Essay on Indian Economy
India’s economy is described as huge, complex and growing. It is one of the most exciting and emerging markets in the world. Since 1951, India has grown as a planned economy. The first few plans focused on growth with the strengthening of the manufacturing sector, emphasising heavy industries to form the backbone of the economy. Other principal areas of planning were agriculture and social development. During the post-independence period and the period of the “Five-year plans”, efforts were focused on identifying the needs of the economy. Further, the economic reforms in the early 90s opened a new chapter in India’s economic history. It gave India an opportunity to shake off the shackles of its past and emerge on the world stage as a progressive nation. This essay on the Indian Economy will help students know about the Indian economy in detail.
Students can go through the list of CBSE Essays on different topics. It will help them to improve their writing skills and also increase their scores on the English exam. Moreover, they can participate in different essay writing competitions which are conducted at the school level.

500+ Words Essay on the Indian Economy
India is on the high road to economic growth. Since 2020, the world economy has declined due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Repeated waves of infection, supply-chain disruptions and inflation have created challenging times. Faced with these challenges, the Government of India has taken immediate action so that it has the least impact on the Indian economy.
The Indian economy has been staging a sustained recovery since the second half of 2020-21. However, the second wave of the pandemic in April-June 2021 was more severe from a health perspective. The national lockdown has affected small businesses, common people and everyone in India. Due to this, the Indian economy has gone down. But now, it is slowly rising up and taking its form.
Role of Agriculture in the Indian Economy
Agriculture is one of the most important sectors of the Indian economy. It supplies food and raw materials in the country. At the time of independence, more than 70% of India’s population depended on agriculture to earn a livelihood. Accordingly, the share of agriculture in the national product/income was as high as 56.6% in 1950-51. However, with the development of industries and the service sector, the percentage of the population depending on agriculture, as well as the share of agriculture in the national product, has come down. Agriculture is the source of food supply. Agriculture is also a major source of foreign exchange earnings through export. The share of agriculture in India’s export in the year 2011-12 was 12.3%. The major items of export include tea, sugar, tobacco, spices, cotton, rice, fruits and vegetables, etc.
Role of Industry in India’s Economy
Industry is the secondary sector of the economy and is another important area of economic activity. After independence, the Government of India emphasised the role of industrialisation in the country’s economic development in the long run. Initially, the public sector contributed the maximum to economic growth. In the early 1990s, it was found that the public sector undertakings were not performing up to expectations. So, in 1991, the Indian Government decided to encourage the role of the private sector in industrial development. This step was taken to strengthen the process of industrialisation in India.
The progress of the Indian economy after independence was impressive indeed. India became self-sufficient in food production due to the green revolution, and industries became far more diversified. However, we still have to go a long way to become a 5 trillion economy by 2025. But, with government effort and the right policymakers, it can be achieved.
Students must have found this essay on the Indian Economy useful for improving their essay-writing skills. They can get the study material and the latest update on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Screen Reader
- Skip to main content
- Text Size A
- Language: English
- Case Studies
- EXIM Procedure
Media & Events
- Image Gallery
- Media Coverage
Other Links
- Discover India
- GI of India
- Experience India
- Indian Trend Fair 2022
- India Organic Biofach 2022
- Gulfood Dubai 2023
Indian Economy Overview
About indian economy growth rate & statistics, introduction.
Strong economic growth in the first quarter of FY23 helped India overcome the UK to become the fifth-largest economy after it recovered from the COVID-19 pandemic shock. Nominal GDP or GDP at Current Prices for Q1 2024-25 is estimated at Rs. 77.31 lakh crores (US$ 928.9 billion) with growth rate of 9.7%, compared to the growth of 8.5% for Q1 2023-24. The growth in nominal GDP during 2023-24 is estimated at 9.6% as compared to 14.2% in 2022-23. Strong domestic demand for consumption and investment, along with Government’s continued emphasis on capital expenditure are seen as among the key driver of the GDP in the second half of FY24. During the period April-September 2025, India’s exports stood at US$ 211.46 billion, with Engineering Goods (26.57%), Petroleum Products (16.51%) and electronic goods (7.39%) being the top three exported commodity. Rising employment and increasing private consumption, supported by rising consumer sentiment, will support GDP growth in the coming months.
Future capital spending of the government in the economy is expected to be supported by factors such as tax buoyancy, the streamlined tax system with low rates, a thorough assessment and rationalisation of the tariff structure, and the digitization of tax filing. In the medium run, increased capital spending on infrastructure and asset-building projects is set to increase growth multipliers. The contact-based services sector has demonstrated promise to boost growth by unleashing the pent-up demand. The sector's success is being captured by a number of HFIs (High-Frequency Indicators) that are performing well, indicating the beginnings of a comeback.
India has emerged as the fastest-growing major economy in the world and is expected to be one of the top three economic powers in the world over the next 10-15 years, backed by its robust democracy and strong partnerships.
India's appeal as a destination for investments has grown stronger and more sustainable because of the current period of global unpredictability and volatility, and the record amounts of money raised by India-focused funds in 2022 are evidence of investor faith in the "Invest in India" narrative.

Market size
Real GDP or GDP at Constant (2011-12) Prices for the period Q1 2024-25 is estimated at Rs. 43.64 lakh crore (US$ 524 billion), against the First Revised Estimates (FRE) of GDP for the year Q1 2023-24 of Rs. 40.91 lakh crore (US$ 491 million). The growth in real GDP during 2023-24 is estimated at 8.2% as compared to 7.0% in 2022-23. There are 113 unicorn startups in India, with a combined valuation of over US$ 350 billion. As many as 14 tech startups are expected to list in 2024 Fintech sector poised to generate the largest number of future unicorns in India. With India presently has the third-largest unicorn base in the world. The government is also focusing on renewable sources by achieving 40% of its energy from non-fossil sources by 2030. India is committed to achieving the country's ambition of Net Zero Emissions by 2070 through a five-pronged strategy, ‘Panchamrit’. Moreover, India ranked 3rd in the renewable energy country attractive index.
According to the McKinsey Global Institute, India needs to boost its rate of employment growth and create 90 million non-farm jobs between 2023 to 2030 in order to increase productivity and economic growth. The net employment rate needs to grow by 1.5% per annum from 2023 to 2030 to achieve 8-8.5% GDP growth between same time periods. India’s current account deficit (CAD) narrowed to 0.7% of GDP in FY24. The CAD stood at US$ 9.7 billion for the Q1 2024-25 from US$ 8.9 billion in Q1 2023-24 or 1.1% of GDP. This was largely due to decrease in merchandise trade deficit.
Exports fared remarkably well during the pandemic and aided recovery when all other growth engines were losing steam in terms of their contribution to GDP. Going forward, the contribution of merchandise exports may waver as several of India’s trade partners witness an economic slowdown. According to Minister of Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and Textiles Mr. Piyush Goyal, Indian exports are expected to reach US$ 1 trillion by 2030.
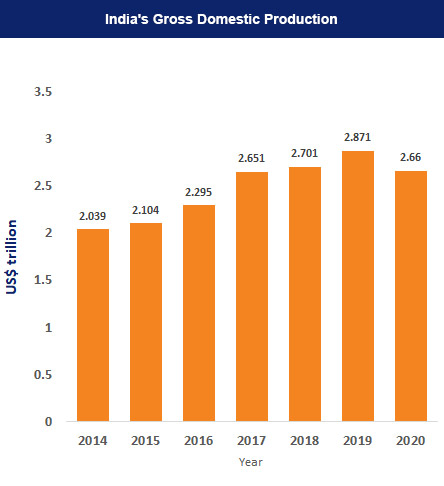
Recent Developments
India is primarily a domestic demand-driven economy, with consumption and investments contributing to 70% of the economic activity. With an improvement in the economic scenario and the Indian economy recovering from the Covid-19 pandemic shock, several investments and developments have been made across various sectors of the economy. According to World Bank, India must continue to prioritise lowering inequality while also putting growth-oriented policies into place to boost the economy. In view of this, there have been some developments that have taken place in the recent past. Some of them are mentioned below.
- According to HSBC Flash India PMI report, business activity surged in April to its highest level in about 14 years as well as sustained robust demand. The composite index reached 62.2, indicating continuous expansion since August 2021, alongside positive job growth and decreased input inflation, affirming India's status as the fastest-growing major economy.
- As of October 11, 2024, India’s foreign exchange reserves stood at US$ 690.43 billion.
- In 1H 2024, India saw a total of US$ 31.5 billion in PE-VC investments.
- India secured 39th position out of 133 economies in the Global Innovation Index 2024. India rose from 81st position in 2015 to 39th position in 2024. India ranks 3rd position in the global number of scientific publications.
- In September 2024, the gross Goods and Services Tax (GST) stood at highest monthly revenue collection at Rs. 1.73 lakh crore (US$ 20.83 billion).
- Between April 2000–June 2024, cumulative FDI equity inflows to India stood at US$ 1,013.45 billion.
- In August 2024, the overall IIP (Index of Industrial Production) stood at 145.6. The Indices of Industrial Production for the mining, manufacturing and electricity sectors stood at 125.1, 147.1 and 219.3, respectively.
- According to data released by the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation (MoSPI), India’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) based retail inflation reached 5.49% (Provisional) for September 2024.
- Foreign Institutional Investors (FII) inflows between April-July (2023-24) were close to Rs. 80,500 crore (US$ 9.67 billion), while Domestic Institutional Investors (DII) sold Rs. 4,500 crore (US$ 540.56 million) in the same period. As per depository data, Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) invested (US$ 13.89 billion) in India during January- (up to 15th July) 2024.
- The wheat procurement during Rabi Marketing Season (RMS) 2024-25 (till May) was estimated to be 266 lakh metric tonnes (LMT) and the rice procured in Kharif Marketing Season (KMS) 2024-25 was 400 LMT.
Government Initiatives
Over the years, the Indian government has introduced many initiatives to strengthen the nation's economy. The Indian government has been effective in developing policies and programmes that are not only beneficial for citizens to improve their financial stability but also for the overall growth of the economy. Over recent decades, India's rapid economic growth has led to a substantial increase in its demand for exports. Besides this, a number of the government's flagship programmes, including Make in India, Start-up India, Digital India, the Smart City Mission, and the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation, is aimed at creating immense opportunities in India. In this regard, some of the initiatives taken by the government to improve the economic condition of the country are mentioned below:
- In July 2024, the Ministry of Finance held the Union Budget and announced that for 2024-25, the total receipts other than borrowings and the total expenditure are estimated at Rs. 32.07 lakh crore (US$ 383.93 billion) and Rs. 48.21 lakh crore (US$ 577.16 billion), respectively.
- In February 2024, the Finance Ministry announced the total expenditure in Interim 2024-25 estimated at Rs. 47,65,768 crore (US$ 571.64 billion) of which total capital expenditure is Rs. 11,11,111 crore (US$ 133.27 billion).
- On January 22, 2024, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi announced the 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana'. Under this scheme, 1 crore households will receive rooftop solar installations.
- On September 17, 2023, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi launched the Central Sector Scheme PM-VISHWAKARMA in New Delhi. The new scheme aims to provide recognition and comprehensive support to traditional artisans & craftsmen who work with their hands and basic tools. This initiative is designed to enhance the quality, scale, and reach of their products, as well as to integrate them with MSME value chains.
- On August 6, 2023, Amrit Bharat Station Scheme was launched to transform and revitalize 1309 railway stations across the nation. This scheme envisages development of stations on a continuous basis with a long-term vision.
- On June 28, 2023, the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change introduced the ‘Draft Carbon Credit Trading Scheme, 2023’.
- From April 1, 2023, Foreign Trade Policy 2023 was unveiled to create an enabling ecosystem to support the philosophy of ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ and ‘Local goes Global’.
- To enhance India’s manufacturing capabilities by increasing investment and production in the sector, the government of India has introduced the Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI) for Pharmaceuticals.
- Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North-East Region (PM-DevINE) was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 with a financial outlay of Rs. 1,500 crore (US$ 182.35 million).
- Prime Minister Mr Narendra Modi has inaugurated a new food security scheme for providing free food grains to Antyodaya Ann Yojna (AAY) & Primary Household (PHH) beneficiaries, called Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Ann Yojana (PMGKAY) from January 1, 2023.
- The Amrit Bharat Station scheme for Indian Railways envisages the development of stations on a continuous basis with a long-term vision, formulated on December 29, 2022, by the Ministry of Railways.
- On October 7, 2022, the Department for Promotion of Industry, and Internal Trade (DPIIT) launched Credit Guarantee Scheme for Start-ups (CGSS) aiming to provide credit guarantees up to a specified limit by start-ups, facilitated by Scheduled Commercial Banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies and Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) registered Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs).
- Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF) Scheme was launched in October 2022 by the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF), a body under the Department of Telecommunications. The objective is to fund R&D in rural-specific communication technology applications and form synergies among academia, start-ups, research institutes, and the industry to build and develop the telecom ecosystem.
- Home & Cooperation Minister Mr. Amit Shah laid the foundation stone and performed Bhoomi Pujan of Tanot Mandir Complex Project under Border Tourism Development Programme in Jaisalmer in September 2022.
- In August 2022, Mr. Narendra Singh Tomar, Minister of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare inaugurated four new facilities at the Central Arid Zone Research Institute (CAZRI), which has been rendering excellent services for more than 60 years under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- In August 2022, a Special Food Processing Fund of Rs. 2,000 crore (US$ 242.72 million) was set up with National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) to provide affordable credit for investments in setting up Mega Food Parks (MFP) as well as processing units in the MFPs.
- In July 2022, Deendayal Port Authority (DPA) announced plans to develop two Mega Cargo Handling Terminals on a Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) basis under Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Mode at an estimated cost of Rs. 5,963 crore (US$ 747.64 million).
- In July 2022, the Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi, approved the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India & Maldives. This MoU will provide a platform to tap the benefits of information technology for court digitization and can be a potential growth area for IT companies and start-ups in both countries.
- India and Namibia entered a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on wildlife conservation and sustainable biodiversity utilization on July 20, 2022, for establishing the cheetah into the historical range in India.
- In July 2022, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) approved international trade settlements in Indian rupees (Rs.) to promote the growth of global trade with emphasis on exports from India and to support the increasing interest of the global trading community.
- The Agnipath Scheme aims to develop a young and skilled armed force backed by an advanced warfare technology scheme by providing youth with an opportunity to serve Indian Army for a 4-year period. It is introduced by the Government of India on June 14, 2022.
- In June 2022, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi inaugurated and laid the foundation stone of development projects worth Rs. 21,000 crore (US$ 2.63 billion) at Gujarat Gaurav Abhiyan at Vadodara.
- Mr. Rajnath Singh, Minister of Defence, launched 75 newly developed Artificial Intelligence (AI) products/technologies during the first-ever ‘AI in Defence’ (AIDef) symposium and exhibition organized by the Ministry of Defence in New Delhi on July 11, 2022.
- In June 2022, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone of 1,406 projects worth more than Rs. 80,000 crore (US$ 10.01 billion) at the ground-breaking ceremony of the UP Investors Summit in Lucknow. The Projects encompass diverse sectors like Agriculture and Allied industries, IT and Electronics, MSME, Manufacturing, Renewable Energy, Pharma, Tourism, Defence & Aerospace, and Handloom & Textiles.
- The Indian Institute of Spices Research (IISR) under the Indian Council for Agricultural Research (ICAR) inked a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Lysterra LLC, a Russia-based company for the commercialization of bio capsule, an encapsulation technology for bio-fertilization on June 30, 2022.
- As of April 2022, India signed 13 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with its trading partners including major trade agreements like the India-UAE Comprehensive Partnership Agreement (CEPA) and the India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (IndAus ECTA).
- 'Mission Shakti' was applicable with effect from April 1, 2022, aimed at strengthening interventions for women’s safety, security, and empowerment.
- The Union Budget of 2022-23 was presented on February 1, 2022, by the Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs, Ms. Nirmala Sitharaman. The budget had four priorities PM GatiShakti, Inclusive Development, Productivity Enhancement and Investment, and Financing of Investments. In the Union Budget 2022-23, effective capital expenditure is expected to increase by 27% at Rs. 10.68 trillion (US$ 142.93 billion) to boost the economy. This will be 4.1% of the total Gross Domestic Production (GDP).
- Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry (SPI) was launched in March 2022 by the Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilisers to provide credit linked capital and interest subsidy for Technology Upgradation of MSME units in pharmaceutical sector, as well as support of up to Rs. 20 crore (US$ 2.4 million) each for common facilities including Research centre, testing labs and ETPs (Effluent Treatment Plant) in Pharma Clusters, to enhance the role of MSMEs.
- Under PM GatiShakti Master Plan, the National Highway Network will develop 25,000 km of new highways network, which will be worth Rs. 20,000 crore (US$ 2.67 billion). In 2022-23. Increased government expenditure is expected to attract private investments, with a production-linked incentive scheme providing excellent opportunities. Consistently proactive, graded, and measured policy support is anticipated to boost the Indian economy.
- In February 2022, The Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment launched the Scheme for Economic Empowerment of Denotified/Nomadic/SemiNomadic tribal communities (DNTs) (SEED) to provide basic facilities like good quality coaching, and health insurance. livelihoods initiative at a community level and financial assistance for the construction of houses.
- In February 2022, Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs Ms. Nirmala Sitharaman said that productivity linked incentive (PLI) schemes would be extended to 14 sectors to achieve the mission of Aatmanirbhar Bharat and create 60 lakh jobs with an additional production capacity of Rs. 30 trillion (US$ 401.49 billion) in the next five years.
- In the Union Budget of 2022-23, the government announced funding for the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for domestic solar cells and module manufacturing of Rs. 24,000 crore (US$ 3.21 billion).
- In the Union Budget of 2022-23, the government announced a production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for Bulk Drugs which was an investment of Rs. 2,500 crore (US$ 334.60 million).
- In the Union Budget of 2022, Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs Ms. Nirmala Sitharaman announced that a scheme for design-led manufacturing in 5G would be launched as part of the PLI scheme.
- In September 2021, Union Cabinet approved major reforms in the telecom sector, which are expected to boost employment, growth, competition, and consumer interests. Key reforms include rationalization of adjusted gross revenue, rationalization of bank guarantees (BGs), and encouragement of spectrum sharing.
- In the Union Budget of 2022-23, the government has allocated Rs. 44,720 crore (US$ 5.98 billion) to Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) for capital investments in the 4G spectrum.
- Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs Ms. Nirmala Sitharaman allocated Rs. 650 crore (US$ 86.69 million) for the Deep Ocean mission that seeks to explore vast marine living and non-living resources. Department of Space (DoS) has got Rs. 13,700 crore (US$ 1.83 billion) in 2022-23 for several key space missions like Gaganyaan, Chandrayaan-3, and Aditya L-1 (sun).
- In May 2021, the government approved the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for manufacturing advanced chemistry cell (ACC) batteries at an estimated outlay of Rs. 18,100 crore (US$ 2.44 billion); this move is expected to attract domestic and foreign investments worth Rs. 45,000 crore (US$ 6.07 billion).
- Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs Ms. Nirmala Sitharaman announced in the Union Budget of 2022-23 that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) would issue Digital Rupee using blockchain and other technologies.
- In the Union Budget of 2022-23, Railway got an investment of Rs. 2.38 trillion (US$ 31.88 billion) and over 400 new high-speed trains were announced. The concept of "One Station, One Product" was also introduced.
- To boost competitiveness, Budget 2022-23 has announced reforming the 16-year-old Special Economic Zone (SEZ) act.
- In June 2021, the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) announced that the investment limit for FPI (foreign portfolio investors) in the State Development Loans (SDLs) and government securities (G-secs) would persist unaffected at 2% and 6%, respectively, in FY22.
- In November 2020, the Government of India announced Rs. 2.65 trillion (US$ 36 billion) stimulus package to generate job opportunities and provide liquidity support to various sectors such as tourism, aviation, construction, and housing. Also, India's cabinet approved the production-linked incentives (PLI) scheme to provide ~Rs. 2 trillion (US$ 27 billion) over five years to create jobs and boost production in the country.
- Numerous foreign companies are setting up their facilities in India on account of various Government initiatives like Make in India and Digital India. Prime Minister of India Mr. Narendra Modi launched the Make in India initiative with an aim to boost the country's manufacturing sector and increase the purchasing power of the average Indian consumer, which would further drive demand and spur development, thus benefiting investors. The Government of India, under its Make in India initiative, is trying to boost the contribution made by the manufacturing sector with an aim to take it to 25% of the GDP from the current 17%. Besides, the government has also come up with the Digital India initiative, which focuses on three core components: the creation of digital infrastructure, delivering services digitally, and increasing digital literacy.
- On January 29, 2022, the National Asset Reconstruction Company Ltd (NARCL) will acquire bad loans worth up to Rs. 50,000 crore (US$ 6.69 billion) about 15 accounts by March 31, 2022. India Debt Resolution Co. Ltd (IDRCL) will control the resolution process. This will clean up India’s financial system, help fuel liquidity, and boost the Indian economy.
- National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) is a bank that will provide non-recourse infrastructure financing and is expected to support projects from the first quarter of FY23; it is expected to raise Rs. 4 trillion (US$ 53.58 billion) in the next three years.
- By November 1, 2021, India, and the United Kingdom hope to begin negotiations on a free trade agreement. The proposed FTA between these two countries is likely to unlock business opportunities and generate jobs. Both sides have renewed their commitment to boost trade in a manner that benefits all.
- In August 2021, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi announced an initiative to start a national mission to reach the US$ 400 billion merchandise export target by FY22.
- In August 2021, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi launched a digital payment solution, e-RUPI, a contactless and cashless instrument for digital payments.
- In April 2021, Dr. Ahmed Abdul Rahman AlBanna, Ambassador of the UAE to India and Founding Patron of IFIICC, stated that trilateral trade between India, the UAE and Israel is expected to reach US$ 110 billion by 2030.
- India is expected to attract investment of around US$ 100 billion in developing the oil and gas infrastructure during 2019-23.
- The Government of India is expected to increase public health spending to 2.5% of the GDP by 2025.
In the second quarter of FY24, the growth momentum of the first quarter was sustained, and high-frequency indicators (HFIs) performed well in July and August of 2023. India's comparatively strong position in the external sector reflects the country's positive outlook for economic growth and rising employment rates. India ranked 5th in foreign direct investment inflows among the developed and developing nations listed for the first quarter of 2022.
India's economic story during the first half of the current financial year highlighted the unwavering support the government gave to its capital expenditure, which, in 2023-24, stood 37.4% higher than the same period last year. In the budget of 2024-25, capital expenditure took lead by steeply increasing the capital expenditure outlay by 17.1 % to Rs.11 lakh crore (US$ 133.51 billion) over Rs. 9.48 lakh crore (US$ 113.91 billion) in 2023-24. Stronger revenue generation because of improved tax compliance, increased profitability of the company, and increasing economic activity also contributed to rising capital spending levels.

Since India’s resilient growth despite the global pandemic, India's exports climbed at the second-highest rate with a year-over-year (YoY) growth of 8.39% in merchandise exports and a 29.82% growth in service exports till April 2023. With a reduction in port congestion, supply networks are being restored. The CPI-C inflation reduction from June 2022 already reflects the impact. In September 2023 (Provisional), CPI-C inflation was 5.02%, down from 7.01% in June 2022. With a proactive set of administrative actions by the government, flexible monetary policy, and a softening of global commodity prices and supply-chain bottlenecks, inflationary pressures in India look to be on the decline overall.

Not a member
GDP of India: Current and historical growth rate, India's rank in the world
Get insights into India's GDP in 2023. Learn about the economy's growth and potential as India propels itself towards a prosperous future
India’s current GDP (Q3 FY24)
Related stories.

Poverty rate in India: Trend over the years and causes

Fiscal deficit: Meaning, history in India, causes, current deficit and more
- India's Current GDP (FY24): $3.9 trillion
- India's GDP Growth Rate (FY24): 8.2%
What is GDP growth rate
Historical gdp and growth rate of india, gdp per capita, india’s rank in gdp*, calculating gdp.
- C represents consumption, which includes spending on services, non-durable goods, and durable goods.
- G represents government expenditure, which includes salaries of employees, construction of roads, railways, airports, schools, and military expenses.
- I denotes investment, which consists of spending on housing and equipment.
- The difference between total exports and imports is referred to as net exports, denoted by (X-M).
- In this context, Y represents the Gross Domestic Product.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Related stories.
- India forex reserves 2023: Exploring current status and historical trends
- " class="general-icons icon-sq-googleplus popup">
- " class="general-icons icon-sq-youtube">
Photo of the Day: Berlin Wall Memorial
Photo of the day: Sanju goes for a century
French parliament approves bill to rein in tourist rentals
On the trail of lemurs in Madagascar
Waste heat from London sewers eyed to warm UK parliament
From Forbes India Under 30 nominations to Swiggy IPO, our top stories of the week
Bimal Das Gupta didn't know anything in the world except his art: Paresh Maity
Companies that read more perform better, researchers say
Photo of the day: Chhath Puja 2024
Private jet carbon emissions soar 46%: study
How ElectricPe is building a one-stop solution for EV two-wheelers
8 years of demonetisation: 90 percent of Indian citizens think black money is still deployed in real estate
Forbes India Under 30 2025: Nomination forms now open
I haven't seen a more interesting and happier time for dealmaking in India than now: JM Financial's Sonia Dasgupta
Tech5: Truecaller's founders step down, InfoEdge backs Nexstem, Infinx centre in Madurai and more

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Indian Economy for Students in 100, 200 and 500 Words

- Updated on
- January 12, 2024

Essay on Indian Economy: The Indian economy is a mixed economy, which is primarily driven by the agriculture and services sectors. The agriculture sector contributes to nearly 20% of India’s GDP. Whereas, the services sector accounts for nearly 50% of the country’s GDP. Furthermore, the manufacturing sector contributes to around 28% of India’s GDP. Globally, India is ranked 142nd and 125th in terms of per capita income and nominal GDP, as per the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Since independence, India has transformed from an agricultural country to a mixed economy due to liberalization in 1991. To read more about the Indian economy, keep reading the blog on sample essays about the same.
Table of Contents
- 1 100 words Essay on Indian Economy
- 2 200 words Essay on Indian Economy
- 3 500 words Essay on Indian Economy
Also Read: Class 12 Macroeconomics
100 words Essay on Indian Economy
The Indian economy is dynamic and rapidly growing. Currently, the economy is characterised by various sectors. The key contributors to the country’s economic growth are the agriculture, services, and manufacturing sectors. However, this was not always the case. India was an agricultural economy when the British left India in 1947 after plundering the sub-continent from 1600 to 1947.
After independence, India became a part of the global economy in 1991, when the central government adopted the Liberalisation, Privatisation, and Globalisation (LPG) policy. Since then, the Indian economy has expanded in the service and manufacturing sectors significantly. At present, the economy is driven by government initiatives like Make in India and Digital India. However, we have a long way to go.
Also Read: Find Economics PYQ UPSC Mains Question Bank: 2021-2018
200 words Essay on Indian Economy
Agriculture is the backbone of the Indian economy and of rural livelihoods. It not only employs a majority of the Indian population but also provides raw materials to different industries. In recent years, advancements and innovations in the industrial sector through schemes like the National Manufacturing Policy (NMP), the Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (TUFS), and Make in India have contributed to the growth of the Indian economy.
Despite progress and innovations in farming practices and the industrial sector both these industries are facing losses. This is due to limitations in government policies and a lack of awareness among the people of India. Even today, the agricultural sector is affected by outdated farming methods, dependency on weather, and a lack of skilled workers. All these issues need to be addressed by government policies that help promote an environment-friendly agriculture system that is profitable in nature. This will help the Indian economy grow.
Also, investment in business, easy bureaucratic processes, skilled development programmes, and research and development initiatives, will help in creating favourable conditions for the growth of the Indian economy.
Thus, to uplift the Indian economy, it is necessary to maintain a mutually beneficial partnership between the government and the agriculture and manufacturing sectors. The agriculture sector can grow by overcoming the challenges in farming practices. Whereas, the industrial sector will expand due to strategic investments and progressive policies.
Also Read: Indian Students Adding to the UK Economy
500 words Essay on Indian Economy
Policies for the growth of the Indian economy aim at overcoming poverty, reducing wealth gaps, and optimising productivity. The main purpose of bridging the wealth gap between different sections of society is to improve the overall well-being of its population for sustainable economic development.
1. Overcome of Poverty
As per the Niti Aayog report of July 17, 2023, there is a decrease in the population of people vulnerable to poverty. The percentage of decline is from 24.8 percent to 14.9 percent for four consecutive years, from 2015-2016 to 2019-2021. However, the government is implementing various policies such as the National Education Policy, 2020 (NEP), the National Health Policy, the National Employment Policy (NEP) and many more important programs and policies to decrease the numbers of percentage so that there can be boosted in education, healthcare, and employment opportunities can be raised.
More educated people with good health will better contribute to the Indian economy. Moreover, creating jobs and small businesses will also lead to increased income levels help reduce poverty and encourage economic growth.
2. Reduction of Wealth Gaps
The second important factor in the rise of the Indian economy is reducing the gap between the poor and the rich. To address the wealth gap, various programmes and schemes, such as the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) and the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna (PMJDY), are implemented. Furthermore, to support business innovators from minority communities, small-scale financing is provided through MUDRA Bank.
For social security, initiatives such as Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Yojana and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Yojana are given to encourage social security. These initiatives contribute not only to narrowing the wealth gap through the even distribution of resources but also to establishing a pathway for economic growth in the Indian economy.
3. Fewer Labour Inputs and More Productivity
To encourage both domestic and international companies to invest in the Indian economy, particularly in manufacturing, and innovation, and more importantly, to achieve higher productivity with less input initiatives such as Make in India are encouraged, which not only helps for advancement in technology but also aid in mastering the skills.
The aim of the government of India’s Make in India scheme is to increase productivity and efficiency and reduce dependence on manpower across the different sectors of the Indian economy.
4. Abundance of Goods and Services
The rise in the production of goods and services for a certain period as compared to a previous period helps in the contribution of increased consumption by promoting market competitiveness and driving the innovation of an Indian economy.
Providing consumers with a good number of goods and services not only helps in catering choices but also creates opportunities for boosting business. An Indian economy with a steadfast supply of goods and services leads to stability of prices and improvement in the standard of living of the people.
In conclusion, addressing poverty, reducing the wealth gaps, increasing productivity with fewer labour inputs, and ensuring an abundant supply of goods and services helps in developing the Indian economy. The Indian government is actively implementing policies and technological advancements to encourage these factors and continually revising them to create a broad and steady Indian economy.
Also Read: BA Economics Jobs
Ans. GDP = Consumption + Investment + Government Spending + Net Exports or GDP = C + I + G +NX. Here, (C) is the consumption that represents private-consumption expenditures by households and nonprofit organizations, (I) is the investment that refers to business expenditures by businesses and home purchases by households, government spending, (G) denotes expenditures on goods and services by the government, and net exports (NX) represents a nation’s exports minus its imports.
Ans. Low per capita income, large population, the service sector and diverse sectors such as manufacturing and agriculture are characteristics of the Indian economy.
Ans. Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru is the father of the Indian economy.
Ans. Agriculture is the backbone of Indian economy as it helps in providing raw materials as well as raw materials to the various industries.
Ans. The full form of GDP is Gross Domestic Production.
Related Articles
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Deepika Joshi
Deepika Joshi is an experienced content writer with educational and informative content expertise. She has hands-on experience in Education, Study Abroad and EdTech SaaS. Her strengths lie in conducting thorough research and analysis to provide accurate and up-to-date information to readers. She enjoys staying updated on new skills and knowledge, particularly in the education domain. In her free time, she loves to read articles, and blogs related to her field to expand her expertise further. In her personal life, she loves creative writing and aspires to connect with innovative people who have fresh ideas to offer.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2025
September 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
Top Schools
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
NCERT Study Material
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Books
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- JEE Main Exam
- JEE Advanced Exam
- BITSAT Exam
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Advanced Cutoff
- JEE Main Cutoff
- GATE Registration 2025
- JEE Main Syllabus 2025
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- JEE Main Question Papers
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- Top MBA Colleges in India
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2025
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2025
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2024
- CAT 2024 College Predictor
- Top MBA Entrance Exams 2024
- SNAP Registration
- GD Topics for MBA
- CAT 2024 Admit Card
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Syllabus 2025
- NEET Study Material 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Exam Date 2025
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- Free CLAT Practice Test
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
- UID DAT 2025
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT 2025
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Cutoff
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC 2024
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam 2024
- IIMC Entrance Exam 2024
- MICAT Exam 2025
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India

Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2025
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA 2 Admit card 2024
- SSC CGL Admit card 2024
- CDS 2 Admit card 2024
- UGC NET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2024
- SSC CHSL Result 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI PO Notification 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2025
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- TS EDCET Exam
- IIT JAM 2025
- AP PGCET Exam
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet 2024
- CUET DU CSAS Portal 2024
- CUET 2025 Syllabus
- CUET PG Syllabus 2025
- CUET Participating Universities 2025
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- IGNOU Result 2024
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET College Predictor 2025
- CUET Exam Date 2025
- CUET Appliaction Form 2024
- CUET PG Exam Date 2025
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Counselling 2025
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Essay on The Indian Economy
The Indian economy has experienced a transformation from being a mixed-planned economy to an emergent middle-income social market economy with strong state intervention in key industries. It ranks third in terms of purchasing power parity and fifth overall in terms of nominal GDP (PPP). India is ranked 125th and 142nd in terms of nominal GDP and per capita income, respectively, by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) (PPP). Below are a few sample essays on the Indian economy.

100 Words Essay On The Indian Economy
The Indian subcontinent was the largest economy in the world throughout the bulk of recorded history, up to the beginnings of colonisation in the early 19th century. India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) makes up 7.5% of the world economy, according to purchasing power parity (PPP). Due to its young population, low dependence ratio, high rates of savings and investments, rising globalisation in India, and interaction with the global economy, the long-term outlook for the Indian economy is still good. The shocks of "demonetisation" in 2016 and the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax in 2017 caused the economy to slow down. India's GDP is powered by domestic private spending to a degree of over 70%. The nation continues to be the sixth-largest consumer market in the globe.
200 Words Essay On the Indian Economy
Before the Covid-19 Pandemic struck in 2020 and had a detrimental effect on trade, India's economy was the world's 14th-largest importer and 21st-largest exporter. India has been a member of the World Trade Organisation since January 1, 1995. It ranks 63 on the Ease of Doing Business Index and 68 on the Global Competitiveness Report. India's nominal GDP swings significantly, which is also a result of the significant fluctuations in the rupee/dollar exchange rate. India has the second-largest labour force in the world, with 50 crores (500 million) workers. India is one of the nations with the highest proportion of billionaires and the widest wealth gaps. Due to several exceptions, just 2% of Indians pay income taxes.
Crisis In 2008 | The GDP somewhat decreased as a result of the global financial crisis in 2008. India started fiscal and monetary stimulus programmes to increase demand and strengthen the economy. Later on, economic growth picked up.
Steps For Sustainable Growth | Indian priorities for achieving sustainable economic growth, according to the World Bank, should be infrastructure development, agricultural and rural development, the abolition of land and labour regulations, financial inclusion, fostering private investment and exports, education, and public health.
500 Words Essay On the Indian economy
For a continuous period of more than 1700 years, starting in the year 1 AD, India was the greatest economy in the world, contributing 35 to 40% of the global GDP . Following the collapse of the British Empire, a combination of protectionist, import-substitution, Fabian socialism, and social democratic policies were used to rule India for a spell. Due to its sluggish growth, extensive regulation, protectionist policies, and government ownership, the economy during the period was referred to as "Drigism." The country has moved closer to a market-based economy since 1991 because of increasing economic liberalisation. Statistics show that by 2008, India's economy was among the fastest-growing in the world.
Ancient and Mediaeval Eras
Let us learn a little about how Indian economy was during the ancient and medieval era.
Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley civilisation, a stable society, emerged between 2800 and 1800 BC. Its residents engaged in agriculture, domesticated animals, used established weights and measures, made tools and weapons, and conducted trade with neighbouring settlements.
From the beginning of time until about the fourteenth century AD, there was a great deal of maritime trade between South India and Southeast and West Asia. Beginning in the first century BC, both the Malabar and Coromandel Coasts served as the locations of significant commercial hubs that served as transit points between the Mediterranean area and Southeast Asia as well as centres of import and export. As time went on, traders formed organisations with official support.
During the 14th and 18th centuries, there may have been active trade from India to West Asia and Eastern Europe. Surakhani, an area of larger Baku, Azerbaijan, became home to Indian traders at this time.
The Gangetic plains and the Indus valley both included a large number of centres of river-borne commerce, while the Saurashtra and Bengal coasts significantly influenced marine trade farther north. The Khyber Pass, which links the Punjab area with Afghanistan, the Middle East, and Central Asia, was the primary route used for overland commerce.
How Covid-19 Impacted The Economy
The center's income collection suffered significantly as a result of the disruption in economic activity caused by the spread of the Covid-19 outbreak. Financial resources were under tremendous strain at the same time due to greater spending to lessen the pandemic's effects on society's most vulnerable groups.
Impact | The Covid-19 pandemic invalidated every calculation. According to data from the Controller General of Accounts, the fiscal deficit for the Center will reach 145.5% of the BE for the full year by December 2020.
The Target | By bringing the budget deficit down to 4% of GDP by 2025–2026, the 15th Finance Commission proposed a course for the government to follow to consolidate its finances.
The Numbers | 6.8% of GDP was projected by the government to be the budget deficit year 2021–22. In contrast to the budget forecast of 3.5%, India's government budget deficit for 2020–21 was larger at 9.40% of GDP. This was mostly brought on by increased spending and decreased income collection as a result of Covid-19.
Applications for Admissions are open.

VMC VIQ Scholarship Test
Register for Vidyamandir Intellect Quest. Get Scholarship and Cash Rewards.

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Accepted by more than 11,000 universities in over 150 countries worldwide

Pearson | PTE
Register now for PTE & Unlock 20% OFF : Use promo code: 'C360SPL20'. Valid till 15th NOV'24! Trusted by 3,500+ universities globally

JEE Main high scoring chapters and topics
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Study 40% syllabus and score upto 100% marks in JEE
Download Careers360 App
All this at the convenience of your phone.
Regular Exam Updates
Best College Recommendations
College & Rank predictors
Detailed Books and Sample Papers
Question and Answers
Scan and download the app
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Essay on Indian Economy

Introduction to Essay on Indian Economy
Indian Economy is a concept which deals with the system which manages all Economic activities of a country. It covers different sectors like agriculture, industry, and services along with their sub-segments.
Importance of Indian Economy:
The Indian Economy is important to study because it is the seventh-largest in terms of purchasing power parity and the third largest in terms of nominal GDP. Inflation in the Indian Economy is a major concern. The growth and development sector of the Indian Economy is an important area of focus. The Foreign exchange reserves of India are also an important aspect to study. Employment generation is an important area of focus for the Indian Economy.
Investment is another major concern when it comes to the Indian Economy. The balance in trade and budget deficit are other aspects that need attention from people studying the Indian Economy. Every year, a lot of research papers on India's Economy are written by various students all over India.
Some Tips to help You write Your Own Essay on the Indian Economy:
First Step: Collecting Information/ Data:
You must collect as much information related to your topic as possible. If necessary, ask experts or professionals who work in that particular field and get their opinions too if required. This would give you more authentic data rather than just reading out general stuff available online or through books.
Second Step: Sorting Information/ Data:
In this step, you must sort out all your collected data and information into separate sections. For example, if the essay is on the Indian Economy then divide it into different parts like Agriculture, Industry, or Services sector, etc. You can also use sub-heads for each of these main divisions to make things easier for yourself while writing down the final draft of your work.
Third Step: Analysis & Research Plan:
In this part, start by researching a particular topic thoroughly so that you have a clear idea as to how to proceed with it in detail before actually starting off with the actual writing process itself. This way there would be no loose ends left at the end of the whole thing and your essay would be complete and well-structured.
Fourth Step: Drafting the Essay:
Start by writing an introduction to your topic, explaining what it is all about in detail. After that, start discussing different points one by one with proper evidence backing up everything you say. Make sure each paragraph flows smoothly into the other so that the reader does not lose focus at any point while reading through it. The conclusion should summarize all your findings and leave a lasting impression on the mind of the reader.
Fifth Step: Editing & Proofreading:
This is an important step where you must check for grammar mistakes, punctuation errors, etc. Also, make sure that the structure of your essay is perfect and there are no loose ends left at the end of it. It is better to ask someone else to proofread your work too if you are not very confident about yours.
Sixth Step: Finalizing & Presenting Your Work in the Form of an Essay/ Paperwork etc.:
Finally, present your paper with proper references and bibliography so that every statement made in the essay has a source backing it up. Make sure everything looks neat and clean before actually sending off this final piece for assessment or assignment purposes.
Conclusion: So these were some tips on how one can write their own essay on Indian Economy which would be useful for students studying it or anyone interested in knowing more about India's Economy.
FAQs on Essay on Indian Economy
1. How much time does it take to write an essay on the Indian Economy? How long should my essay be?
It totally depends on the length of your topic and how much information you have collected for writing it. Usually, an essay takes around four to six hours to complete depending upon its size.
2. Where can I get authentic data regarding the Indian Economy?
There are various websites like IMF (International Monetary Fund), World Bank, etc which provide useful data on the Indian Economy.
3. Is there a specific thesis statement that I should focus on when writing my essay?
Yes, there should be a clear thesis statement that you must mention at the beginning of your essay. It can also follow throughout the entire course of it so as to maintain a good flow and structure in your work.
4. Who is my audience? How do I write an authentic essay for them?
Your audience would mostly comprise students and researchers who are interested in knowing more about the Indian Economy. So make sure your language and tone are appropriate for them, and all the information you provide is accurate and backed up by authentic sources.
5. What are some good transition words that I can use to connect my ideas?
There are many transition words that can be used. For example, you could start off with "firstly", "next" or even use phrases like "in the second place" to make your sentence flow smoothly into another one.
6. How will I know if my essay is well-structured? What does it need?
Your essay should be well-structured and organized according to the points you are discussing. Each paragraph must flow smoothly into another one, starting with a topic sentence that summarizes the main point of that particular section in your work. After every point is discussed there needs to be some sort of conclusion at the end which sums up all your findings.
7. What are large-scale industries?
The industries with large capital requirements engaging strong manpower. These organizations have a fixed asset worth more than 10 crore rupees and are considered to be large-scale industries. In India, the large-scale industries are those industries that have a fixed asset which is more than one hundred million rupees or Rs. 10 crores.
8. In India which place is known as the Industrial Hub?
Tamil Nadu is the state with the largest number of factories situated overall in India. Tamil Nadu is the capital city Chennai with the largest industrial and commercial centre in the whole of South India. India has 13 minor industrial regions located in 15 industrial districts.
9. How is the Indian Economy in recent times?
India's GDP was estimated at Rs. 33.14 trillion in the year 2011 and 2012, US$452.74 billion for the second quarter of the FY2020-21, against Rs. 35.84 trillion US$489.62 billion in the second quarter of FY2019-20.

- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal
Essay on Indian Economy for Students in English | 500 Words Essay
December 20, 2020 by Sandeep
Essay on Indian Economy: India is mainly an agrarian economy with agricultural supplies contributing up to 50% of the GDP index. The government has created fair policies with wage revisions and labourers rights to boost economic growth. The service sectors, manufacturing units, iron and steel companies, chemical and textile sectors, automobile industries contribute to the economy of the country. Privatisation of many sectors along with demonetization has affected both big and small businesses in the country.
Essay on Indian Economy 500 Words in English
Below we have provided Indian Economy Essay in English, written in easy and simple words for class 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 school students.
“There can be economy only where there is efficiency.” – Benjamin Disraeli
Indian economy is the fifth largest economy in the world currently. It is a developing market economy. The economic growth of India has even surpassed that of China in recent years. India has been able to successfully jump up ranks in various indexes, including the Ease of doing business index. Agriculture still remains the largest employer in the country, with the construction and real estate sector right behind it. India is the world’s second-largest coal and cement producer. The government has had a major role in accelerating the economic growth of the country.
The way industries operate in our country has been enhanced by the Industrial Policy. Many industries have been freed from the system of licensing and have no restriction on importing new and latest technology from other countries. The government has also taken up disinvestment in the industries where it is unprofitable. The focus on privatisation is being increased to intensify healthy competition. The government is also making efforts to revive and promote small scale industries and businesses.
The New Trade Policy has made it extremely easy for traders to carry out imports and exports. The trade of all items barring a restricted few has been allowed. Also, the tax on many items has been abolished, while for others, the amount has been visibly minimised. A lot of incentives are also being provided to exporters to encourage foreign trade and gain foreign currency.
History of the Indian Economy
For continuous 1700 years starting from the 1st century A.D., the Indian economy constituted about 35 to 40 percent of the world’s GDP and was the topmost flourishing economy. The Indus Valley civilisation proved to provide a form of permanent settlement to the people of the country alongside efficient water supply, urban planning and sanitation.
The silk route provides proof of early Indian trade. Under the Mughal empire, the Indian economy thrived and prospered. It was during this time that a focus on industrial production was also seen. Under the British rule, the Indian economy suffered some significant setbacks and was downtrodden. There were major changes seen in the agricultural sector. The commercialisation of agriculture increased. Farmers were forced to grow cash crops that were used in trade, rather than producing food crops.
This resulted in numerous famines. The once rich handicrafts and handloom sector also dipped and sunk during the British Raj. However, the colonial rule is responsible for giving the country railways, a legal system and a single currency exchange rate. The British era in India was rather exploitative, but our economy has come a long way since then with the help of policies pertaining to privatisation, liberalisation and globalisation .
Sectors of the Indian Economy
As the Indian economy has vastly diversified and grown in the previous years, the GDP contributed by the agricultural sector has reduced. However, it still continues to employ more than 50 percent of the country’s population . India is the largest producer of milk, pulses and jute and is the second-largest producer of wheat, rice and cotton. The agricultural sector accounts for about 20% of India’s GDP.
The main industries included in the Indian industrial sector include textile, construction, power, food processing, etc. The industrial sector employs around 22 percent of the country’s workforce and accounts for 26 percent of India’s GDP. Foreign Direct Investment is one measure by the government, which has increased foreign investments in the country, leading to further growth in this sector.
The services sector contributes the maximum to the GDP of the country. It includes financial services, aviation, insurance, hospitality, entertainment, etc. This sector employs around 23 percent of the Indian population. The main reason why the service sector has been able to do exceedingly well is because of outsourcing. The working population here is skilled, highly educated and cheaper than the labour in other countries.
Problems facing the Indian Economy
Unemployment is a problematic issue for the working-age population of India. The rate of unemployment has increased, and so has the population between the age bracket of 15-59 years. This unemployment is prevalent in the rural as well as the urban areas and is more widespread among the unskilled workers. A significant chunk, including women, especially those that live in rural areas are illiterate and have low educational standards. This leaves so much potential untapped and opportunities unexplored.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay on Indian Economy is provided here to give you an overview of the current situation of Indian Economy, and the role that agriculture and industrial sector plays in Indian Economy.
Explore the info on the economy of India, including growth rates, GDP, economic structure dynamics, and key factors driving India's economic growth from IBEF.
Get insights into India's GDP in 2023. Learn about the economy's growth and potential as India propels itself towards a prosperous future
Essay on Indian Economy: The Indian economy is a mixed economy, which is primarily driven by the agriculture and services sectors. The agriculture sector contributes to nearly 20% of India’s GDP. Whereas, the services sector accounts for nearly 50% of the country’s GDP.
India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) makes up 7.5% of the world economy, according to purchasing power parity (PPP). Due to its young population, low dependence ratio, high rates of savings and investments, rising globalisation in India, and interaction with the global economy, the long-term outlook for the Indian economy is still good.
The National Statistics Office (NSO) announced in late August, 2023 that India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) had surged in the April-June quarter, showing an impressive annual growth rate of 7.8%.
India has emerged as the fastest-growing major economy, supported by a resilient PFCE. Robust increase in Per Capita Real Gross National Income (GNI) in the nine years before the pandemic. Registered a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from FY12 to FY20.
The economy of India is a developing mixed economy with a notable public sector in strategic sectors. [5] It is the world's fifth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP); on a per capita income basis, India ranked 136th by GDP (nominal) and 125th by GDP (PPP) . [ 61 ]
The Indian Economy is important to study because it is the seventh-largest in terms of purchasing power parity and the third largest in terms of nominal GDP. Inflation in the Indian Economy is a major concern. The growth and development sector of the Indian Economy is an important area of focus.
Essay on Indian Economy: India is mainly an agrarian economy with agricultural supplies contributing up to 50% of the GDP index. The government has created fair policies with wage revisions and labourers rights to boost economic growth.