Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals

Condensed-matter physics articles from across Nature Portfolio
Condensed-matter physics is the study of substances in their solid state. This includes the investigation of both crystalline solids in which the atoms are positioned on a repeating three-dimensional lattice, such as diamond, and amorphous materials in which atomic position is more irregular, like in glass.
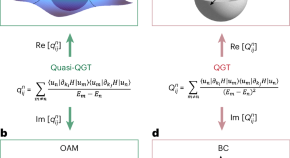
Quantum geometry in solids measured using photo-emitted electrons
Quantum geometry gives rise to many fascinating phenomena in solids that go beyond Landau theory. A general framework is now introduced to measure the quantum geometric tensor in solids — a fundamental physical quantity that encodes the complete geometric information of the Bloch state.
Nematic fluctuations shape Cooper pairs
Experimental evidence of nematic-fluctuation-mediated superconductivity has been observed in an iron-based superconductor near the quantum critical point.
- Lingyuan Kong
Polarization detection in miniature
A compact on-chip polarimeter can be created using subpixels made from metasurface photodetectors and a machine learning algorithm.
- Fengnian Xia
Related Subjects
- Bose–Einstein condensates
- Electronic properties and materials
- Ferroelectrics and multiferroics
- Ferromagnetism
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Molecular electronics
- Phase transitions and critical phenomena
- Quantum fluids and solids
- Quantum Hall
- Semiconductors
- Spintronics
- Structure of solids and liquids
- Superconducting properties and materials
- Surfaces, interfaces and thin films
- Topological matter
Latest Research and Reviews
Integrated ab initio modelling of atomic ordering and magnetic anisotropy for design of FeNi-based magnets
- Christopher D. Woodgate
- Laura H. Lewis
- Julie B. Staunton
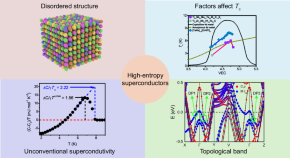
Recent advances in high-entropy superconductors
The discovery of superconductivity in high-entropy materials has garnered considerable interest, leading to accelerated advancements in this field in recent years. Some interesting phenomena have been found in high-entropy superconductors, such as the robustness of superconductivity to pressure, large upper critical field, strong coupling behavior, and topological band structure. Accordingly, the present review article is dedicated to summarizing the recently reported works on the structural type and physical properties of high-entropy superconductors, as well as their potential applications. Finally, we provide our perspective on the future challenges of high-entropy superconductors.
- Lingyong Zeng
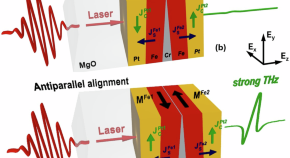
THz generation by exchange-coupled spintronic emitters
- Claus M. Schneider
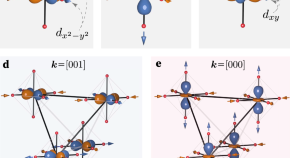
Spectroscopic signatures and origin of hidden order in Ba 2 MgReO 6
Charge quadrupole order was predicted in several 5 d 1 and 5 d 2 double perovskite systems, but experimental verification has been challenging. Here the authors provide experimental and theoretical evidence of simultaneous charge quadrupole order and local structural distortions in Ba 2 MgReO 6 .
- Jian-Rui Soh
- Maximilian E. Merkel
- Henrik M. Rønnow

Influence of atomic configuration on electronic and magnetic properties of complex Ruddlesden-Popper oxides La 2− x Sr x Co 1/2 Fe 1/2 O 4
- Dina I. Fazlizhanova
- Sergey V. Levchenko
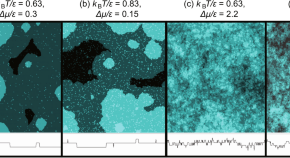
Competition between Kardar–Parisi–Zhang and Berezinskii–Kosterlitz–Thouless kinetic roughening on (001) singular surface during steady crystal growth
- Noriko Akutsu
- Yoshihiro Kangawa
News and Comment
Hidden in not-so-plain sight: altermagnets.
Recently, altermagnets emerged as a new class of magnets which have re-energized efforts to describe the fundamentals of magnetism. This Editorial introduces the concept of altermagnetism and describes recent breakthroughs in its comprehension.
- Hendrik Ohldag
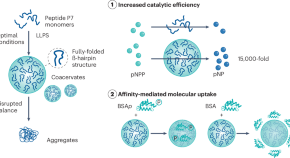
Coacervation-enhanced peptide catalysis
- Voeller Jan-Stefan
The future of 2D spintronics
The rapid advances in van der Waals magnets provide a platform for exploring spintronics in the 2D limit. Leveraging the unique properties of 2D magnets with new tuning knobs could see 2D spintronics find its applications in both quantum and classic information processing.
- Tiancheng Song
- Xiaodong Xu
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies


Solid-State Physics
Introduction to the Theory
- © 2018
- Latest edition
- James D. Patterson 0 ,
- Bernard C. Bailey 1
Rapid City, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Cape Canaveral, USA
- Written by two experienced researchers with years of teaching experience
- Features a wealth of problems and solutions
- Includes 90 biographical snapshots of prominent researchers in solid state physics
- An expanded and fully updated new edition
54k Accesses
19 Citations
3 Altmetric
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
About this book
This book teaches solid state physics in a comprehensive way, covering all areas. It begins with three broad topics: how and why atoms bind together to form solids, lattice vibrations and phonons, and electrons in solids. It then applies this knowledge to interactions, especially those between electrons and phonons, metals, the Fermi surface and alloys, semiconductors, magnetism, superconductivity, dielectrics and ferroelectrics, optical properties, defects, layered materials, quantum Hall effect, mesoscopics, nanophysics and soft condensed matter. Further important topics of the book are the evolution of BEC to BCS phenomena, conducting polymers, graphene, iron pnictide superconductors, light emitting diodes, N-V centers, nanomagnetism, negative index of refraction, optical lattices, phase transitions, phononics, photonics, plasmonics, quantum computing, solar cells, spin Hall effect and spintronics.
In this 3rd edition, topics such as topological insulators, quantum computing, Bose–Einstein transitions, highly correlated electron systems and several others have been added. New material on magnetism in solids, as well as a discussion of semiconductors and a changed set of problems with solutions, are also included. The book also discusses “folk theorems” to remind readers of the essence of the physics without mathematics, and includes 90 mini-biographies of prominent solid state physicists of the past and present to put a human face on the subject. An extensive solutions manual rounds out the book.
Similar content being viewed by others

The physics of quantum materials

Semiconductor Fundamentals

Nanostructured Materials
- Theory of Crystalline Solids
- Fundaments of Magnetism in Solid State Physics
- Electrons, Phonons, and Solid State
- Semiconductors and Superconductors
- Solid State Quasiparticles
- Binding in Solids
- Fermi Surface of Metals
Defects in Solids
- Solid State Optical Properties
- Magnetism and Magnons
Table of contents (12 chapters)
Front matter, crystal binding and structure.
- James D. Patterson, Bernard C. Bailey
Lattice Vibrations and Thermal Properties
Electrons in periodic potentials, the interaction of electrons and lattice vibrations, metals, alloys, and the fermi surface, semiconductors, magnetism, magnons, and magnetic resonance, superconductivity.
- Bernard C. Bailey, Bernard C. Bailey
Dielectrics and Ferroelectrics
Optical properties of solids, current topics in solid condensed–matter physics, back matter, authors and affiliations.
James D. Patterson
Bernard C. Bailey
About the authors
James D. Patterson: obtained his AB degree from the University of Missouri, Columbia, SM degree from the University of Chicago, Illinois, and PhD degree from the University of Kansas, Lawrence. He has held academic positions at Idaho State College, SD School of Mines and Technology, and Florida Institute of Technology (Head of Physics and Space Science 1988–1999). He has held visiting positions in Physics at the University of Notre Dame and University of Nebraska, Federal University of Pernambuco in Brazil, Marshall Space Flight Center, Sandia, Wright Patterson AFB, Ames Laboratory of Iowa State University, Argonne National Laboratory, and others. He is the author of many refereed articles on defects in crystals, magnetism, semiconductors and other areas, as well as previous editions of this Solid State Physics book. He has extensive teaching and advising experience in all areas related to Solid State Physics.
Bernard C. Bailey: obtained his BS, MS and PhD degrees, all from the Florida Institute of Technology, Melbourne. He has an engineering career of 31 years in Manned Space Flight with the Space Shuttle Program. The author of numerous refereed journal articles on optics, he is the co-author of all previous editions of this Solid State Physics book.
Bibliographic Information
Book Title : Solid-State Physics
Book Subtitle : Introduction to the Theory
Authors : James D. Patterson, Bernard C. Bailey
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75322-5
Publisher : Springer Cham
eBook Packages : Physics and Astronomy , Physics and Astronomy (R0)
Copyright Information : Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2018
Hardcover ISBN : 978-3-319-75321-8 Published: 07 March 2019
eBook ISBN : 978-3-319-75322-5 Published: 20 February 2019
Edition Number : 3
Number of Pages : XXV, 954
Number of Illustrations : 285 b/w illustrations
Topics : Solid State Physics , Optical and Electronic Materials , Microwaves, RF and Optical Engineering , Semiconductors , Mathematical Methods in Physics
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as solid-state chemistry, quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics.
Theory and applications of solid-state physics. | Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on SOLID STATE PHYSICS.
Condensed-matter physics is the study of substances in their solid state. This includes the investigation of both crystalline solids in which the atoms are positioned on a repeating...
Density functional theory (DFT) has been used in many fields of the physical sciences, but none so successfully as in the solid state. From its origins in condensed matter physics, it has expanded ...
Physics of the Solid State is a peer-reviewed journal covering all areas of solid-state physics. Presents the latest results from leading researchers in condensed matter physics. Includes solid-state optics, acoustics, electronic and vibrational spectra, phase transition, ferroelectricity, magnetism, and superconductivity.
physica status solidi (b) – basic solid state physics (pss b), a Wiley physics journal, is a forum for quality research on solid state and condensed matter physics. Our focus is on experiments, theory and computations that advance our fundamental understanding of the quantum physics of solid materials.
Solid State Sciences is the journal for researchers from the broad solid state chemistry and physics community. It publishes key articles on all aspects of solid state synthesis , structure-property relationships, theory and functionalities, in relation with experiments.
Professor Yi's main topics of theoretical solid state physics have been the physics of reduced dimensional solid state systems. Research subjects currently under investigation include the quantum mechanical many-body problem; the study of elementary excitations and optical and transport properties of artificially structured low dimensional ...
• Service for Experimental Solid State Physics. • Emphasis on the explanation of concepts and basic ideas, not always quantitative, justification of the use of simplified ‘model Hamiltonians’. • Raise some understanding why many-body physics is mostly phenomenology.
This book teaches solid state physics in a comprehensive way, covering all areas. It begins with three broad topics: how and why atoms bind together to form solids, lattice vibrations and phonons, and electrons in solids.