

Business Valuation

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on February 26, 2024
Are You Retirement Ready?
Table of contents, what is business valuation.
Business valuation is the process of estimating the economic value of a business or its ownership interest which involves taking into account its financial performance, assets, liabilities, and other relevant factors.
Business valuation is crucial for several reasons, including providing an accurate understanding of a company's value, facilitating informed decision-making, and ensuring transparency in financial transactions like mergers and acquisitions, sales, taxation, and legal disputes.
An accurate business valuation can help business owners and investors make strategic decisions about growth, financing, and exit strategies.
Additionally, business valuation is often required for legal purposes, such as taxation, estate planning, and dispute resolution. In these cases, a thorough and accurate valuation can help ensure compliance with legal requirements and protect the interests of all parties involved.
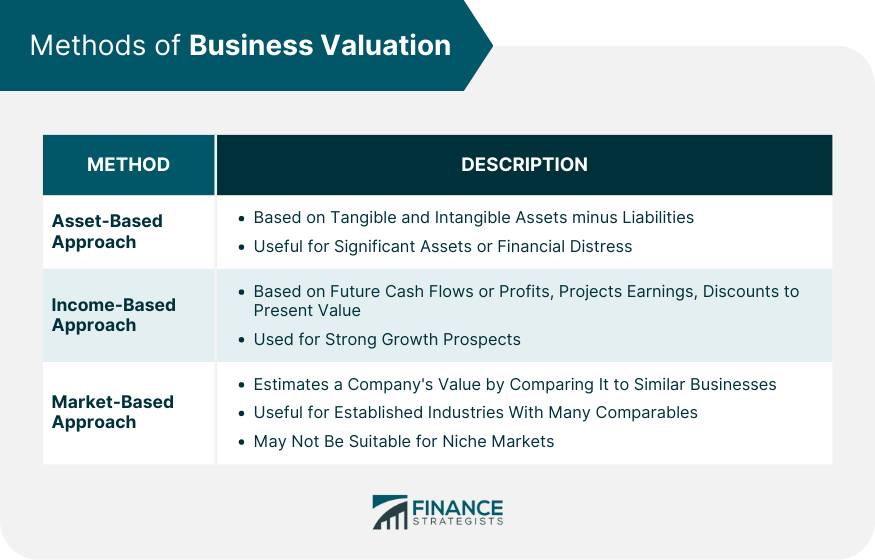
Methods of Business Valuation
Asset-based approach.
The asset-based approach to business valuation focuses on determining the value of a company based on the value of its tangible and intangible assets .
This approach involves identifying and valuing the company's assets , then deducting its liabilities to arrive at the net asset value . The asset-based approach is particularly useful for companies with significant assets, as well as for those in financial distress or facing liquidation.
However, this approach has its limitations, as it does not take into account the company's future earnings potential or the value of its intangible assets, which may be significant for some businesses.
Income-Based Approach
The income-based approach to business valuation focuses on estimating the company's value based on its ability to generate future cash flows or profits .
This approach involves projecting the company's future earnings, then discounting those earnings to their present value using a discount rate that reflects the risks associated with the company's operations.
The income-based approach is often used for valuing companies with strong growth prospects or those that derive a significant portion of their value from their ability to generate future cash flows.
However, this approach relies heavily on assumptions about future earnings and can be subject to significant uncertainty and subjectivity.
Market-Based Approach
The market-based approach to business valuation estimates the value of a company by comparing it to similar businesses in the market.
This approach involves analyzing comparable companies or transactions to determine valuation multiples, such as price-to-earnings or price-to-sales ratios , which are then applied to the company being valued.
The market-based approach is useful for valuing companies in well-established industries with a large number of comparable businesses or transactions. However, it may not be suitable for companies in niche markets or industries with limited comparables.
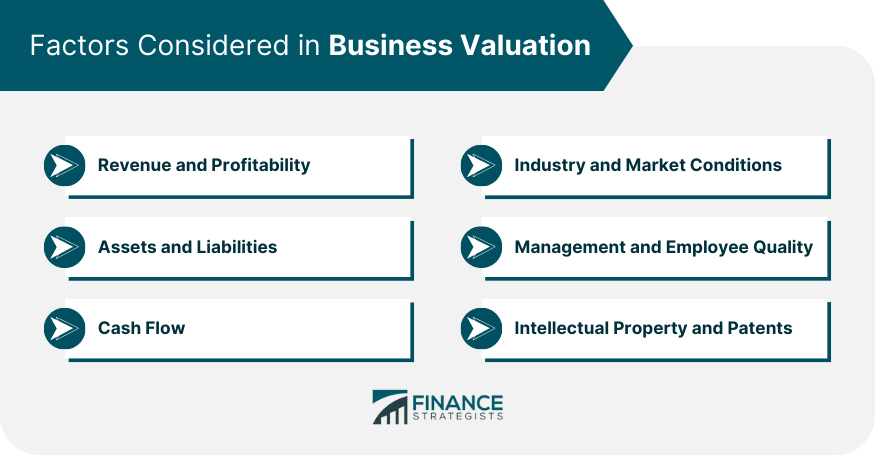
Factors Considered in Business Valuation
Revenue and profitability.
Revenue and profitability are critical factors in determining a company's value, as they reflect the company's ability to generate income and maintain sustainable growth.
A company with consistently strong revenue and profitability is likely to be valued more highly than a company with weaker financial performance.
In business valuation, analysts typically review historical financial statements to assess a company's revenue and profitability trends, as well as to identify any anomalies or patterns that may impact the company's value.
Assets and Liabilities
A company's assets and liabilities play a significant role in its valuation , as they represent the resources available to generate income and the obligations that must be met.
Assets, both tangible and intangible, can contribute to a company's overall value, while liabilities can reduce it.
In the valuation process, analysts review a company's balance sheet to identify and value its assets and liabilities, taking into account factors such as depreciation , market conditions, and potential future growth or decline in asset values.
Cash flow is a critical factor in business valuation, as it represents the company's ability to generate cash from its operations, which can be used to fund growth, pay dividends , or meet debt obligations.
A company with strong, consistent cash flows is generally considered more valuable than a company with volatile or weak cash flows.
Analysts typically examine a company's cash flow statement to assess its cash generation and use patterns, as well as to identify any potential issues or opportunities that may impact its value.
Industry and Market Conditions
Industry and market conditions can have a significant impact on a company's value, as they influence factors such as demand for products or services, competitive dynamics, and regulatory environment.
A company operating in a growing industry with strong market demand may be valued more highly than a company in a stagnant or declining industry.
During the valuation process, analysts consider the company's industry and market conditions, as well as any trends or external factors that may influence its future performance and value.
Management and Employee Quality
The quality of a company's management and employees can also impact its value, as it influences the company's ability to execute its strategies, adapt to changes, and maintain a competitive edge.
Companies with strong, experienced management teams and skilled employees are often valued more highly than those with weaker leadership or workforce capabilities.
In business valuation, analysts may assess the company's management and employee quality through factors such as executive and employee backgrounds, turnover rates, and organizational structure .
Intellectual Property and Patents
Intellectual property (IP) and patents can significantly contribute to a company's value, particularly in industries such as technology, pharmaceuticals, or creative sectors, where innovation and unique assets are critical.
Companies with strong IP portfolios or valuable patents are often valued more highly than those with limited or less valuable IP assets.
During the valuation process, analysts may assess the value of a company's IP and patents by considering factors such as the potential future cash flows generated from those assets, the competitive advantages provided, and the remaining life of the patents.
Types of Business Valuation
Fair market value.
Fair market value is a type of business valuation that estimates the price at which a company would change hands between a willing buyer and a willing seller, with both parties having reasonable knowledge of the relevant facts and neither being under any compulsion to buy or sell.
This is often used in legal contexts, such as taxation and estate planning, as well as for setting transaction prices in business sales or acquisitions .
Investment Value
Investment value is a type of business valuation that estimates the value of a company to a specific investor, taking into account the investor's unique circumstances, objectives, and risk tolerance .
This type of valuation may differ from the fair market value, as it reflects the individual investor's perspective rather than the broader market.
Investment value is often used by investors when evaluating potential investments or determining the value of their existing holdings in a company.
Liquidation Value
Liquidation value is a type of business valuation that estimates the net amount a company would realize if it were to sell its assets and settle its liabilities immediately.
Liquidation value is typically lower than other types of valuation, as it assumes a rapid sale of assets, often at a discount to their fair market value.
This is often used in situations where a company is facing financial distress or bankruptcy and needs to quickly monetize its assets to satisfy its obligations.
Uses of Business Valuation
Sale of business.
Business valuation is essential in the sale of a business, as it provides an objective estimate of the company's worth, which can be used as a basis for negotiating the transaction price.
A thorough and accurate valuation can help business owners ensure they receive a fair price for their company and enable potential buyers to make informed decisions about the investment.
Mergers and Acquisitions
In mergers and acquisitions , business valuation plays a crucial role in determining the value of the target company and assessing the potential benefits and risks of the transaction.
A comprehensive valuation can help acquirers identify synergies, assess the target company's financial health, and determine a fair offer price.
Likewise, for the target company, a thorough valuation can help its owners understand their company's worth and negotiate favorable terms in the transaction.
Taxation and Estate Planning
Business valuation is often required for taxation and estate planning purposes, such as determining the value of a company for tax reporting, gift tax , or inheritance tax purposes.
An accurate valuation ensures compliance with tax regulations and helps business owners and their heirs plan for future tax obligations.
In estate planning , business valuation can also assist business owners in developing succession plans and strategies to preserve and transfer their company's value to future generations.
Litigation and Dispute Resolution
In litigation and dispute resolution, business valuation is often necessary to determine damages, quantify losses, or assess the value of a company in the context of legal disputes, such as shareholder disputes, divorce proceedings, or contractual disputes.
A thorough and accurate business valuation can help parties in a dispute reach a fair resolution and support their legal claims or defenses.
Business Valuation Process
Preparing for valuation.
Before beginning the business valuation process, it is essential to gather all necessary information about the company, including its financial statements , business plan, and other relevant documents.
This information will be used to analyze the company's financial performance , assets, and liabilities, as well as to assess its growth prospects and industry position.
It is also crucial to engage the services of a qualified business valuation professional or firm, who can provide an objective, expert assessment of the company's worth.
Selecting a Valuation Method
Once the necessary information has been gathered, the next step is to select the appropriate valuation method based on the company's characteristics and the purpose of the valuation.
The choice of method will depend on factors such as the company's industry, size, growth prospects, and the availability of comparable transactions or companies.
The selected valuation method should be appropriate for the company's unique circumstances and provide an accurate, objective estimate of its worth.
Collecting and Analyzing Data
After selecting a valuation method, the next step is to collect and analyze the relevant data, such as financial statements, industry reports, and market data.
This analysis will inform the valuation process by providing insights into the company's financial performance, market position, and growth prospects. The data analysis should be thorough and accurate to ensure a reliable valuation.
Applying Discounts and Premiums
In some cases, it may be necessary to apply discounts or premiums to the company's valuation to account for factors such as liquidity , marketability, or control. Discounts and premiums should be applied judiciously, based on objective criteria and supported by empirical evidence.
Finalizing Valuation Report
Once the valuation process is complete, the valuation professional or firm will prepare a comprehensive valuation report that outlines the methodology, data, and assumptions used in the valuation, as well as the final valuation result.
This report should be clear, well-organized, and supported by relevant data and analysis.
The Bottom Line
Business valuation is the process of estimating a company's worth by analyzing its financial performance, assets, liabilities, and other relevant factors. It is essential for various purposes, including sales, mergers and acquisitions, taxation, and legal disputes.
There are several methods of business valuation, including asset-based, income-based, and market-based approaches. Each method has its unique characteristics and is suitable for different situations and types of businesses.
The choice of the valuation method depends on factors such as the company's industry, size, growth prospects, and the availability of comparable transactions or companies.
Various factors are considered in business valuation, including revenue and profitability, assets and liabilities, cash flow, industry and market conditions, management and employee quality, and intellectual property and patents.
Understanding the different valuation methods, factors, and types of valuation can help business owners, investors, and other stakeholders navigate the complex world of business valuation and ensure that they have an accurate, objective assessment of a company's value.
Business Valuation FAQs
What is business valuation.
Business valuation is the process of determining the economic value of a business or company.
What are the methods used in business valuation?
There are three methods used in business valuation: asset-based approach, income-based approach, and market-based approach.
What factors are considered in business valuation?
The financial factors considered in business valuation include revenue and profitability, assets and liabilities, and cash flow. Non-financial factors include industry and market conditions, management and employee quality, and intellectual property.

What are the types of business valuation?
The three types of business valuation are fair market value, investment value, and liquidation value.
What are the uses of business valuation?
Business valuation is used for a variety of purposes, including the sale of a business, merger and acquisition, taxation and estate planning, and litigation and dispute resolution.
About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- AML Regulations for Cryptocurrencies
- Active vs Passive Investment Management
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Cryptocurrencies
- Aggressive Investing
- Asset Management vs Investment Management
- Becoming a Millionaire With Cryptocurrency
- Burning Cryptocurrency
- Cheapest Cryptocurrencies With High Returns
- Complete List of Cryptocurrencies & Their Market Capitalization
- Countries Using Cryptocurrency
- Countries Where Bitcoin Is Illegal
- Crypto Investor’s Guide to Form 1099-B
- Cryptocurrency Airdrop
- Cryptocurrency Alerting
- Cryptocurrency Analysis Tool
- Cryptocurrency Cloud Mining
- Cryptocurrency Risks
- Cryptocurrency Taxes
- Depth of Market
- Digital Currency vs Cryptocurrency
- Fundamental Analysis in Cryptocurrencies
- Global Macro Hedge Fund
- Gold-Backed Cryptocurrency
- How Much Does a Wealth Manager Make?
- How to Buy a House With Cryptocurrencies
- How to Cash Out Your Cryptocurrency
- Inventory Turnover Rate (ITR)
- Largest Cryptocurrencies by Market Cap
- Types of Fixed Income Investments
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Discover wealth management solutions near you.
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
To ensure one vote per person, please include the following info, great thank you for voting., get in touch with a financial advisor, submit your info below and someone will get back to you shortly..

IMAGES
VIDEO