufacturers. • Originally designed at AT&T, UNIX split into two camps early on: BSD (Berkeley software distribution) and system 5 (AT&T license).
What is an operating system? • The BSD version was developed as a research project at the university of Berkeley, California. • Many of the networking and user-friendly features originate from these modifications.
What is an operating system? • Unix is generally regarded as the most portable and powerful operating system available today by impartial judges, but NT is improving quickly. • Unix runs on everything from laptop computers to CRAY mainframes. • It is particularly good at managing large database applications and can run on systems with hundreds of processors. • Most Unix types support symmetric multithreaded processing and all support simultaneous logins by multiple users.
What is an operating system? • NT is a `new' operating system from Microsoft based on the old VAX/VMS kernel from the Digital Equipment Corporation (VMS's inventor moved to Microsoft) and the Windows32 API. • Initially it reinvented many existing systems, but it is gradually being forced to adopt many open standards from the Unix world.
What is an operating system? • It is fully multitasking, and can support multiple users (but only one at a time-- multiple logins by different users is not possible). • It has virtual memory and multithreaded support for several processors. NT has a built in object model and security framework which is amongst the most modern in us
Hierarchies and black boxes • A hierarchy is a way of organizing information using levels of detail. • The phrase high-level implies few details, whereas low-level implies a lot of detail, down in the guts of things. • A hierarchy usually has the form of a tree, which branches from the highest level to the lowest, since each high-level object is composed of several lower-level objects.
Hierarchies and black boxes • The key to making large computer programs and to solving difficult problems is to create a hierarchical structure, in which large high-level problems are gradually broken up into manageable low-level problems. • Each level works by using a series of `black boxes' (e.g. subroutines) whose inner details are not directly visible. • This allows us to hide details and remain sane as the complexity builds up.
Resources and sharing • A computer is not just a box which adds numbers together. • It has resources like the keyboard and the screen, the disk drives and the memory. • In a multi-tasking system there may be several programs which need to receive input or write output simultaneously and thus the operating system may have to share these resources between several running programs.
Resources and sharing • If the system has two keyboards (or terminals) connected to it, then the OS can allocate both to different programs. • If only a single keyboard is connected then competing programs must wait for the resources to become free.
Resources and sharing • Most multi-tasking systems have only a single central processor unit and yet this is the most precious resource a computer has. • An multi-tasking operating system must therefore share cpu-time between programs. • That is, it must work for a time on one program, then work a while on the next program, and so on. • If the first program was left unfinished, it must then return to work more on that, in a systematic way. The way an OS decides to share its time between different tasks is called scheduling.
Communication, protocols, data types • The exchange of information is an essential part of computing. • Suppose computer A sends a message to computer B reporting on the names of all the users and how long they have been working. • To do this it sends a stream of bits across a network. • When computer B receives a stream of bits, it doesn't automatically know what they mean.
Communication, protocols, data types • It must decide if the bits represent numbers or characters, integers or floating point numbers, or a mixture of all of them. • These different types of data are all stored as binary information - the only difference between them is the way one chooses to interpret them.
Communication, protocols, data types • The resolution to this problem is to define a protocol. • This is a convention or agreement between the operating systems of two machines on what messages may contain. • The agreement may say, for instance, that the first thirty-two bits are four integers which give the address of the machine which sent the message. • The next thirty-two bits are a special number telling the OS which protocol to use in order to interpret the data.
Communication, protocols, data types • The OS can then look up this protocol and discover that the rest of the data are arranged according to a pattern of • <name><time><name><time>... • where the name is a string of bytes, terminated by a zero, and the time is a four byte digit containing the time in hours. Computer B now knows enough to be able to extract the information from the stream of bits.
Communication, protocols, data types • It is important to understand that all computers have to agree on the way in which the data are sent in advance. • If the wrong protocol is diagnosed, then a string of characters could easily be converted into a floating point number - but the result would have been nonsense.
Communication, protocols, data types • Similarly, if computer A had sent the information incorrectly, computer B might not be able to read the data and a protocol error would arise. • More generally, a protocol is an agreed sequence of behavior which must be followed. • For example, when passing parameters to functions in a computer program, there are rules about how the parameter should be declared and in which order they are sent.
System overhead • An operating system is itself a computer program which must be executed. • It therefore requires its own share of a computer's resources. • This is especially true on multitasking systems, such as UNIX, where the OS is running all the time along side users' programs. • Since user programs have to wait for the OS to perform certain services, such as allocating resources, they are slowed down by the OS
System overhead • The time spent by the OS servicing user requests is called the system overhead. • On a multi-user system one would like this overhead to be kept to a minimum, since programs which make many requests of the OS slow not only themselves down, but all other programs which are queuing up for resources.
Caching • Caching is a technique used to speed up communication with slow devices. • Usually the CPU can read data much faster from memory than it can from a disk or network connection, so it would like to keep an up-to-date copy of frequently used information in memory. • The memory area used to do this is called a cache. • You can think of the whole of the primary memory as being a cache for the secondary memory (disk). • Sometimes caching is used more generally to mean `keeping a local copy of data for convenience'.
Hardware • The CPU • Memory • Devices
Interrupts, traps, exceptions • Interrupts are hardware signals which are sent to the CPU by the devices it is connected to. • These signals literally interrupt the CPU from what it is doing and demand that it spend a few clock cycles servicing a request. • For example, interrupts may come from the keyboard because a user pressed a key. • Then the CPU must stop what it is doing and read the keyboard, place the key value into a buffer for later reading, and return to what it was doing.
Interrupts, traps, exceptions • Other `events' generate interrupts: the system clock sends interrupts at periodic intervals, disk devices generate interrupts when they have finished an I/O task and interrupts can be used to allow computers to monitor sensors and detectors. • User programs can also generate `software interrupts' in order to handle special situations like a `division by zero' error. • These are often called traps or exceptions on some systems.
Interrupts, traps, exceptions • Interrupts are graded in levels. • Low level interrupts have a low priority, whereas high level interrupts have a high priority. • A high level interrupt can interrupt a low level interrupt, so that the CPU must be able to recover from several `layers' of interruption and end up doing what it was originally doing.
Resource management • In order to keep track of how the system resources are being used, an OS must keep tables or lists telling it what is free an what is not. • For example, data cannot be stored neatly on a disk. As files become deleted, holes appear and the data become scattered randomly over the disk surface.
Spooling • Spooling is a way of processing data serially. • Print jobs are spooled to the printer, because they must be printed in the right order (it would not help the user if the lines of his/her file were liberally mixed together with parts of someone elses file). • During a spooling operation, only one job is performed at a time and other jobs wait in a queue to be processed. Spooling is a form of batch processing.
System calls • An important task of an operating system is to provide black-box functions for the most frequently needed operations, so that users do not have to waste their time programming very low level code which is irrelevant to their purpose. • These ready-made functions comprise frequently used code and are called system calls.
System calls • For example, controlling devices requires very careful and complex programming. • Users should not have to write code to position the head of the disk drive at the right place just to save a file to the disk. • This is a very basic operation which everyone requires and thus it becomes the responsibility of the OS. Another example is mathematical functions or graphics primitives.
Filesystem • Should the filesystem distinguish between types of files e.g. executable files, text files, scripts. • If so how? One way is to use file extensions, or a naming convention to identify files, like myprog.exe, SCRIPT.BAT, file.txt. • The problem with this is that the names can be abused by users.
Filesystem • Protection. If several users will be storing files together on the same disk, should each user's files be exclusive to him or her? • Is a mechanism required for sharing files between several users?
Filesystem • A hierarchical filesystem is a good starting point for organizing files, but it can be too restrictive. Sometimes it is useful to have a file appear in several places at one time. • This can be accomplished with links. A link is not a copy of a file, but a pointer to where a file really is. • By making links to other places in a hierarchical filesystem, its flexibility is increased considerably.
Single-task OS • Memory map and registers • Roughly speaking, at the hardware level a computer consists of a CPU, memory and a number of peripheral devices. • The CPU contains registers or `internal variables' which control its operation. • The CPU can store information only in the memory it can address and in the registers of other microprocessors it is connected to. • The CPU reads machine code instructions, one at a time, from the memory and executes them forever without stopping.
Single-task OS • Memory map and registers • The memory, as seen by the CPU, is a large string of bytes starting with address and increasing up to the maximum address. • Physically it is made up, like a jigsaw puzzle, of many memory chips and control chips. mapped into the diagram shown. • Normally, because of the hardware design of the CPU, not all of the memory is available to the user of the machine. Some of it is required for the operation of the CPU.
Single-task OS • Memory map and registers -The roughly distinguished areas are • Zero page: The first t `page' of the memory is often reserved for a special purpose. It is often faster to write to the zero page because you don't have to code the leading zero for the address - special instructions for the zero page can leave the `zero' implicit. • Stack: Every CPU needs a stack for executing subroutines. The stack is explained in more detail below. • User programs: Space the user programs can `grow into'.
Single-task OS • Memory map and registers -The roughly distinguished areas are • Screen memory: What you see on the screen of a computer is the image of an area of memory, converted into colours and positions by a hardware video-controller. The screen memory is the area of memory needed to define the colour of every `point' or `unit' on the screen. Depending on what kind of visual system a computer uses, this might be one byte per character and it might be four bytes per pixel!
Single-task OS • Memory map and registers -The roughly distinguished areas are • Memory mapped I/O: Hardware devices like disks and video controllers contain smaller microprocessors of their own. The CPU gives them instructions by placing numbers into their registers. To make this process simpler, these device registers (only a few bytes per device, perhaps) are `wired' into the main memory map, so that writing to the device is the same as writing to the rest of the memory. • Operating system: The operating system itself is a large program which often takes up a large part of the available memory.
Single-task OS • Memory map and registers -The roughly distinguished areas are
Single-task OS • Stack • A stack is a so-called last-in first-out (LIFO) data structure. • That is to say - the last thing to be placed on top of a stack, when making it, is the first item which gets removed when un-making it. • Stacks are used by the CPU to store the current position within a program before jumping to subroutines, so that they remember where to return to after the subroutine is finished.
Single-task OS • Stack • Because of the nature of the stack, the CPU can simply deposit the address of the next instruction to be executed (after the subroutine is finished) on top of the stack. • When the subroutine is finished, the CPU pulls the first address it finds off the top of the stack and jumps to that location.
Single-task OS • Stack • Notice that the stack mechanism will continue to work even if the subroutine itself calls another subroutine, since the second subroutine causes another stack frame to be saved on the top of the stack. • When that is finished, it returns to the first subroutine and then to the original program in the correct order.
- More by User

Operating system
Operating system. Part four. Introduction to computer, 2nd semester, 2010/2011 Mr.Nael Aburas [email protected] Faculty of Information Technology Islamic University of Gaza. Security. The security of a computer system requires a well-designed operating system.
5.11k views • 8 slides

The operating system controls your computer's tasks and manages system resources to optimize performance.
2.3k views • 25 slides

Operating system . Priyanka Thakkar Rhythm Shah Rohan Thakkar Sarvesh Kapre Shardul Mahadik. What Is It?. It is the first program to be loaded on boot. It is a software that acts as a bridge between the hardware and the applications .
1.79k views • 16 slides

OPERATING SYSTEM
OPERATING SYSTEM. LESSON 8 (DEADLOCKS). DEADLOCKS.
811 views • 47 slides

OPERATING SYSTEM. LESSON 3. OPERATING SYSTEM CONCEPTS. All operating systems have certain basic concepts such as processes, memory, and files. A general OS do following jobs in a computer system :. Process Management Scheduling Inter - process Communication Memory Management.
1.4k views • 34 slides

OPERATING SYSTEM. LESSON 1. HISTORY OF OPERATING SYS TEM. The First Generation (1945-55) The Second Generation (1955-65) The Third Generation (1965-1980) The Fourth Generation (1980-Present). 1. The First Generation (1945-55) .
1.03k views • 25 slides

OPERATING SYSTEM. LESSON 7. SCHEDUL I NG.
550 views • 31 slides

Operating System. U2M3 Lecture 4 Process Management – Scheduling Algorithms. Objectives. Explain the purpose of scheduling List scheduling Criteria Discuss types of scheduling algorithms. Scheduling Algorithm. The scheduling algorithm is a part of the operating system that
589 views • 13 slides

Operating System. Introduction. What Operating Systems Do Computer-System Organization Computer-System Architecture Operating-System Structure Operating-System Operations Process Management Memory Management Storage Management Protection and Security Distributed Systems
1.35k views • 39 slides

Operating System. A program that controls the execution of application programs An interface between applications and hardware Main objectives of an OS: Convenience Efficiency Ability to evolve. Layers and Views. Services Provided by the Operating System. Program development
1.14k views • 60 slides

Operating System. Allen C.-H. Wu Department of Computer Science Tsing Hua University. Part I: Overview Ch. 1 Introduction.
2.65k views • 229 slides

Operating System. Hardware. Operating System (OS). Programming Language (e.g. PASCAL). Application Programs (e.g. WORD, EXCEL). Architecture of Computer System. Detail Layered View of Computer. System Software, Application Software and Driver Programs.
816 views • 30 slides

OPERATING SYSTEM. Dalia AL-Dabbagh 120090285. Define AN OPERATING SYSTEM?. WHAT IS AN OPERATING SYSTEM? An interface between users and hardware - an environment "architecture” Allows convenient usage; hides the tedious stuff Allows efficient usage; parallel activity, avoids wasted cycles
812 views • 15 slides

COMMENTS
Template 7: Examples of Batch Processing Operating System. The batch processing operating system has components that this PPT Template highlights for you. Get this template to highlight elements like Payroll, Ban Invoice System, Transaction Process, Billing, Daily report, and Research segment through creative charts and effective icons.
Operating System Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles. Deliver a lucid presentation by utilizing this Operating System Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles. Use it to present an overview of the topic with the right visuals, themes, shapes, and graphics. This is an expertly designed complete deck that reinforces positive thoughts and actions.
To create a PowerPoint presentation on an operating system, you will need to follow a series of steps designed to ensure a comprehensive, informative, and engaging presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide: Research: Start by conducting thorough research on the operating system you plan to discuss. Make sure to understand its key features ...
Our picture-perfect Operating System Concepts PPT template is the best pick for software and hardware experts to impart knowledge on the environment created by an operating system to help users execute and manage programs. You can also capitalize on the set to illustrate how operating systems make it convenient for users to use the computer system.
Operating System Concepts Ninth Edition ... Click on the links below to download the slides in Powerpoint format. We also provide zip files of the all Powerpoint files, PDF files, and all figures used in the text . Chapter: Powerpoint : Last Updated : Part 1: Overview : 1. Introduction : ppt: Sep 21, 2013 : 2. Operating-System Structures : ppt ...
3 What is an Operating System (OS)? A program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware. A set of programs that coordinates all activities among computer hardware resources. Operating system goals: Execute user programs and make solving user problems easier. Make the computer system convenient to use. Use the computer hardware in an efficient manner.
Chapter 10: Operating Systems. An operating system is a set of programs through which a computer manages its resources. Its main functions are to:. Manage the computer hardware CPU performance & utilization Memory allocation & protection Input-output management Keyboard control
Examples of such operating systems are PalmOS and Windows CE (Consumer Electronics). 47. Smart Card OS The smallest operating systems run on smart cards, whichare credit card-sized devices containing a CPU chip. They have very severe processing power and memoryconstraints. Some of them can handle only a single function, such as electronic ...
Multi User • more than one user accessing the system at the same time • most commonly: network operating system • server computer connected to a number of terminals • client-server LAN, ATM, ticket booking • O/S allocates a time slice to each user • switches from user to user • the larger the number of users the slower the system ...
To make this process simpler, these device registers (only a few bytes per device, perhaps) are `wired' into the main memory map, so that writing to the device is the same as writing to the rest of the memory. • Operating system: The operating system itself is a large program which often takes up a large part of the available memory.