An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Group work as an incentive for learning – students’ experiences of group work
Eva hammar chiriac.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Edited by: Carl Senior, Aston University, UK
Reviewed by: Gareth J. Williams, Nottingham Trent University, UK; Carl Senior, Aston University, UK
*Correspondence: Eva Hammar Chiriac, Division of Psychology, Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning, Linköping University, SE-581 83 Linköping, Sweden e-mail: [email protected]
This article was submitted to Educational Psychology, a section of the journal Frontiers in Psychology.
Accepted 2014 May 20; Collection date 2014.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in educational systems. There is strong scientific support for the benefits of having students learning and working in groups. Nevertheless, studies about what occurs in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students’ ability to learn is still lacking. Similarly, the question of why some group work is successful and other group work results in the opposite is still unsolved. The aim of this article is to add to the current level of knowledge and understandings regarding the essence behind successful group work in higher education. This research is focused on the students’ experiences of group work and learning in groups, which is an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work prior to the beginning of the 21st century. A primary aim is to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view and how the students assess learning when working in groups. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work ends up being a positive experience resulting in successful learning, while in other cases, the result is the reverse, are of interest. Data were collected through a study-specific questionnaire, with multiple choice and open-ended questions. The questionnaires were distributed to students in different study programs at two universities in Sweden. The present result is based on a reanalysis and qualitative analysis formed a key part of the study. The results indicate that most of the students’ experiences involved group work that facilitated learning, especially in the area of academic knowledge. Three important prerequisites (learning, study-social function, and organization) for group work that served as an effective pedagogy and as an incentive for learning were identified and discussed. All three abstractions facilitate or hamper students’ learning, as well as impact their experiences with group work.
Keywords: group work, collaborative learning, cooperative learning, higher education, students’ perspectives, qualitative research
INTRODUCTION
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in most educational systems, from compulsory education to higher education. The overarching purpose of group work in educational practice is to serve as an incentive for learning. For example, it is believed that the students involved in the group activity should “learn something.” This prerequisite has influenced previous research to predominantly focus on how to increase efficiency in group work and how to understand why some group work turns out favorably and other group work sessions result in the opposite. The review of previous research shows that in the 20th century, there has been an increase in research about students’ cooperation in the classroom ( Lou et al., 1996 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). This increasing interest can be traced back to the fact that both researchers and teachers have become aware of the positive effects that collaboration might have on students’ ability to learn. The main concern in the research area has been on how interaction and cooperation among students influence learning and problem solving in groups ( Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ).
Two approaches concerning learning in group are of interest, namely cooperative learning and collaborative learning . There seems to be a certain amount of confusion concerning how these concepts are to be interpreted and used, as well as what they actually signify. Often the conceptions are used synonymously even though there are some differentiations. Cooperative group work is usually considered as a comprehensive umbrella concept for several modes of student active working modes ( Johnson and Johnson, 1975 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ), whereas collaboration is a more of an exclusive concept and may be included in the much wider concept cooperation ( Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Cooperative learning may describe group work without any interaction between the students (i.e., the student may just be sitting next to each other; Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ), while collaborative learning always includes interaction, collaboration, and utilization of the group’s competences ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ).
At the present time, there is strong scientific support for the benefits of students learning and working in groups. In addition, the research shows that collaborative work promotes both academic achievement and collaborative abilities ( Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). According to Gillies and Boyle (2011) , the benefits are consistent irrespective of age (pre-school to college) and/or curriculum. When working interactively with others, students learn to inquire, share ideas, clarify differences, problem-solve, and construct new understandings. Gillies (2003a , b ) also stresses that students working together are more motivated to achieve than they would be when working individually. Thus, group work might serve as an incentive for learning, in terms of both academic knowledge and interpersonal skills. Nevertheless, studies about what occur in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students’ ability to learn is still lacking in the literature, especially when it comes to addressing the students’ points of view, with some exceptions ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Similarly, the question of why some group work turns out successfully and other work results in the opposite is still unsolved. In this article, we hope to contribute some new pieces of information concerning the why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while others result in the opposite.
GROUP WORK IN EDUCATION
Group work is frequently used in higher education as a pedagogical mode in the classroom, and it is viewed as equivalent to any other pedagogical practice (i.e., whole class lesson or individual work). Without considering the pros and cons of group work, a non-reflective choice of pedagogical mode might end up resulting in less desirable consequences. A reflective choice, on the other hand, might result in positive experiences and enhanced learning ( Galton et al., 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ).
GROUP WORK AS OBJECTIVE OR MEANS
Group work might serve different purposes. As mentioned above, the overall purpose of the group work in education is that the students who participate in group work “learn something.” Learning can be in terms of academic knowledge or “group knowledge.” Group knowledge refers to learning to work in groups ( Kutnick and Beredondini, 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Affiliation, fellowship, and welfare might be of equal importance as academic knowledge, or they may even be prerequisites for learning. Thus, the group and the group work serve more functions than just than “just” being a pedagogical mode. Hence, before group work is implemented, it is important to consider the purpose the group assignment will have as the objective, the means, or both.
From a learning perspective, group work might function as both an objective (i.e., learning collaborative abilities) and as the means (i.e., a base for academic achievement) or both ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). If the purpose of the group work is to serve as an objective, the group’s function is to promote students’ development of group work abilities, such as social training and interpersonal skills. If, on the other hand, group work is used as a means to acquire academic knowledge, the group and the collaboration in the group become a base for students’ knowledge acquisition ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). The group contributes to the acquisition of knowledge and stimulates learning, thus promoting academic performance. Naturally, group work can be considered to be a learning environment, where group work is used both as an objective and as the means. One example of this concept is in the case of tutorial groups in problem-based learning. Both functions are important and might complement and/or even promote each other. Albeit used for different purposes, both approaches might serve as an incentive for learning, emphasizing different aspect knowledge, and learning in a group within an educational setting.
WORKING IN A GROUP OR AS A GROUP
Even if group work is often defined as “pupils working together as a group or a team,” ( Blatchford et al., 2003 , p. 155), it is important to bear in mind that group work is not just one activity, but several activities with different conditions ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 , 2010 ). This implies that group work may change characteristics several times during a group work session and/or during a group’s lifetime, thus suggesting that certain working modes may be better suited for different parts of a group’s work and vice versa ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 , 2010 ). It is also important to differentiate between how the work is accomplished in the group, whether by working in a group or working as a group.
From a group work perspective, there are two primary ways of discussing cooperation in groups: working in a group (cooperation) or working as a group (collaboration; Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Situations where students are sitting together in a group but working individually on separate parts of a group assignment are referred to as working in a group . This is not an uncommon situation within an educational setting ( Gillies and Boyle, 2011 ). Cooperation between students might occur, but it is not necessary to accomplish the group’s task. At the end of the task, the students put their separate contributions together into a joint product ( Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2010 , 2011a ). While no cooperative activities are mandatory while working in a group, cooperative learning may occur. However, the benefits in this case are an effect of social facilitation ( Zajonc, 1980 ; Baron, 1986 ; Uziel, 2007 ) and are not caused by cooperation. In this situation, social facilitation alludes to the enhanced motivational effect that the presence of other students have on individual student’s performance.
Working as a group, on the other hand, causes learning benefits from collaboration with other group members. Working as a group is often referred to as “real group work” or “meaningful group work,” and denotes group work in which students utilizes the group members’ skills and work together to achieve a common goal. Moreover, working as a group presupposes collaboration, and that all group members will be involved in and working on a common task to produce a joint outcome ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Working as a group is characterized by common effort, the utilization of the group’s competence, and the presence of problem solving and reflection. According to Granström (2006) , working as a group is a more uncommon activity in an educational setting. Both approaches might be useful in different parts of group work, depending on the purpose of the group work and type of task assigned to the group ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ). Working in a group might lead to cooperative learning, while working as group might facilitate collaborative learning. While there are differences between the real meanings of the concepts, the terms are frequently used interchangeably ( Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ).
PREVIOUS RESEARCH OF STUDENTS’ EXPERIENCES
As mentioned above, there are a limited number of studies concerning the participants’ perspectives on group work. Teachers often have to rely upon spontaneous viewpoints and indications about and students’ experiences of group work in the form of completed course evaluations. However, there are some exceptions ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson, 2007 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). To put this study in a context and provide a rationale for the present research, a selection of studies focusing on pupils’ and/or students’ experiences and conceptions of group work will be briefly discussed below. The pupils’ and/or students inside knowledge group work may present information relevant in all levels of educational systems.
Hansen (2006) conducted a small study with 34 participating students at a business faculty, focusing on the participants’ experiences of group work. In the study different aspects of students’ positive experiences of group work were identified. For example, it was found to be necessary that all group members take part and make an effort to take part in the group work, clear goals are set for the work, role differentiation exists among members, the task has some level of relevance, and there is clear leadership. Even though Hansen’s (2006) study was conducted in higher education, these findings may be relevant in other levels in educational systems.
To gain more knowledge and understand about the essence behind high-quality group work, Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson (2007) turned their focus toward students’ experiences and conceptions of group work in higher education. A primary aim was to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating their students’ points of view and how the students assess working in groups. Do the students’ appreciate group projects or do they find it boring and even as a waste of time? Would some students prefer to work individually, or even in “the other group?” The study was a part of a larger research project on group work in education and only a small part of the data corpus was analyzed. Different critical aspects were identified as important incitements for whether the group work turned out to be a success or a failure. The students’ positive, as well as negative, experiences of group work include both task-related (e.g., learning, group composition, participants’ contribution, time) and socio-emotional (e.g., affiliation, conflict, group climate) aspects of group work. The students described their own group, as well as other groups, in a realistic way and did not believe that the grass was greener in the other group. The same data corpus is used in this article (see under Section The Previous Analysis). According to Underwood (2003) and Peterson and Miller (2004) , the students’ enthusiasm for group work is affected by type of task, as well as the group’s members. One problem that recurred frequently concerned students who did not contribute to the group work, also known as so-called free-riders ( Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Students are, in general, reluctant to punish free-riders and antipathy toward working in groups is often associated with a previous experience of having free-riders in the group ( Peterson and Miller, 2004 ). To accomplish a favorable attitude toward group work, the advantages of collaborative activities as a means for learning must be elucidated. Furthermore, students must be granted a guarantee that free-riders will not bring the group in an unfavorable light. The free-riders, on the other hand, must be encouraged to participate in the common project.
Hammar Chiriac and Granström (2012) were also interested in students’ experiences and conceptions of high-quality and low-quality group work in school and how students aged 13–16 describe good and bad group work? Hammar Chiriac and Granström (2012) show that the students seem to have a clear conception of what constitutes group work and what does not. According to the students, genuine group work is characterized by collaboration on an assignment given by the teacher. They describe group work as working together with their classmates on a common task. The students are also fully aware that successful group work calls for members with appropriate skills that are focused on the task and for all members take part in the common work. Furthermore, the results disclose what students consider being important requisites for successful versus more futile group work. The students’ inside knowledge about classroom activities ended up in a taxonomy of crucial conditions for high-quality group work. The six conditions were: (a) organization of group work conditions, (b) mode of working in groups, (c) tasks given in group work, (d) reporting group work, (e) assessment of group work, and (f) the role of the teacher in group work. The most essential condition for the students seemed to be group composition and the participants’ responsibilities and contributions. According to the students, a well-organized group consists of approximately three members, which allows the group to not be too heterogeneous. Members should be allotted a reasonable amount of time and be provided with an environment that is not too noisy. Hence, all six aspects are related to the role of the teacher’s leadership since the first five points concern the framework and prerequisites created by the teacher.
Näslund (2013) summarized students’ and researchers’ joint knowledge based on experience and research on in the context of shared perspective for group work. As a result, Näslund noticed a joint apprehension concerning what constitutes “an ideal group work.” Näslund (2013) highlighted the fact that both students and researchers emphasized for ideal group work to occur, the following conditions were important to have: (a) the group work is carried out in supportive context, (b) cooperation occurs, (c) the group work is well-structured, (d) students come prepared and act as working members during the meetings, and (e) group members show respect for each other.
From this brief exposition of a selection of research focusing on students’ views on group work, it is obvious that more systematic studies or documentations on students’ conceptions and experiences of group work within higher education are relevant and desired. The present study, which is a reanalysis of a corpus of data addressing the students’ perspective of group, is a step in that direction.
AIM OF THE STUDY
The overarching knowledge interest of this study is to enhance the body of knowledge regarding group work in higher education. The aim of this article is to add knowledge and understanding of what the essence behind successful group work in higher education is by focusing on the students’ experiences and conceptions of group work and learning in groups , an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work until the beginning of the 21st century. A primary aim is to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view and how the students assess learning when working in groups. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases, the result is the opposite, are of interest.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
To capture university students’ experiences and conceptions of group work, an inductive qualitative approach, which emphasizes content and meaning rather than quantification, was used ( Breakwell et al., 2006 ; Bryman, 2012 ). The empirical data were collected through a study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire and a qualitative content analysis was performed ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ).
PARTICIPANTS
All participating students attended traditional university programs where group work was a central and frequently used pedagogical method in the educational design. In addition, the participants’ programs allowed the students to be allocated to the same groups for a longer period of time, in some cases during a whole semester. University programs using specific pedagogical approaches, such as problem-based learning or case method, were not included in this study.
The participants consisted of a total of 210 students, 172 female and 38 male, from two universities in two different cities (approximately division: 75 and 25%). The students came from six different populations in four university programs: (a) The Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology, (b) The Human Resource Management and Work Sciences Program, (c) Social Work Program, and (d) The Bachelor’s Programs in Biology. The informants were studying in their first through eighth terms, but the majority had previous experiences from working in other group settings. Only 2% of the students had just started their first term when the study was conducted, while the vast majority (96%) was participating in university studies in their second to sixth semester.
The teacher most frequently arranged the group composition and only a few students stated that they have had any influence on the group formation. There were, with a few exceptions, between 6 and 10 groups in each of the programs included in this study. The groups consisted of between four to eight members and the differences in sizes were almost proportionally distributed among the research group. The groups were foremost heterogeneous concerning gender, but irrespective of group size, there seems to have been a bias toward more women than men in most of the groups. When there was an underrepresented sex in the group, the minority mostly included two students of the same gender. More than 50% of the students answered that in this particularly group, they worked solely with new group members, i.e., students they had not worked with in previous group work during the program.
To collect data about students’ experiences and conceptions of group work, a study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire was constructed. The questionnaire approached the students’ experiences regarding the specific group work they were working in at the time of the data collection (spring 2006), not their experiences of group work in general. The questionnaire contained a total of 18 questions, including both multiple choice and open-ended questions. The multiple choice questions concerned background variables and information about the present group. The seven open-ended questions were designed to gather data about the students’ experiences and perceptions of group work in higher education. The questionnaires were distributed to the different populations of students (some populations studied at the same program) at two universities in Sweden. During the time the questionnaires were completed, the researcher or an assistant was present to answer possible questions. In all, 210 students answered the questionnaire.
The previous analysis
As described above (Section Previous Research of Students’ Experiences) a previous analysis based on the same data corpus revealed that most of the students included in the study found group work to be an enjoyable and stimulating working method ( Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson, 2007 ). The data were analyzed using a qualitative content analysis based on three different research questions. There were two main criticisms of the previous study presented from other researchers. The criticism conveyed applied mostly to the question of whether we could assemble these groups into a joint research group and second to the fact that the results were mostly descriptive. To counter this criticism and to elaborate on the analysis, a further analysis was conducted.
The present analysis
The present analysis (or reanalysis) was conducted by using an inductive qualitative content analysis based on three open-ended research questions:
(1) In what ways does group work contribute to your learning?
(2) What positive experiences have you had while working in your present group?
(3) What negative experiences have you had while working in your present group?
Each question corresponds to one aspect of the research’s objective, but together, they might support and enrich each other and unravel new information based on the students’ experiences and conceptions of group work. Research question 1, listed above, was not included in the first analysis and is being investigated for the first time in this study, while the other two questions are being reanalyzed. An inductive, qualitative content analysis is applicable when the aim of the research is a description of the meaning or of a phenomenon in conceptual form ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ).
The analysis was carried out over several steps, following the basic principles of an inductive, qualitative content analysis ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). The steps included three phases: preparation, organizing, and reporting ( Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). Each question was treated as a unit of analysis and was thus analyzed separately. In the preparation phase, the researcher tried to make sense of the data by becoming familiar with the data corpus. In the current study, this included transcription and thorough reading of the answers. An open coding system composed of marginal notes and headings began the second phase, which included organizing the data. This second phase, in turn, included open coding, creating categories, and abstraction. The notes and the headings from the open coding were transferred to coding sheets and then grouped into categories. Categories were formed through the interpretation of the codes that described the same meaning or phenomenon. Finally, an abstraction process began, where a general description of the grouped categories formed an abstraction (see Table 1 ). An abstraction was denominated using the content-characteristic words for this paper: learning, study-social function, and organization . The third phase, reporting , addressed the presentation of the process of analysis and the results.
Examples from the organization phase of the coding process.
The final aim of this study is to present the phenomenon studied in a model or conceptual map of the categories ( Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). In following these procedures, we aim to expand our understanding of the existing work and to counter the second part of the criticisms, which included criticisms stating that the results were mostly descriptive in nature. To counter the criticisms regarding the question of whether we could assemble these groups into a joint research group, the qualitative abstraction that emerged from the qualitative content analysis was compared to background information by using SPSS. Three background variables were used: gender, cities, and programs.
ETHICS AND QUALITY
The ethical principles provided by the British Psychology Society have formed a guideline [ British Psychology Society (BPS), 2006 ] for the present study. The ethical principles, which emphasize the concern for participants’ interest, have been applied throughout the study [ American Psychological Association (APA), 2002 ; British Psychology Society (BPS), 2004 ; Barett, 2007 ]. To facilitate trustworthiness, a thorough description of the analysis process has been presented ( Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). Translated citations are also included to increase trustworthiness.
As described above, the analysis resulted in three abstraction emerging: learning, study-social function , and organization . Each abstraction includes both a positive variant (i.e., facilitating learning, study-social function, and/or organization) as well as a negative alternative (i.e., hampering learning, study-social function, and/or organization). The results will be presented in three different sections, with each section corresponding to one abstraction. However, we would like to call attention to the fact that one fifth (20%, including missing value 8%) of the students included in this study did not perceive and/or mention any negative experiences at all in their present group. From a general point of view, there is no difference with respect to gender or city regarding the distribution of positive and negative experiences concerning the abstractions, neither concerning different programs nor the distribution of negative experiences (all p > 0.05). In contrast, there is a difference between the various programs and the distribution of positive experiences (χ 2 = 14.474; df: 6; p < 0.025). The students from the social work program display a higher amount of positive experiences in connection with a study-social function and organizing in comparison with the other programs.
The majority of the students (97%) responded that working in group somehow facilitated learning, academic knowledge, collaborative abilities or both. They learned more or different things when working in groups than they would have if working alone. By discussing and questioning each other’s points of view and listening to their fellow students’ contributions, thus obtaining different perspectives, the participants experienced an enhanced academic learning, compared to working alone. “I learn much more by working in groups than working individually. I obtain more through interaction with the other group members.” Academic knowledge is not the only type of knowledge learned through group work. In addition to academic knowledge, students also gain advanced knowledge about how groups work, how the students function as individual members of groups and how other members behave and work in groups. Some of the respondents also argued that group work in group courses strengthen the combination between empirical and theoretical learning, thus learning about groups by working in groups. “Through practical knowledge demonstrate several of the phenomena we read about in theory (group psychology and sociology).”
The results show no difference when considering either gender or city. However, when comparing the four programs included in the study and the types of learning, a difference occurs (χ 2 = 14.474; df: 6; p < 0.025). A division into two parts seems to generate the difference. On the one hand, the students from the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the students from the Human Resource Management and Work Sciences Program emphasize academic knowledge. On the other hand, students from the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program more often mentioned learning collaborative abilities single handed, as well as a combination of academic knowledge and group learning.
Even though the participants did not expressly report that group work hampered learning, they often mentioned that they perceived group work as being ineffective due to loss of focus and the presence of conflicts, thereby hampering conceivable learning. One respondent stated, “that you sometimes are out of focus in the discussion and get side-tracked instead of considering the task.” Another offered the following perspective: “Occasionally, it is too little task related and feels unnecessary sometimes. Individual work is, in certain situations, preferable.” Group work might be perceived as ineffective and time consuming considering long working periods with tedious discussions. One participant stated, “The time aspect, everything is time consuming.” The absence or presence of conflicts in the group affects students’ experiences, and conflicts not handled may influence learning in a negative way. The students perceived that it was difficult to come to an agreement and experience those conflicts and the need to compromise hampered individual learning. Accordingly, the absence of conflicts seemed to be an important incitement for learning. However, fear of conflicts can lead to reduced learning and cause negative experiences, but to a considerably lesser extent than does the presence of actual conflicts. “A great fear of conflicts sometimes raises an oppressive atmosphere.” “Fear of conflicts leads to much not made known.”
A STUDY-SOCIAL FUNCTION
Group work also has an important study - social function according to the students. They describe their membership in groups as an important aspect of affiliation. In general, the total number of students at a program is approximately 60–80 or more. In contexts with a large population of students, the smaller group gives the participants an opportunity to feel affiliated with the group and to each other. “Feels safe to have a certain group to prepare oneself together with before, for instance, an upcoming seminar.” The group gives the individual student a platform of belonging, which might serve as an important arena for learning ( facilitate ) and finding friends to spend leisure time with. Many of the participants also reported feeling a positive atmosphere in the group, which is important for the satisfaction of being in the group together with the fellow students.
To be a member of a group may also serve as a function of relief, both academically and socially, for the individual student. The participants reported that many of the tasks assigned by the university teachers are difficult to handle on their own. “The others explain to me. We help one another.” However, the students reported that they helped and supported each other, even if the task did not demand cooperation. “As a student, you get more active. You help one another to extract the groups’ common knowledge. Forward info if somebody is missing.” Being a member of a group also affects students’ motivation to study. They prepare themselves by reading texts and other material before the next group session. Group work may also have positive effects on achievement. Students’ total amount of time and effort on their work may also increase. Through group work, the participants also get confirmation of who they are and what their capacities are.
Being a member of a group also has its downside, which often has to do with the group climate and/or group processes, both of which have multiple and complex features. Many students reported that both the group climate and group processes might be the source of negative conceptions of the group and hamper learning. “Process losses.” The respondents described negative conceptions based on the feeling of not having enough time to get to know each other in the group or being in situations where no cooperation occurred. Other students referred to the fact that the group’s life is too long, which may lead to group members not only wearing each other out, but also having a negative effect on each other’s mood. “Influenced by each other’s mood.” Examples of negative experiences are process losses in general, including insufficient communication, unclear roles, and problems with one group member. As mentioned above, the students from the Social Work Program display a higher number of positive experiences in connection with a study-social function and organizing in comparison with students from the other programs.
ORGANIZATION
O rganization concerns the structure of group work and includes different aspects, all describing group work from different angles. The aspects are relevant no matter how the participants perceive the group work, whether as positive or negative. Unlike the other two abstractions (learning and study-social function), organization includes the same aspects no matter what the experiences are, namely group composition , group structure , way of working and contributions.
Whether the group is composed in a homogeneous or heterogeneous way seems to be experienced in both a positive and negative sense. A well-thought-out group composition , including both group size and mix of members, is essential. A just large-enough group for the task, consisting of a population of members that is not too heterogeneous, facilitates a joyful experience and learning. A homogeneous mix of members might be perceived as positive, as the students feel that they have similar life situations, opinions, and skills, thereby causing positive conditions for collaboration within the group. Conversely, in a group with a heterogeneous mix, different members contribute with different knowledge and/or prior experiences, which can be used in the group for collective and collaborative learning. “Good group composition, distribution of age groups that leads to fruitful discussions.”
An additional facilitating prerequisite is that the group develops adequate ways of working together, which includes a well-organized group structure . Well-working groups are characterized as having developed adequate ways of working together, while groups that work less well together lack a developed way of cooperation. “Well-organized working group with clear and distinct rules and structure.” Preparation and attendance for group work are aspects mentioned as facilitating (and hampering) incitements. Group work in educational settings sometimes entails that you, as a student, are forced to read and learn within a certain period of time that is beyond your control. Some participants find the pressure positive, hence “increase the pressure to read chapters in time.” The members’ contribution to the group is also a central factor for the students’ apprehension of how the group works. This is, in short, about how much each member ought to contribute to the group and to the work. Groups considered to be well-working are ones where all members contribute to the group’s work, but the content of the contribution may vary according to the single member’s qualifications. “We work well together (most of us). Everybody participates in different ways and seems committed.” “Good, everybody participates the same amount. We complement each other well.”
The same prerequisites can lead to the reverse result, i.e., hampering learning and stirring up negative experiences. If the group members are too identical (a homogeneous group composition ), it might lead to a lack of opinions, which several participants perceived as being negative. “That we do not get a male perspective about the subject. We are all girls, at the age of 20, which also means that we have pretty much the same experiences that may be seen as both positive and negative. The negative is the lack of opinion.” If the group is considered to be too small, students seems to find it troublesome, as the relationships are few, but there are also few people who are available to handle the workload allotted to the group. Nevertheless, a group that is too large could also lead to negative experiences. “It is far too large a group.”
A lack of group structure might lead to a lower degree of satisfaction with the group’s way of working . A commonly expressed point of view seen in the students’ answers involved the occurrences of when all members did not attend the meetings (absence). In these cases, it was also viewed that the work in the group often was characterized as unstructured. “Sometimes a bit unclear structures, some students have difficulties with coming in time.” Not attending or coming unprepared or badly prepared to the group work is other aspect that is commented on. “Low degree of fellowship, punctuality is a problem, an insecure group.” Some students find it frustrating to prepare for a certain time decided that is beyond their control. “A necessity to read certain chapters within a specific period of time is never stimulating.”
One characteristic of groups that are not working well is that contribution varies among the members. In group work, students with different levels of ambition are assembled, which may result in different levels of interest and commitment, as well as differences in the willingness to take on responsibilities or part of the workload of the group’s work. Some members are active and do much of the work, while others barely contribute at all. “Some don’t do anything while others pull the heaviest burden. Two out of three prepare before the meeting, the rest think that they are able to read during the group work and do not supply the group with anything else other than delays and frustration.” A common answer seen in the questionnaires that concerns negative experiences of group work as they relate to contribution is: “Everybody does not contribute just as much.” or “There is always someone who just glides along and doesn’t take part.”
SUMMARY OF THE RESULTS
The results are summarized in a model illustrating the relationship between abstractions (i.e., learning, study-social function, and organization) and result (i.e., enhanced or reduced learning), as well as positive or negative experiences (see Figure 1 ).
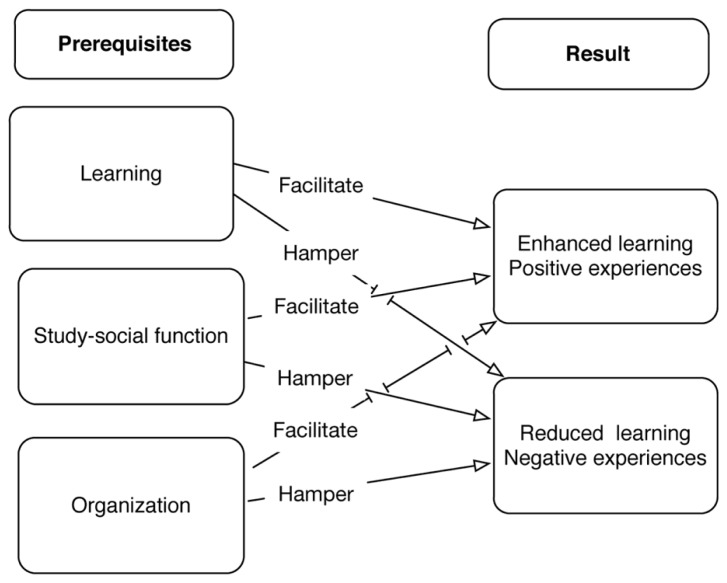
A model illustrating the relationship between abstractions and result .
The figure shows that all three abstractions may facilitate or hamper learning as well as the experiences of group work. To piece together, the difficult and extensive jigsaw puzzle concerning why some group work result in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases the result is the reverse is still not solved. In this article, we propose that the prerequisites learning, study-social function, and organization influence learning and experiences of working in group, thus, providing additional pieces of information to the jigsaw puzzle ( Figure 2 ).
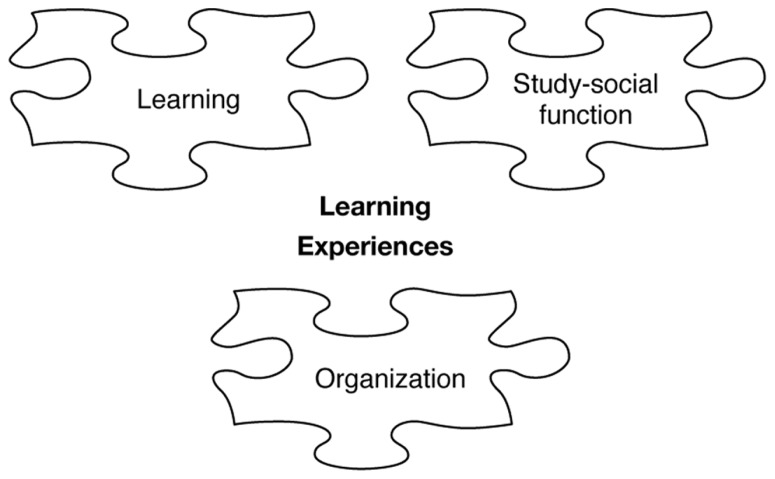
Pieces of jigsaw puzzle influence learning and experiences .
The current study focuses on university students’ experiences and conceptions of group work and learning in groups. A primary aim was to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view, as well as how the students’ assess learning when working in groups. The analysis resulted in the emergence of three different abstractions: learning, study-social function, and organizations. Each abstraction also included a positive and a negative variant. In other words, all three abstractions either facilitated or hampered university students’ learning, as well as their experiences of group work.
LEARNING IN GROUP WORK
The result shows that the majority of the students (97%) experience that working in group facilitated learning, either academic knowledge, collaborative abilities or both, accordingly confirming previous research ( Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). According to the students, they learn more or different things when working in groups compared with working individually. Academic knowledge was not the only type of knowledge learned through group work. In addition to academic knowledge, students also gained advanced knowledge about how groups work, how the students function as individual members of groups and how other members behave and work in groups. Some of the respondents also argued that group work might strengthen the combination between empirical and theoretical learning, thus the students were learning about groups by working in groups. This implies that group work, from a learning perspective, serves several functions for the students ( Kutnick and Beredondini, 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Group work also seems to have an important study-social function for the university students, hence confirming that group work serves more functions than just being a pedagogical mode.
Affiliation, fellowship, and welfare seem to be highly important, and may even be essential prerequisites for learning. Accordingly, group work functions as both as an objective (i.e., learning collaborative abilities), and as the means (i.e., a base for academic achievement), or both, for the students ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). Moreover, the students from the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the students from the Program for Human Resources seem to use group work more as means for obtaining academic knowledge. In contrast, students from the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program more often mentioned learning collaborative abilities alone, as well as a combination of academic knowledge and group learning, thus using group work as an objective, as a means, or as a combination of both. One interpretation might be that the type of task assigned to the students differs in various programs. This can be valid both concerning the purpose of group work (group work as objective or as the means), but also arrangement (working in a group or as a group; Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Another possible explanation might be that the main emphasis in the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the Program for Human Resources is on product and academic knowledge, while in the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program, the process is more articulated and demanded. However, this is only speculation and further research is needed.
Even though the participants did not explicitly state that group work hampered learning, they mentioned that they perceived group work to be ineffective due to the loss of focus and/or the presence of conflicts with other group members, thereby hampering conceivable learning. This may also be an effect of the purpose or arrangement of the group work ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ).
EXPERIENCES OF GROUP WORK
The results revealed that several aspects of group work are important incentives for learning. In addition, this study revealed students’ experiences of group work (i.e., facilitating or hampering positive/negative experiences), which is in line with the previous studies on students’ experiences of working in groups ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Group composition, group structure, ways of working, and participants’ contributions are aspects put forward by the university students as either facilitating or hampering the positive experience of group work ( Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ).
Several of the aspects bear reference to whether the group members work in a group or as a group ( Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Working as a group is characterized by common effort, utilization of the group’s competence, and includes problem solving and reflection. All group members are involved in and working on a common task to produce a joint outcome ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). According to the results, not all groups are working as a group but rather working in a group, which, according to Granström (2006) , is common in an educational setting.
Due to problems with group composition, members’ contributions, and group structure, including rules and ways of cooperation, some students end up with negative experiences of group work. Additionally, the university students allude to the fact that a well-functioning supportive study-social context is an essential prerequisite not only for positive experiences of group work, but also for learning ( Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Both working in a group and working as group might be useful in different parts of the group work ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ) and cause learning. Hence working in a group causes cooperative learning based on social facilitation ( Zajonc, 1980 ; Baron, 1986 ; Uziel, 2007 ) while working as group causes learning benefits through collaboration with other group members. Although both approaches might cause positive or negative experiences, a conceivable interpretation is that working as a group has a greater potential to enhance positive experiences. The findings suggest a need for further research to fully understand why some group work causes positive experiences and other instances of group work cause negative experiences.
The findings in the current study develop the findings from Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson (2007) . First, it shows that it is possible to assemble all groups in to a joint research group (see below). Second, a thorough reanalysis, using an inductive qualitative content analysis, resulted in the emergence of three different abstractions: learning, study-social function, and organizations as either facilitating or hampering learning, and experiences.
METHODOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS
There are some limitations in the current study and most of them have to do with the construction of the study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire. First, the questions do not discriminate between (a) the type of group work, (b) the purpose with the group work, (c) the structure of the group work (i.e., extent and/or time); or (d) ways of working in the group (i.e., cooperation or collaboration). Second, the design of the questionnaire does not facilitate comparison between the populations included in the group. The questionnaire treated group work as one activity and did not acknowledge that group work can serve different functions and include various activities ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ). This simplification of the phenomena group work causes criticism concerning whether or not it is possible to assemble these populations into a joint research group. An elaborated description of the analysis process and the comparison to three background variables has been used to counter this criticism. The thin results from the comparison, indicate that based on the question used in the study-specific questionnaire, it is possible to assemble the results into a corpus of joint results.
CONCLUSION/CONCLUDING REMARKS
The results indicate that most of the students’ experienced that group work facilitated learning, especially concerning academic knowledge. Three important prerequisites (learning, study-social function, and organization) for group work that serve as an effective pedagogy and as an incentive for learning were identified and discussed. All three abstractions either facilitated or hampered university students’ learning, as well as their experiences of group work. By listening to the university students’ voices and elucidating their experiences and conceptions, we have been able to add new knowledge and understanding of what the essence is behind successful group work in higher education. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases, the result is the opposite, can be of use for further development of group work as a pedagogical practice.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges Ph.D. Faculty Program Director, Charlotta Einarsson, for her contribution to the design of this study and contribution to early stages of the data analysis and manuscript.
- American Psychological Association (APA). (2002). The Ethical Principles of Psychologists and Code of Conduct . Available at: http://www.apa.org/ethics/code2002.html [ Google Scholar ]
- Baines E., Blatchford P., Chowne A. (2007). Improving the effectiveness of collaborative group work in primary schools: effects on science attainment. Br. Educ. Res. J. 33 663–680 10.1080/01411920701582231 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barett M. (2007). “Practical and ethical issues in planning research,” in Research Methods in Psychology eds Breakell G., Hammond S., Fife-Schaw C., Smith J. A. (London: Sage Publications) 24–48 [ Google Scholar ]
- Baron R. S. (1986). Distraction-conflict theory: progress and problems. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 19 1–40 10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60211-7 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bennet N., Dunne E. (1992). Managing Classroom Groups . Hemel Hempstead: Simon & Schuster Education [ Google Scholar ]
- Blatchford P., Kutnick P., Baines E., Galton M. (2003). Toward a social pedagogy of classroom group work. Int. J. Educ. Res. 39 153–172 10.1016/S0883-0355(03)00078-8 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Breakwell G. M, Hammond F., Fife-Schaw C., Smith J. A. (eds) (2006). Research Methods in Psychology . London: Sage Publications [ Google Scholar ]
- British Psychology Society (BPS). (2004). Code of Conduct, Ethical Principles, and Guidelines . Available at: http://www.bps.org.uk/document-download-area/document-download.cfm?file_uuid=6D0645CC-7E96-C67F-D75E2648E5580115&ext=pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- British Psychology Society (BPS). (2006). Code of Ethics and Conduct . Available at: http://www.bps.org.uk/the-society/code-of-conduct/code-of-conduct_home.cfm [ Google Scholar ]
- Bryman A. (2012). Social Research Methods . Oxford: University Press [ Google Scholar ]
- Cantwell R. H., Andrews B. (2002). Cognitive and psychological factors underlying secondary school students’ feeling towards group work. Educ. Psychol. 22 75–91 10.1080/01443410120101260 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elo S, Kyngäs H. (2007). The qualitative content analysis process. J. Adv. Nurs. 62 107–115 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04569.x [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galton M., Williamson J. (1992). Group Work in the Primary Classroom . London: Routledge [ Google Scholar ]
- Galton M. J., Hargreaves L., Pell T. (2009). Group work and whole-class teaching with 11–14-years-old compared. Cambridge J. Educ . 39 119–147 10.1080/03057640802701994 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gillies R. M. (2003a). The behaviours, interactions, and perceptions of junior high school students during small-group learning. J. Educ. Psychol. 95 137–147 10.1037/0022-0663.95.1.137 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gillies R. M. (2003b). Structuring cooperative group work in classrooms. Int. J. Educ. Res. 39 35–49 10.1016/S0883-0355(03)00072-7 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gillies R. M., Boyle M. (2010). Teachers’ reflections on cooperative learning: Issues of implementation. Teach. Teach. Educ. 26 933–940 10.1016/j.tate.2009.10.034 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gillies R. M., Boyle M. (2011). Teachers’ reflections on cooperative learning (CL): a two-year follow-up. Teach. Educ. 1 63–78 10.1080/10476210.2010.538045 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Graneheim U. H., Lundman B. (2003). Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse Educ. Today 24 105–112 10.1016/j.nedt.2003.10.001 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Granström K. (2006). “Group phenomena and classroom management in Sweden,” in Handbook of Classroom Management: Research, Practice, and Contemporary Issues eds Evertson C. M., Weinstein C. S. (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum) 1141–1160 [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammar Chiriac E. (2008). A scheme for understanding group processes in problem-based learning. High. Educ. 55 505–518 10.1007/s10734-007-9071-7 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammar Chiriac E. (2010). “Group work is not one, but a great many processes – understanding group work dynamics,” in Group Theory: Classes, Representation and Connections, and Applications ed. Danellis C. W. (New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.) 153–166 [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammar Chiriac E. (2011a). Research on Group Work in Education . New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammar Chiriac E. (2011b). “Research on group work in education,” in Emerging Issues in Compulsory Education [Progress in Education. Volume 20] ed Nata R. (New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.) 25–44 [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammar Chiriac E., Einarsson C. (2007). “Is the grass greener in the other group? Students’ experiences of group-work” [“är gräset grönare i den andra gruppen? Studenters erfarenheter av grupparbete”] [Published in Swedish], in Interaction on the Edge 2. Proceedings from the 5th GRASP Conference ed. Näslund J. (Linköping: Linköping University) [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammar Chiriac E, Granström K. (2012). Teachers’ leadership and students’ experience of group work. Teach. Teach. Theor. Pract. 3 345–363 10.1080/13540602.2012.629842 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammar Chiriac E., Hempel A. (2013), Handbook for Group Work [Published in Swedish: Handbok för grupparbete – att skapa fungerande grupper i undervisningen] . Lund: Studentlitteratur [ Google Scholar ]
- Hansen R. S. (2006). Benefits and problems with student teams: suggestions for improving team projects. J. Educ. Bus. 82 11–19 10.3200/JOEB.82.1.11-19 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson D. W., Johnson R. T. (1975). Learning Together and Alone. Cooperative, Competitive and Individualistic Learning (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall) [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson D. W., Johnson R. T. (2004). Assessing Students in Groups: Promoting Group Responsibility and Individual Accountability . Thousand Oaks: Sage [ Google Scholar ]
- Kutnick P., Beredondini L. (2009). Can the enhancement of group work in classrooms provide a basis for effective communication in support of school-based cognitive achievement in classrooms of young learners? Cambridge J. Educ . 39 71–94 10.1080/03057640902836880 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lou Y., Abrami P. C., Spence J. C., Poulsen C., Chambers B, d’Apllonia S. (1996). Within-class grouping: a meta analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 66 423–458 10.3102/00346543066004423 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mayring P. (2000). Qualitative Content Analysis. Forum: Qualitative Social Research 1:2 . Available at: http://qualitative-research.net/fqs/fqs-e/2-00inhalt-e.htm_140309 [ Google Scholar ]
- Näslund J. (2013). “Pupils’ and students’ view on group work” [Published in Swedish: Elevers och studenters syn på grupparbete] in Handbook for Group Work [Published in Swedish: Handbok för grupparbete – att skapa fungerande grupper i undervisningen] eds Hammar Chiriac E., Hempel A. (Lund: Studentlitteratur) 233–242 [ Google Scholar ]
- Peterson S, Miller J. A. (2004). Quality of college students’ experiences during cooperative learning. Soc. Psychol. Learn. 7 161–183 [ Google Scholar ]
- Underwood J. D. M. (2003). Student attitudes towards socially acceptable and unacceptable group working practices. Br. J. Psychol. 94 319–337 10.1348/000712603767876253 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uziel L. (2007). Individual differences in the social facilitation effect: a review and meta-analysis. J. Res. Person. 41 579–601 10.1016/j.jrp.2006.06.008 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Webb N. M., Palincsar A. S. (1996). “Group processes in the classroom,” in Handbook of Educational Psychology eds Berliner D. C., Calfee R. C. (New York: Macmillan) 841–873 [ Google Scholar ]
- Zajonc R. B. (1980). “Compresence,” in Psychology of Group Influence ed. Paulus P. B. (New York, NY: Lawrence Erlbaum) 35–60 [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (413.7 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Group work as an incentive for learning – students’ experiences of group work.

- Division of Psychology, Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in educational systems. There is strong scientific support for the benefits of having students learning and working in groups. Nevertheless, studies about what occurs in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students’ ability to learn is still lacking. Similarly, the question of why some group work is successful and other group work results in the opposite is still unsolved. The aim of this article is to add to the current level of knowledge and understandings regarding the essence behind successful group work in higher education. This research is focused on the students’ experiences of group work and learning in groups, which is an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work prior to the beginning of the 21st century. A primary aim is to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view and how the students assess learning when working in groups. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work ends up being a positive experience resulting in successful learning, while in other cases, the result is the reverse, are of interest. Data were collected through a study-specific questionnaire, with multiple choice and open-ended questions. The questionnaires were distributed to students in different study programs at two universities in Sweden. The present result is based on a reanalysis and qualitative analysis formed a key part of the study. The results indicate that most of the students’ experiences involved group work that facilitated learning, especially in the area of academic knowledge. Three important prerequisites (learning, study-social function, and organization) for group work that served as an effective pedagogy and as an incentive for learning were identified and discussed. All three abstractions facilitate or hamper students’ learning, as well as impact their experiences with group work.
Introduction
Group work is used as a means for learning at all levels in most educational systems, from compulsory education to higher education. The overarching purpose of group work in educational practice is to serve as an incentive for learning. For example, it is believed that the students involved in the group activity should “learn something.” This prerequisite has influenced previous research to predominantly focus on how to increase efficiency in group work and how to understand why some group work turns out favorably and other group work sessions result in the opposite. The review of previous research shows that in the 20th century, there has been an increase in research about students’ cooperation in the classroom ( Lou et al., 1996 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). This increasing interest can be traced back to the fact that both researchers and teachers have become aware of the positive effects that collaboration might have on students’ ability to learn. The main concern in the research area has been on how interaction and cooperation among students influence learning and problem solving in groups ( Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ).
Two approaches concerning learning in group are of interest, namely cooperative learning and collaborative learning . There seems to be a certain amount of confusion concerning how these concepts are to be interpreted and used, as well as what they actually signify. Often the conceptions are used synonymously even though there are some differentiations. Cooperative group work is usually considered as a comprehensive umbrella concept for several modes of student active working modes ( Johnson and Johnson, 1975 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ), whereas collaboration is a more of an exclusive concept and may be included in the much wider concept cooperation ( Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Cooperative learning may describe group work without any interaction between the students (i.e., the student may just be sitting next to each other; Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ), while collaborative learning always includes interaction, collaboration, and utilization of the group’s competences ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ).
At the present time, there is strong scientific support for the benefits of students learning and working in groups. In addition, the research shows that collaborative work promotes both academic achievement and collaborative abilities ( Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). According to Gillies and Boyle (2011) , the benefits are consistent irrespective of age (pre-school to college) and/or curriculum. When working interactively with others, students learn to inquire, share ideas, clarify differences, problem-solve, and construct new understandings. Gillies (2003a , b ) also stresses that students working together are more motivated to achieve than they would be when working individually. Thus, group work might serve as an incentive for learning, in terms of both academic knowledge and interpersonal skills. Nevertheless, studies about what occur in groups during group work and which factors actually influence the students’ ability to learn is still lacking in the literature, especially when it comes to addressing the students’ points of view, with some exceptions ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Similarly, the question of why some group work turns out successfully and other work results in the opposite is still unsolved. In this article, we hope to contribute some new pieces of information concerning the why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while others result in the opposite.
Group Work in Education
Group work is frequently used in higher education as a pedagogical mode in the classroom, and it is viewed as equivalent to any other pedagogical practice (i.e., whole class lesson or individual work). Without considering the pros and cons of group work, a non-reflective choice of pedagogical mode might end up resulting in less desirable consequences. A reflective choice, on the other hand, might result in positive experiences and enhanced learning ( Galton et al., 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ).
Group Work as Objective or Means
Group work might serve different purposes. As mentioned above, the overall purpose of the group work in education is that the students who participate in group work “learn something.” Learning can be in terms of academic knowledge or “group knowledge.” Group knowledge refers to learning to work in groups ( Kutnick and Beredondini, 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Affiliation, fellowship, and welfare might be of equal importance as academic knowledge, or they may even be prerequisites for learning. Thus, the group and the group work serve more functions than just than “just” being a pedagogical mode. Hence, before group work is implemented, it is important to consider the purpose the group assignment will have as the objective, the means, or both.
From a learning perspective, group work might function as both an objective (i.e., learning collaborative abilities) and as the means (i.e., a base for academic achievement) or both ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). If the purpose of the group work is to serve as an objective, the group’s function is to promote students’ development of group work abilities, such as social training and interpersonal skills. If, on the other hand, group work is used as a means to acquire academic knowledge, the group and the collaboration in the group become a base for students’ knowledge acquisition ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). The group contributes to the acquisition of knowledge and stimulates learning, thus promoting academic performance. Naturally, group work can be considered to be a learning environment, where group work is used both as an objective and as the means. One example of this concept is in the case of tutorial groups in problem-based learning. Both functions are important and might complement and/or even promote each other. Albeit used for different purposes, both approaches might serve as an incentive for learning, emphasizing different aspect knowledge, and learning in a group within an educational setting.
Working in a Group or as a Group
Even if group work is often defined as “pupils working together as a group or a team,” ( Blatchford et al., 2003 , p. 155), it is important to bear in mind that group work is not just one activity, but several activities with different conditions ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 , 2010 ). This implies that group work may change characteristics several times during a group work session and/or during a group’s lifetime, thus suggesting that certain working modes may be better suited for different parts of a group’s work and vice versa ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 , 2010 ). It is also important to differentiate between how the work is accomplished in the group, whether by working in a group or working as a group.
From a group work perspective, there are two primary ways of discussing cooperation in groups: working in a group (cooperation) or working as a group (collaboration; Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Situations where students are sitting together in a group but working individually on separate parts of a group assignment are referred to as working in a group . This is not an uncommon situation within an educational setting ( Gillies and Boyle, 2011 ). Cooperation between students might occur, but it is not necessary to accomplish the group’s task. At the end of the task, the students put their separate contributions together into a joint product ( Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2010 , 2011a ). While no cooperative activities are mandatory while working in a group, cooperative learning may occur. However, the benefits in this case are an effect of social facilitation ( Zajonc, 1980 ; Baron, 1986 ; Uziel, 2007 ) and are not caused by cooperation. In this situation, social facilitation alludes to the enhanced motivational effect that the presence of other students have on individual student’s performance.
Working as a group, on the other hand, causes learning benefits from collaboration with other group members. Working as a group is often referred to as “real group work” or “meaningful group work,” and denotes group work in which students utilizes the group members’ skills and work together to achieve a common goal. Moreover, working as a group presupposes collaboration, and that all group members will be involved in and working on a common task to produce a joint outcome ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Working as a group is characterized by common effort, the utilization of the group’s competence, and the presence of problem solving and reflection. According to Granström (2006) , working as a group is a more uncommon activity in an educational setting. Both approaches might be useful in different parts of group work, depending on the purpose of the group work and type of task assigned to the group ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ). Working in a group might lead to cooperative learning, while working as group might facilitate collaborative learning. While there are differences between the real meanings of the concepts, the terms are frequently used interchangeably ( Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ).
Previous Research of Students’ Experiences
As mentioned above, there are a limited number of studies concerning the participants’ perspectives on group work. Teachers often have to rely upon spontaneous viewpoints and indications about and students’ experiences of group work in the form of completed course evaluations. However, there are some exceptions ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson, 2007 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). To put this study in a context and provide a rationale for the present research, a selection of studies focusing on pupils’ and/or students’ experiences and conceptions of group work will be briefly discussed below. The pupils’ and/or students inside knowledge group work may present information relevant in all levels of educational systems.
Hansen (2006) conducted a small study with 34 participating students at a business faculty, focusing on the participants’ experiences of group work. In the study different aspects of students’ positive experiences of group work were identified. For example, it was found to be necessary that all group members take part and make an effort to take part in the group work, clear goals are set for the work, role differentiation exists among members, the task has some level of relevance, and there is clear leadership. Even though Hansen’s (2006) study was conducted in higher education, these findings may be relevant in other levels in educational systems.
To gain more knowledge and understand about the essence behind high-quality group work, Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson (2007) turned their focus toward students’ experiences and conceptions of group work in higher education. A primary aim was to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating their students’ points of view and how the students assess working in groups. Do the students’ appreciate group projects or do they find it boring and even as a waste of time? Would some students prefer to work individually, or even in “the other group?” The study was a part of a larger research project on group work in education and only a small part of the data corpus was analyzed. Different critical aspects were identified as important incitements for whether the group work turned out to be a success or a failure. The students’ positive, as well as negative, experiences of group work include both task-related (e.g., learning, group composition, participants’ contribution, time) and socio-emotional (e.g., affiliation, conflict, group climate) aspects of group work. The students described their own group, as well as other groups, in a realistic way and did not believe that the grass was greener in the other group. The same data corpus is used in this article (see under Section The Previous Analysis). According to Underwood (2003) and Peterson and Miller (2004) , the students’ enthusiasm for group work is affected by type of task, as well as the group’s members. One problem that recurred frequently concerned students who did not contribute to the group work, also known as so-called free-riders ( Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Students are, in general, reluctant to punish free-riders and antipathy toward working in groups is often associated with a previous experience of having free-riders in the group ( Peterson and Miller, 2004 ). To accomplish a favorable attitude toward group work, the advantages of collaborative activities as a means for learning must be elucidated. Furthermore, students must be granted a guarantee that free-riders will not bring the group in an unfavorable light. The free-riders, on the other hand, must be encouraged to participate in the common project.
Hammar Chiriac and Granström (2012) were also interested in students’ experiences and conceptions of high-quality and low-quality group work in school and how students aged 13–16 describe good and bad group work? Hammar Chiriac and Granström (2012) show that the students seem to have a clear conception of what constitutes group work and what does not. According to the students, genuine group work is characterized by collaboration on an assignment given by the teacher. They describe group work as working together with their classmates on a common task. The students are also fully aware that successful group work calls for members with appropriate skills that are focused on the task and for all members take part in the common work. Furthermore, the results disclose what students consider being important requisites for successful versus more futile group work. The students’ inside knowledge about classroom activities ended up in a taxonomy of crucial conditions for high-quality group work. The six conditions were: (a) organization of group work conditions, (b) mode of working in groups, (c) tasks given in group work, (d) reporting group work, (e) assessment of group work, and (f) the role of the teacher in group work. The most essential condition for the students seemed to be group composition and the participants’ responsibilities and contributions. According to the students, a well-organized group consists of approximately three members, which allows the group to not be too heterogeneous. Members should be allotted a reasonable amount of time and be provided with an environment that is not too noisy. Hence, all six aspects are related to the role of the teacher’s leadership since the first five points concern the framework and prerequisites created by the teacher.
Näslund (2013) summarized students’ and researchers’ joint knowledge based on experience and research on in the context of shared perspective for group work. As a result, Näslund noticed a joint apprehension concerning what constitutes “an ideal group work.” Näslund (2013) highlighted the fact that both students and researchers emphasized for ideal group work to occur, the following conditions were important to have: (a) the group work is carried out in supportive context, (b) cooperation occurs, (c) the group work is well-structured, (d) students come prepared and act as working members during the meetings, and (e) group members show respect for each other.
From this brief exposition of a selection of research focusing on students’ views on group work, it is obvious that more systematic studies or documentations on students’ conceptions and experiences of group work within higher education are relevant and desired. The present study, which is a reanalysis of a corpus of data addressing the students’ perspective of group, is a step in that direction.
Aim of the Study
The overarching knowledge interest of this study is to enhance the body of knowledge regarding group work in higher education. The aim of this article is to add knowledge and understanding of what the essence behind successful group work in higher education is by focusing on the students’ experiences and conceptions of group work and learning in groups , an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work until the beginning of the 21st century. A primary aim is to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view and how the students assess learning when working in groups. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases, the result is the opposite, are of interest.
Materials and Methods
To capture university students’ experiences and conceptions of group work, an inductive qualitative approach, which emphasizes content and meaning rather than quantification, was used ( Breakwell et al., 2006 ; Bryman, 2012 ). The empirical data were collected through a study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire and a qualitative content analysis was performed ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ).
Participants
All participating students attended traditional university programs where group work was a central and frequently used pedagogical method in the educational design. In addition, the participants’ programs allowed the students to be allocated to the same groups for a longer period of time, in some cases during a whole semester. University programs using specific pedagogical approaches, such as problem-based learning or case method, were not included in this study.
The participants consisted of a total of 210 students, 172 female and 38 male, from two universities in two different cities (approximately division: 75 and 25%). The students came from six different populations in four university programs: (a) The Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology, (b) The Human Resource Management and Work Sciences Program, (c) Social Work Program, and (d) The Bachelor’s Programs in Biology. The informants were studying in their first through eighth terms, but the majority had previous experiences from working in other group settings. Only 2% of the students had just started their first term when the study was conducted, while the vast majority (96%) was participating in university studies in their second to sixth semester.
The teacher most frequently arranged the group composition and only a few students stated that they have had any influence on the group formation. There were, with a few exceptions, between 6 and 10 groups in each of the programs included in this study. The groups consisted of between four to eight members and the differences in sizes were almost proportionally distributed among the research group. The groups were foremost heterogeneous concerning gender, but irrespective of group size, there seems to have been a bias toward more women than men in most of the groups. When there was an underrepresented sex in the group, the minority mostly included two students of the same gender. More than 50% of the students answered that in this particularly group, they worked solely with new group members, i.e., students they had not worked with in previous group work during the program.
To collect data about students’ experiences and conceptions of group work, a study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire was constructed. The questionnaire approached the students’ experiences regarding the specific group work they were working in at the time of the data collection (spring 2006), not their experiences of group work in general. The questionnaire contained a total of 18 questions, including both multiple choice and open-ended questions. The multiple choice questions concerned background variables and information about the present group. The seven open-ended questions were designed to gather data about the students’ experiences and perceptions of group work in higher education. The questionnaires were distributed to the different populations of students (some populations studied at the same program) at two universities in Sweden. During the time the questionnaires were completed, the researcher or an assistant was present to answer possible questions. In all, 210 students answered the questionnaire.

The previous analysis
As described above (Section Previous Research of Students’ Experiences) a previous analysis based on the same data corpus revealed that most of the students included in the study found group work to be an enjoyable and stimulating working method ( Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson, 2007 ). The data were analyzed using a qualitative content analysis based on three different research questions. There were two main criticisms of the previous study presented from other researchers. The criticism conveyed applied mostly to the question of whether we could assemble these groups into a joint research group and second to the fact that the results were mostly descriptive. To counter this criticism and to elaborate on the analysis, a further analysis was conducted.
The present analysis
The present analysis (or reanalysis) was conducted by using an inductive qualitative content analysis based on three open-ended research questions:
(1) In what ways does group work contribute to your learning?
(2) What positive experiences have you had while working in your present group?
(3) What negative experiences have you had while working in your present group?
Each question corresponds to one aspect of the research’s objective, but together, they might support and enrich each other and unravel new information based on the students’ experiences and conceptions of group work. Research question 1, listed above, was not included in the first analysis and is being investigated for the first time in this study, while the other two questions are being reanalyzed. An inductive, qualitative content analysis is applicable when the aim of the research is a description of the meaning or of a phenomenon in conceptual form ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ).
The analysis was carried out over several steps, following the basic principles of an inductive, qualitative content analysis ( Mayring, 2000 ; Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). The steps included three phases: preparation, organizing, and reporting ( Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). Each question was treated as a unit of analysis and was thus analyzed separately. In the preparation phase, the researcher tried to make sense of the data by becoming familiar with the data corpus. In the current study, this included transcription and thorough reading of the answers. An open coding system composed of marginal notes and headings began the second phase, which included organizing the data. This second phase, in turn, included open coding, creating categories, and abstraction. The notes and the headings from the open coding were transferred to coding sheets and then grouped into categories. Categories were formed through the interpretation of the codes that described the same meaning or phenomenon. Finally, an abstraction process began, where a general description of the grouped categories formed an abstraction (see Table 1 ). An abstraction was denominated using the content-characteristic words for this paper: learning, study-social function, and organization . The third phase, reporting , addressed the presentation of the process of analysis and the results.
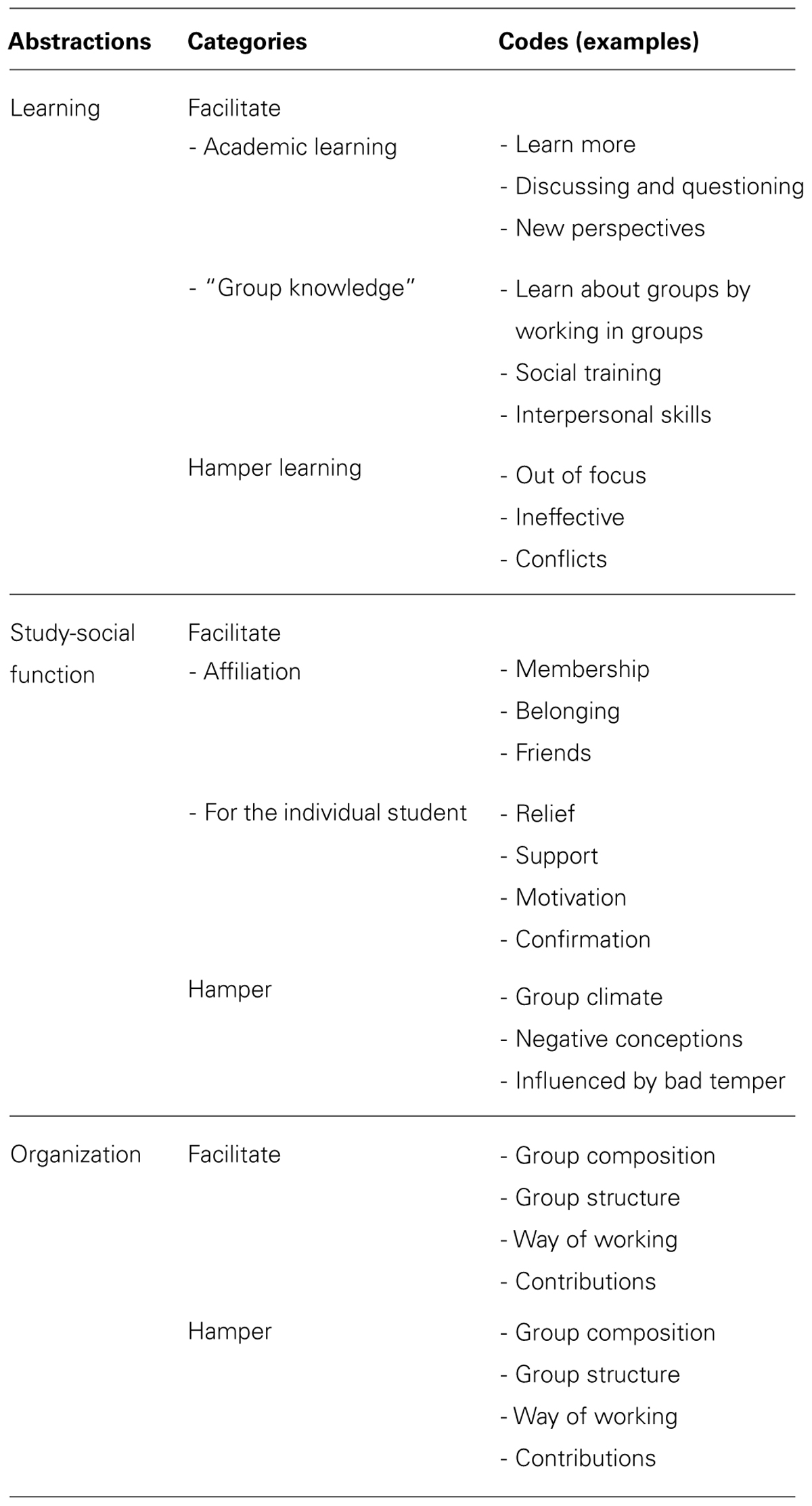
TABLE 1. Examples from the organization phase of the coding process.
The final aim of this study is to present the phenomenon studied in a model or conceptual map of the categories ( Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). In following these procedures, we aim to expand our understanding of the existing work and to counter the second part of the criticisms, which included criticisms stating that the results were mostly descriptive in nature. To counter the criticisms regarding the question of whether we could assemble these groups into a joint research group, the qualitative abstraction that emerged from the qualitative content analysis was compared to background information by using SPSS. Three background variables were used: gender, cities, and programs.
Ethics and Quality
The ethical principles provided by the British Psychology Society have formed a guideline [ British Psychology Society (BPS), 2006 ] for the present study. The ethical principles, which emphasize the concern for participants’ interest, have been applied throughout the study [ American Psychological Association (APA), 2002 ; British Psychology Society (BPS), 2004 ; Barett, 2007 ]. To facilitate trustworthiness, a thorough description of the analysis process has been presented ( Graneheim and Lundman, 2003 ; Elo and Kyngäs, 2007 ). Translated citations are also included to increase trustworthiness.
As described above, the analysis resulted in three abstraction emerging: learning, study-social function , and organization . Each abstraction includes both a positive variant (i.e., facilitating learning, study-social function, and/or organization) as well as a negative alternative (i.e., hampering learning, study-social function, and/or organization). The results will be presented in three different sections, with each section corresponding to one abstraction. However, we would like to call attention to the fact that one fifth (20%, including missing value 8%) of the students included in this study did not perceive and/or mention any negative experiences at all in their present group. From a general point of view, there is no difference with respect to gender or city regarding the distribution of positive and negative experiences concerning the abstractions, neither concerning different programs nor the distribution of negative experiences (all p > 0.05). In contrast, there is a difference between the various programs and the distribution of positive experiences (χ 2 = 14.474; df: 6; p < 0.025). The students from the social work program display a higher amount of positive experiences in connection with a study-social function and organizing in comparison with the other programs.
The majority of the students (97%) responded that working in group somehow facilitated learning, academic knowledge, collaborative abilities or both. They learned more or different things when working in groups than they would have if working alone. By discussing and questioning each other’s points of view and listening to their fellow students’ contributions, thus obtaining different perspectives, the participants experienced an enhanced academic learning, compared to working alone. “I learn much more by working in groups than working individually. I obtain more through interaction with the other group members.” Academic knowledge is not the only type of knowledge learned through group work. In addition to academic knowledge, students also gain advanced knowledge about how groups work, how the students function as individual members of groups and how other members behave and work in groups. Some of the respondents also argued that group work in group courses strengthen the combination between empirical and theoretical learning, thus learning about groups by working in groups. “Through practical knowledge demonstrate several of the phenomena we read about in theory (group psychology and sociology).”
The results show no difference when considering either gender or city. However, when comparing the four programs included in the study and the types of learning, a difference occurs (χ 2 = 14.474; df: 6; p < 0.025). A division into two parts seems to generate the difference. On the one hand, the students from the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the students from the Human Resource Management and Work Sciences Program emphasize academic knowledge. On the other hand, students from the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program more often mentioned learning collaborative abilities single handed, as well as a combination of academic knowledge and group learning.
Even though the participants did not expressly report that group work hampered learning, they often mentioned that they perceived group work as being ineffective due to loss of focus and the presence of conflicts, thereby hampering conceivable learning. One respondent stated, “that you sometimes are out of focus in the discussion and get side-tracked instead of considering the task.” Another offered the following perspective: “Occasionally, it is too little task related and feels unnecessary sometimes. Individual work is, in certain situations, preferable.” Group work might be perceived as ineffective and time consuming considering long working periods with tedious discussions. One participant stated, “The time aspect, everything is time consuming.” The absence or presence of conflicts in the group affects students’ experiences, and conflicts not handled may influence learning in a negative way. The students perceived that it was difficult to come to an agreement and experience those conflicts and the need to compromise hampered individual learning. Accordingly, the absence of conflicts seemed to be an important incitement for learning. However, fear of conflicts can lead to reduced learning and cause negative experiences, but to a considerably lesser extent than does the presence of actual conflicts. “A great fear of conflicts sometimes raises an oppressive atmosphere.” “Fear of conflicts leads to much not made known.”
A Study-Social Function
Group work also has an important study - social function according to the students. They describe their membership in groups as an important aspect of affiliation. In general, the total number of students at a program is approximately 60–80 or more. In contexts with a large population of students, the smaller group gives the participants an opportunity to feel affiliated with the group and to each other. “Feels safe to have a certain group to prepare oneself together with before, for instance, an upcoming seminar.” The group gives the individual student a platform of belonging, which might serve as an important arena for learning ( facilitate ) and finding friends to spend leisure time with. Many of the participants also reported feeling a positive atmosphere in the group, which is important for the satisfaction of being in the group together with the fellow students.
To be a member of a group may also serve as a function of relief, both academically and socially, for the individual student. The participants reported that many of the tasks assigned by the university teachers are difficult to handle on their own. “The others explain to me. We help one another.” However, the students reported that they helped and supported each other, even if the task did not demand cooperation. “As a student, you get more active. You help one another to extract the groups’ common knowledge. Forward info if somebody is missing.” Being a member of a group also affects students’ motivation to study. They prepare themselves by reading texts and other material before the next group session. Group work may also have positive effects on achievement. Students’ total amount of time and effort on their work may also increase. Through group work, the participants also get confirmation of who they are and what their capacities are.
Being a member of a group also has its downside, which often has to do with the group climate and/or group processes, both of which have multiple and complex features. Many students reported that both the group climate and group processes might be the source of negative conceptions of the group and hamper learning. “Process losses.” The respondents described negative conceptions based on the feeling of not having enough time to get to know each other in the group or being in situations where no cooperation occurred. Other students referred to the fact that the group’s life is too long, which may lead to group members not only wearing each other out, but also having a negative effect on each other’s mood. “Influenced by each other’s mood.” Examples of negative experiences are process losses in general, including insufficient communication, unclear roles, and problems with one group member. As mentioned above, the students from the Social Work Program display a higher number of positive experiences in connection with a study-social function and organizing in comparison with students from the other programs.
Organization
O rganization concerns the structure of group work and includes different aspects, all describing group work from different angles. The aspects are relevant no matter how the participants perceive the group work, whether as positive or negative. Unlike the other two abstractions (learning and study-social function), organization includes the same aspects no matter what the experiences are, namely group composition , group structure , way of working and contributions.
Whether the group is composed in a homogeneous or heterogeneous way seems to be experienced in both a positive and negative sense. A well-thought-out group composition , including both group size and mix of members, is essential. A just large-enough group for the task, consisting of a population of members that is not too heterogeneous, facilitates a joyful experience and learning. A homogeneous mix of members might be perceived as positive, as the students feel that they have similar life situations, opinions, and skills, thereby causing positive conditions for collaboration within the group. Conversely, in a group with a heterogeneous mix, different members contribute with different knowledge and/or prior experiences, which can be used in the group for collective and collaborative learning. “Good group composition, distribution of age groups that leads to fruitful discussions.”
An additional facilitating prerequisite is that the group develops adequate ways of working together, which includes a well-organized group structure . Well-working groups are characterized as having developed adequate ways of working together, while groups that work less well together lack a developed way of cooperation. “Well-organized working group with clear and distinct rules and structure.” Preparation and attendance for group work are aspects mentioned as facilitating (and hampering) incitements. Group work in educational settings sometimes entails that you, as a student, are forced to read and learn within a certain period of time that is beyond your control. Some participants find the pressure positive, hence “increase the pressure to read chapters in time.” The members’ contribution to the group is also a central factor for the students’ apprehension of how the group works. This is, in short, about how much each member ought to contribute to the group and to the work. Groups considered to be well-working are ones where all members contribute to the group’s work, but the content of the contribution may vary according to the single member’s qualifications. “We work well together (most of us). Everybody participates in different ways and seems committed.” “Good, everybody participates the same amount. We complement each other well.”
The same prerequisites can lead to the reverse result, i.e., hampering learning and stirring up negative experiences. If the group members are too identical (a homogeneous group composition ), it might lead to a lack of opinions, which several participants perceived as being negative. “That we do not get a male perspective about the subject. We are all girls, at the age of 20, which also means that we have pretty much the same experiences that may be seen as both positive and negative. The negative is the lack of opinion.” If the group is considered to be too small, students seems to find it troublesome, as the relationships are few, but there are also few people who are available to handle the workload allotted to the group. Nevertheless, a group that is too large could also lead to negative experiences. “It is far too large a group.”
A lack of group structure might lead to a lower degree of satisfaction with the group’s way of working . A commonly expressed point of view seen in the students’ answers involved the occurrences of when all members did not attend the meetings (absence). In these cases, it was also viewed that the work in the group often was characterized as unstructured. “Sometimes a bit unclear structures, some students have difficulties with coming in time.” Not attending or coming unprepared or badly prepared to the group work is other aspect that is commented on. “Low degree of fellowship, punctuality is a problem, an insecure group.” Some students find it frustrating to prepare for a certain time decided that is beyond their control. “A necessity to read certain chapters within a specific period of time is never stimulating.”
One characteristic of groups that are not working well is that contribution varies among the members. In group work, students with different levels of ambition are assembled, which may result in different levels of interest and commitment, as well as differences in the willingness to take on responsibilities or part of the workload of the group’s work. Some members are active and do much of the work, while others barely contribute at all. “Some don’t do anything while others pull the heaviest burden. Two out of three prepare before the meeting, the rest think that they are able to read during the group work and do not supply the group with anything else other than delays and frustration.” A common answer seen in the questionnaires that concerns negative experiences of group work as they relate to contribution is: “Everybody does not contribute just as much.” or “There is always someone who just glides along and doesn’t take part.”
Summary of the Results
The results are summarized in a model illustrating the relationship between abstractions (i.e., learning, study-social function, and organization) and result (i.e., enhanced or reduced learning), as well as positive or negative experiences (see Figure 1 ).
FIGURE 1. A model illustrating the relationship between abstractions and result .
The figure shows that all three abstractions may facilitate or hamper learning as well as the experiences of group work. To piece together, the difficult and extensive jigsaw puzzle concerning why some group work result in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases the result is the reverse is still not solved. In this article, we propose that the prerequisites learning, study-social function, and organization influence learning and experiences of working in group, thus, providing additional pieces of information to the jigsaw puzzle (Figure 2 ).
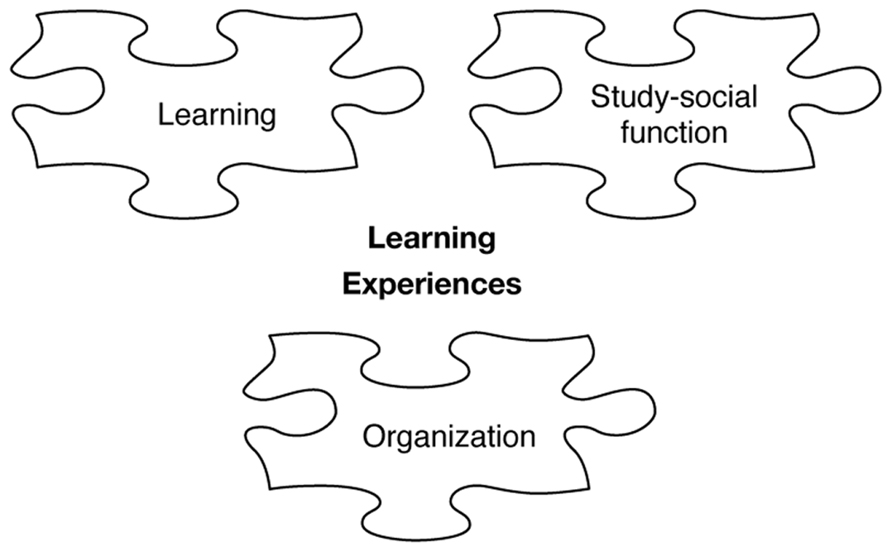
FIGURE 2. Pieces of jigsaw puzzle influence learning and experiences.
The current study focuses on university students’ experiences and conceptions of group work and learning in groups. A primary aim was to give university students a voice in the matter by elucidating the students’ positive and negative points of view, as well as how the students’ assess learning when working in groups. The analysis resulted in the emergence of three different abstractions: learning, study-social function, and organizations. Each abstraction also included a positive and a negative variant. In other words, all three abstractions either facilitated or hampered university students’ learning, as well as their experiences of group work.
Learning in Group Work
The result shows that the majority of the students (97%) experience that working in group facilitated learning, either academic knowledge, collaborative abilities or both, accordingly confirming previous research ( Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ). According to the students, they learn more or different things when working in groups compared with working individually. Academic knowledge was not the only type of knowledge learned through group work. In addition to academic knowledge, students also gained advanced knowledge about how groups work, how the students function as individual members of groups and how other members behave and work in groups. Some of the respondents also argued that group work might strengthen the combination between empirical and theoretical learning, thus the students were learning about groups by working in groups. This implies that group work, from a learning perspective, serves several functions for the students ( Kutnick and Beredondini, 2009 ; Gillies and Boyle, 2010 , 2011 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). Group work also seems to have an important study-social function for the university students, hence confirming that group work serves more functions than just being a pedagogical mode.
Affiliation, fellowship, and welfare seem to be highly important, and may even be essential prerequisites for learning. Accordingly, group work functions as both as an objective (i.e., learning collaborative abilities), and as the means (i.e., a base for academic achievement), or both, for the students ( Gillies, 2003a , b ; Johnson and Johnson, 2004 ; Baines et al., 2007 ). Moreover, the students from the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the students from the Program for Human Resources seem to use group work more as means for obtaining academic knowledge. In contrast, students from the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program more often mentioned learning collaborative abilities alone, as well as a combination of academic knowledge and group learning, thus using group work as an objective, as a means, or as a combination of both. One interpretation might be that the type of task assigned to the students differs in various programs. This can be valid both concerning the purpose of group work (group work as objective or as the means), but also arrangement (working in a group or as a group; Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Another possible explanation might be that the main emphasis in the Bachelor’s Program in Biology and the Program for Human Resources is on product and academic knowledge, while in the Psychologist Program/Master of Science in Psychology and Social Work Program, the process is more articulated and demanded. However, this is only speculation and further research is needed.
Even though the participants did not explicitly state that group work hampered learning, they mentioned that they perceived group work to be ineffective due to the loss of focus and/or the presence of conflicts with other group members, thereby hampering conceivable learning. This may also be an effect of the purpose or arrangement of the group work ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ).
Experiences of Group Work
The results revealed that several aspects of group work are important incentives for learning. In addition, this study revealed students’ experiences of group work (i.e., facilitating or hampering positive/negative experiences), which is in line with the previous studies on students’ experiences of working in groups ( Cantwell and Andrews, 2002 ; Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Group composition, group structure, ways of working, and participants’ contributions are aspects put forward by the university students as either facilitating or hampering the positive experience of group work ( Underwood, 2003 ; Peterson and Miller, 2004 ; Hansen, 2006 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ; Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ).
Several of the aspects bear reference to whether the group members work in a group or as a group ( Underwood, 2003 ; Hammar Chiriac and Granström, 2012 ). Working as a group is characterized by common effort, utilization of the group’s competence, and includes problem solving and reflection. All group members are involved in and working on a common task to produce a joint outcome ( Bennet and Dunne, 1992 ; Galton and Williamson, 1992 ; Webb and Palincsar, 1996 ; Hammar Chiriac, 2011a , b ). According to the results, not all groups are working as a group but rather working in a group, which, according to Granström (2006) , is common in an educational setting.
Due to problems with group composition, members’ contributions, and group structure, including rules and ways of cooperation, some students end up with negative experiences of group work. Additionally, the university students allude to the fact that a well-functioning supportive study-social context is an essential prerequisite not only for positive experiences of group work, but also for learning ( Hammar Chiriac and Hempel, 2013 ). Both working in a group and working as group might be useful in different parts of the group work ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ) and cause learning. Hence working in a group causes cooperative learning based on social facilitation ( Zajonc, 1980 ; Baron, 1986 ; Uziel, 2007 ) while working as group causes learning benefits through collaboration with other group members. Although both approaches might cause positive or negative experiences, a conceivable interpretation is that working as a group has a greater potential to enhance positive experiences. The findings suggest a need for further research to fully understand why some group work causes positive experiences and other instances of group work cause negative experiences.
The findings in the current study develop the findings from Hammar Chiriac and Einarsson (2007) . First, it shows that it is possible to assemble all groups in to a joint research group (see below). Second, a thorough reanalysis, using an inductive qualitative content analysis, resulted in the emergence of three different abstractions: learning, study-social function, and organizations as either facilitating or hampering learning, and experiences.
Methodological Considerations
There are some limitations in the current study and most of them have to do with the construction of the study-specific, semi-structured questionnaire. First, the questions do not discriminate between (a) the type of group work, (b) the purpose with the group work, (c) the structure of the group work (i.e., extent and/or time); or (d) ways of working in the group (i.e., cooperation or collaboration). Second, the design of the questionnaire does not facilitate comparison between the populations included in the group. The questionnaire treated group work as one activity and did not acknowledge that group work can serve different functions and include various activities ( Hammar Chiriac, 2008 ). This simplification of the phenomena group work causes criticism concerning whether or not it is possible to assemble these populations into a joint research group. An elaborated description of the analysis process and the comparison to three background variables has been used to counter this criticism. The thin results from the comparison, indicate that based on the question used in the study-specific questionnaire, it is possible to assemble the results into a corpus of joint results.
Conclusion/Concluding Remarks
The results indicate that most of the students’ experienced that group work facilitated learning, especially concerning academic knowledge. Three important prerequisites (learning, study-social function, and organization) for group work that serve as an effective pedagogy and as an incentive for learning were identified and discussed. All three abstractions either facilitated or hampered university students’ learning, as well as their experiences of group work. By listening to the university students’ voices and elucidating their experiences and conceptions, we have been able to add new knowledge and understanding of what the essence is behind successful group work in higher education. Furthermore, the students’ explanations of why some group work results in positive experiences and learning, while in other cases, the result is the opposite, can be of use for further development of group work as a pedagogical practice.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges Ph.D. Faculty Program Director, Charlotta Einarsson, for her contribution to the design of this study and contribution to early stages of the data analysis and manuscript.
American Psychological Association (APA). (2002). The Ethical Principles of Psychologists and Code of Conduct . Available at: http://www.apa.org/ethics/code2002.html
Baines, E., Blatchford, P., and Chowne, A. (2007). Improving the effectiveness of collaborative group work in primary schools: effects on science attainment. Br. Educ. Res. J. 33, 663–680. doi: 10.1080/01411920701582231
CrossRef Full Text
Barett, M. (2007). “Practical and ethical issues in planning research,” in Research Methods in Psychology , eds G. Breakell, S. Hammond, C. Fife-Schaw, and J. A. Smith (London: Sage Publications), 24–48.
Baron, R. S. (1986). Distraction-conflict theory: progress and problems. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 19, 1–40. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60211-7
Bennet, N., and Dunne, E. (1992). Managing Classroom Groups. Hemel Hempstead: Simon & Schuster Education.
Blatchford, P., Kutnick, P., Baines, E., and Galton, M. (2003). Toward a social pedagogy of classroom group work. Int. J. Educ. Res. 39, 153–172. doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(03)00078-8
Breakwell, G. M., and Hammond, F., Fife-Schaw, C., and Smith, J. A. (eds). (2006). Research Methods in Psychology . London: Sage Publications.
British Psychology Society (BPS). (2004). Code of Conduct, Ethical Principles, and Guidelines . Available at: http://www.bps.org.uk/document-download-area/document-download.cfm?file_uuid=6D0645CC-7E96-C67F-D75E2648E5580115&ext=pdf
British Psychology Society (BPS). (2006). Code of Ethics and Conduct . Available at: http://www.bps.org.uk/the-society/code-of-conduct/code-of-conduct_home.cfm
Bryman, A. (2012). Social Research Methods . Oxford: University Press.
Cantwell, R. H., and Andrews, B. (2002). Cognitive and psychological factors underlying secondary school students’ feeling towards group work. Educ. Psychol. 22, 75–91. doi: 10.1080/01443410120101260
Elo, S., and Kyngäs, H. (2007). The qualitative content analysis process. J. Adv. Nurs. 62, 107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04569.x
Pubmed Abstract | Pubmed Full Text | CrossRef Full Text
Galton, M., and Williamson, J. (1992). Group Work in the Primary Classroom . London: Routledge.
Galton, M. J., Hargreaves, L., and Pell, T. (2009). Group work and whole-class teaching with 11–14-years-old compared. Cambridge J. Educ . 39, 119–147. doi: 10.1080/03057640802701994
Gillies, R. M. (2003a). The behaviours, interactions, and perceptions of junior high school students during small-group learning. J. Educ. Psychol. 95, 137–147. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.95.1.137
Gillies, R. M. (2003b). Structuring cooperative group work in classrooms. Int. J. Educ. Res. 39, 35–49. doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(03)00072-7
Gillies, R. M., and Boyle, M. (2010). Teachers’ reflections on cooperative learning: Issues of implementation. Teach. Teach. Educ. 26, 933–940. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2009.10.034
Gillies, R. M., and Boyle, M. (2011). Teachers’ reflections on cooperative learning (CL): a two-year follow-up. Teach. Educ. 1, 63–78. doi: 10.1080/10476210.2010.538045
Graneheim, U. H., and Lundman, B. (2003). Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse Educ. Today 24, 105–112. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2003.10.001
Granström, K. (2006). “Group phenomena and classroom management in Sweden,” in Handbook of Classroom Management: Research, Practice, and Contemporary Issues , eds C. M. Evertson and C. S. Weinstein (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum), 1141–1160.
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2008). A scheme for understanding group processes in problem-based learning. High. Educ. 55, 505–518. doi: 10.1007/s10734-007-9071-7
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2010). “Group work is not one, but a great many processes – understanding group work dynamics,” in Group Theory: Classes, Representation and Connections, and Applications , ed. C. W. Danellis (New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.), 153–166.
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2011a). Research on Group Work in Education . New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
Hammar Chiriac, E. (2011b). “Research on group work in education,” in Emerging Issues in Compulsory Education [Progress in Education. Volume 20 ], ed R. Nata (New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.), 25–44.
Hammar Chiriac, E., and Einarsson, C. (2007). “Is the grass greener in the other group? Students’ experiences of group-work” [“Är gräset grönare i den andra gruppen? Studenters erfarenheter av grupparbete”] [Published in Swedish], in Interaction on the Edge 2. Proceedings from the 5th GRASP Conference , ed. J. Näslund (Linköping: Linköping University).
Hammar Chiriac, E., and Granström, K. (2012). Teachers’ leadership and students’ experience of group work. Teach. Teach. Theor. Pract. 3, 345–363. doi: 10.1080/13540602.2012.629842
Hammar Chiriac, E., and Hempel, A. (2013), Handbook for Group Work [Published in Swedish: Handbok för grupparbete – att skapa fungerande grupper i undervisningen] . Lund: Studentlitteratur.
Hansen, R. S. (2006). Benefits and problems with student teams: suggestions for improving team projects. J. Educ. Bus. 82, 11–19. doi: 10.3200/JOEB.82.1.11-19
Johnson, D. W., and Johnson, R. T. (1975). Learning Together and Alone. Cooperative, Competitive and Individualistic Learning (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall).
Johnson, D. W., and Johnson, R. T. (2004). Assessing Students in Groups: Promoting Group Responsibility and Individual Accountability . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Kutnick, P., and Beredondini, L. (2009). Can the enhancement of group work in classrooms provide a basis for effective communication in support of school-based cognitive achievement in classrooms of young learners? Cambridge J. Educ . 39, 71–94. doi: 10.1080/03057640902836880
Lou, Y., Abrami, P. C., Spence, J. C., Poulsen, C., Chambers, B., and d’Apllonia, S. (1996). Within-class grouping: a meta analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 66, 423–458. doi: 10.3102/00346543066004423
Mayring, P. (2000). Qualitative Content Analysis. Forum: Qualitative Social Research 1:2. Available at: http://qualitative-research.net/fqs/fqs-e/2-00inhalt-e.htm_140309
Näslund, J. (2013). “Pupils’ and students’ view on group work” [Published in Swedish: Elevers och studenters syn på grupparbete] in Handbook for Group Work [Published in Swedish: Handbok för grupparbete – att skapa fungerande grupper i undervisningen] , eds E. Hammar Chiriac and A. Hempel (Lund: Studentlitteratur), 233–242.
Peterson, S, and Miller, J. A. (2004). Quality of college students’ experiences during cooperative learning. Soc. Psychol. Learn. 7, 161–183.
Underwood, J. D. M. (2003). Student attitudes towards socially acceptable and unacceptable group working practices. Br. J. Psychol. 94, 319–337. doi: 10.1348/000712603767876253
Uziel, L. (2007). Individual differences in the social facilitation effect: a review and meta-analysis. J. Res. Person. 41, 579–601. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2006.06.008
Webb, N. M., and Palincsar, A. S. (1996). “Group processes in the classroom,” in Handbook of Educational Psychology , eds D. C. Berliner and R. C. Calfee (New York: Macmillan), 841–873.
Zajonc, R. B. (1980). “Compresence,” in Psychology of Group Influence , ed. P. B. Paulus (New York, NY: Lawrence Erlbaum), 35–60.
Keywords : group work, collaborative learning, cooperative learning, higher education, students’ perspectives, qualitative research
Citation: Hammar Chiriac E (2014) Group work as an incentive for learning – students’ experiences of group work. Front. Psychol. 5 :558. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00558
Received: 30 Mar 2014; Accepted: 20 May 2014; Published online: 05 June 2014.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2014 Hammar Chiriac. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eva Hammar Chiriac, Division of Psychology, Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning, Linköping University, SE-581 83 Linköping, Sweden e-mail: [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 30 April 2021
How role-taking in a group-work setting affects the relationship between the amount of collaboration and germane cognitive load
- Jamie Costley ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1685-3863 1
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education volume 18 , Article number: 24 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
24k Accesses
5 Citations
12 Altmetric
Metrics details
This research investigates how learning groups affect student learning from two perspectives: first, the amount of group work students do, and second, the role that they take within the group. It is not clear from the current research how a student’s role in collaborative learning affects his/her development of critical thinking and the construction of knowledge. The present study looks into whether the positive relationships found between collaboration and germane cognitive load are affected by a learner’s role within the group. Using cognitive load theory, this study analyzed survey responses from a group of university students (n = 1399) who engaged in collaborative study groups when taking online classes in South Korea. While it was found that the amount of collaboration a student engaged in positively affected levels of germane load and that their level of contribution negatively moderated that relationship. In other words, while more group work is beneficial, students who contribute less to the group have greater gains from higher levels of collaboration than students who take a more active role.
Introduction
Developing an understanding of how an individual’s ability to contribute to online group work and how those groups collaborate and share information is an important aspect of research into online learning at the tertiary level (Herrmann, 2013 ). Group work and study groups are ubiquitous in higher education and have been shown to benefit students in terms of their performance and learning (Chen & Yang, 2019 ). When dealing with the complex and sophisticated problems facing many learners, the shared and complementary skills and knowledge of a group may be beneficial in processing information (Swanson et al., 2019 ). To help understand how and why group work might benefit learners, we should consider the cognitive underpinnings of how collaboration interacts with learning (DeChurch & Mesmer-Magnus, 2010 ). From this perspective, group work is effective for several reasons. The first is how it might overcome limitations learners have in processing certain pieces of information (Zhang et al., 2016 ). The second is the potential for increasing individual performance and metacognitive abilities by going through the processes of collaboration (Zheng et al., 2019 ). Finally, increasing student’s feelings of emotional support while learning may help overcome some issues of information processing (Hernández-Sellés et al., 2019 ).
One way of understanding these cognitive processes occurring during collaborative learning is through cognitive load theory. There are three elements that make up cognitive load theory: germane load (effort to store information), extraneous load (processing of unnecessary information), and intrinsic load (content complexity). All three elements are connected to how learners process information from their long-term memories to their short-term memories and subsequently retain the information (Klepsch & Seufert, 2020 ). Germane cognitive load is the mental effort that is devoted to retaining information and generating schema of the knowledge to be learned. This system focuses cognitive resources on the processes that will benefit learning (Kirschner et al., 2011 ). For this reason, germane cognitive load is a useful way to understand how different aspects of group work interact with an individual’s cognitive processing during group work. There is a well subscribed body of research using cognitive load theory to understand collaboration in online learning environments (Kirschner et al., 2018 ). However, there is a gap in the research regarding the degree to which the amount of interaction and roles learners take in collaboration will cognitively benefit them. The debate is focused on two differing claims, with the first being that highly motivated students who also contribute substantially to group work are likely to gain the most from learner-to-learner interaction (Homer et al., 2008 ). This perspective argues that learners who have high levels of motivation are likely to participate more and make greater contributions to planning and leadership in groups than those with lower levels of motivation, which may lead to greater gains in learning (Rienties et al., 2009 ). The second, opposing claim is that group work offers a type of scaffolding for learners who may lack motivation or contribute relatively little to the group and that they have the most to gain when engaged in group work (Costley & Lange, 2018 ).
To understand collaboration from two different points of view, two constructs related to group work that were used: group role or contribution , which measured the degree to which each member of the group perceived they contributed to the work that was done; and the amount of group work, which measured the different types of group work students did and how often they engaged in group work. The types of group activities the students engaged in included talking about how they felt about the class, discussing the contents and general information about the class (for example, assignment due dates, checking of the answers to essay questions). The distinction between these two constructs is that the amount of group work refers to the amount and types of group work that the learners engaged in as a part of their class. For example, groups that met more often and engaged in more varied group work (e.g., sharing notes, opinions, and support) would score more highly on this metric. The second construct role or contribution in group work refers to how participants behaved once they were in their groups. This categorized group members into those who contributed a high, moderate, or low amount when they met together. To examine the impact of group work on learning, the present study draws upon literature related to cognitive load theory to gauge and to compare the effects of two different factors in student-to-student interaction: learner role and amount of group work. This research intends to explore the current lack of clarity over the relationship between how students collaborate and how they process information in the form of germane cognitive load. In particular, this research asks the following questions:
Is there an association between the amount of group work learners engage in and their levels of germane cognitive load?
Does that association vary according to the group members’ roles as high, moderate, or low contributors?
In order to understand the interactions between the group and learning, this study will empirically test a conceptual framework that centers on the moderating effects of the following three factors and the relationships among them: group member roles, amount of group, and germane cognitive load. The students who participated in this study were engaged in a wide variety of types of group work. This study seeks to give an overview of group work in general and its effects on cognitive load. Therefore, the current study examines the following hypotheses:
H1: There is a positive relationship between the amount of group work and germane load.
H2: There is a positive relationship between the group work role and germane load.
H3: The role in group work moderates the relationship between the amount of group work and germane load.
Literature review
The amount of group work and germane cognitive load.
The self-explanation principle claims that when students teach themselves something, it may enhance their own levels of germane load for that particular unit of information (Hefter & Berthold, 2020 ). The corollary to this is that students who teach information to others will also tend to have a more thorough and deeper grasp of that subject (Duran, 2017 ). Furthermore, as students engage in more of these types of interactions, the processes that are involved in the development and building of complex and authentic learning are further developed (Andriessen et al., 2003 ). This benefits learning in online contexts, with learners who work together showing higher levels of cognition (Akyol & Garrison, 2008 ). Tsay and Brady ( 2012 ) have shown that students who are engaged in group work learn more, and the more the students interact with one another, the greater the learning.
While the benefits to learning that are gained through group work are clear and well established, not all contexts in which students interact with one another benefit students’ levels of learning (Thom, 2020 ). A fundamental issue with any task or learning activity that a group may need to complete is the cognitive transaction cost that is born by the members of the group when participating in the student-to-student distribution of information, or in the completion of any given group task (Kirschner et al., 2009 ). The groups’ increase in cognitive processing through the division of assignments across differing members may be counteracted or neutralized by the transaction cost of interaction. From this perspective, we need to consider whether all increases in collaboration will lead to improvements in learning. However, the majority of research into collaborative learning suggest that the more types of group work students engage in, and the more often they engage in that group work, the better their levels of engagement with the contents and subsequent learning of the materials. Collaborative learning does have some theoretical basis for affecting a learner’s levels of cognitive load, with some evidence showing improvements in levels of germane load when learners collaborate, as well as a mitigating effect of collaboration on the more challenging elements of some learning environments (Kirschner et al., 2011 ).
Role-taking in group settings and germane cognitive load
Teams that are efficient and effective link compatible elements of each individual’s cognitive understanding of their tasks (Cooke et al., 2007 ). In group-based tasks, a group of individuals must coalesce and contribute together towards the objective of what is to be learned to augment in-class learning (Johnson et al., 2014 ). In this context learners will take on different roles and contribute to different levels. Learners with high levels of motivation are more likely to contribute to group work through planning, sharing of information, and cognitively-focused discourse in group learning contexts (Rienties et al., 2009 ). When learners interact, they must subsume their own goals to the goals of the group to some degree (Wosnitza & Volet, 2009 ). Highly motivated students who are likely to contribute substantially may face greater challenges in a group as they bring a stronger sense of their own goals, which may conflict with the group goals (Järvelä et al., 2010 ). Regardless, there is some suggestion that those who contribute more in collaboration learning environments will have greater cognitive benefits (Kirschner et al., 2018 ).
Role-takings affect on the relationship between amount of group work and germane cognitive load
The question of who within a group benefits the most from higher levels of interaction is open, and an understanding of how different types of learners may benefit is an important part of research into learner-to-learner interactions. More motivated and active students tend to push in a positive direction only when they realize they can succeed only if the whole group does, which tends to lead them to make greater contributions and share more information that benefits all learners (Johnson & Johnson, 2003 ). This allows all group members to support each other, and students who may have contributed less to knowledge sharing receive all of the benefits of the group’s knowledge and production (Pee et al., 2010 ). Therefore, students who are less active and who may not have contributed greatly to the group directly are able to be scaffolded by the students who have made greater contributions through the adoption of the goals of the group as a whole (Johnson & Johnson, 2003 ). This suggests that role-taking may moderate the relationship between the amount of group work and germane load, as students who have a lesser role in group work benefit more from higher amounts of collaboration.
Research procedures and data collection
A quantitative approach was employed, using surveys to help understand the research questions that were a part of the present study. The survey used in this research was the fourth in a series of large surveys into the OCU. The items were written first in English and then translated into Korean, which is the native language of students taking OCU classes. From there, an expert in online learning, in general, and the OCU as a learning platform, specifically, checked the survey’s translated items to verify that they were accurate reliable translations of the English items. The survey in a Google Sheets form, was then sent to the main ethics and administrative offices of the OCU for verification that the items and survey were appropriate for distribution to the students of the OCU. The OCU administration then posted a link to the survey, inviting students to participate in the research project.
Respondent profile
The intent of this study was to investigate the direct and moderating effects of perceptions of the types of study group activities on perceived germane cognitive load in online learning situations. In order to do so, the study draws on research from the fields of educational technology and cognitive psychology. The present research examined learners taking classes at the Open Cyber University (OCU) in South Korea, which provides credit classes online for students who are enrolled at traditional brick-and-mortar universities. Twenty-three member universities make up the OCU, which offers 400 classes and serves 120,000 students per year (Open Cyber University of Korea, n.d.). In total, 2260 valid surveys were submitted, and after receiving the data file, responses from subjects who did not engage in any group work were excluded. This left 1455 subjects who were appropriate for participation in this study. Following this, linear regression of group work level and group work roles onto germane load was used to generate Mahalanobis, Cook’s, and Leverage values in order to find outliers. Those participants whose results failed the standard for two or more of these tests were removed from the analysis, leaving 1399 eligible participants. No traits were shared when comparing the whole original set of surveys and the final 1399 eligible participants. The subsequent results and tables following this are derived from the 1399 remaining participants. Of 1399 remaining participants, 706 (50.5%) were female and 693 (49.5%) were male. The youngest subject was 18, and the oldest subject was 52, with a mean age of 23.63. The students who took part in this study took a variety of classes which filled a wide range of subject categories with the greatest number being liberal arts courses (31% of subjects), social science courses (17%), information technology courses (15%), lifestyle and health courses (14%), management and business classes (7%), foreign languages classes (7%), natural sciences classes (5%), and finally students taking design courses (4%). The class distributions and break down of demographic variables is similar to previous research into cyber universities in South Korea in general (Suh & Kim, 2013 ) and from research into the OCU specifically (Hughes et al., 2019 ).
Instrument development
To measure germane load, four items from Leppink et al. ( 2013 ) paper titled “The development of an instrument for measuring cognitive load” were adopted. This scale used Likert-type items ranging from 1 to 7, with 1 being “strongly disagree” and 7 being “strongly agree”. The four items measuring germane load used in the present study are as follows: (1) The lecture really enhanced my understanding of the topic , (2) the lecture really enhanced my knowledge and understanding of the of the class subject , (3) the lecture really enhanced my understanding of the concepts associated with the class subject, and (4) the lecture really enhanced my understanding of concepts and definitions. The four items were combined and averaged into a single construct labeled germane load. The Cronbach’s alpha for the germane load variable was 0.956, which is appropriate for this type of research. In regards to germane cognitive load’s validity and reliability, research by Klepsch and Seufert, ( 2020 ), showed that Leppink et al’s ( 2013 ) cognitive load items are reasonably defined that germane load was a separated construct from the other aspects of cognitive load. Furthermore, even as a subjective judgement of learning, the conceptualization of germane load provides valuable insight into students’ cognitive development (Leppink et al., 2015 ).
To measure the amount of group work, two variables were used: (1) group work variety and (2) group work regularity. In order to discover group work variety, participants were asked to respond to a single item which asked: How did you interact with people you know offline who were taking the same class? (Please check all that apply) . The participants could respond by checking boxes with seven options: (1) we talked generally about the class (“The class is easy, the class is stressful”) ; (2) we talked about the contents of the class ; (3) we studied together ; (4) we shared notes or materials ; (5) other (activities falling under this category included but were not limited to editing others work, checking answers, and reminders about dates/times/assessment); and (6) I never interacted with anyone offline. How the participants responded were then coded in six separate variables as either not occurring or occurring , with the five positive indicators (with the exclusion of I never interacted with anyone offline ) being combined into a single additive index labeled group work variety . To generate the group work regularity variable, a single item was used. This read, Approximately, how much offline interaction did you have? The participants were then given five options to respond: (1) more than once a week (2) once a week , (3) once every 2 weeks , (4) once a month, and (5) I wasn’t part of a study group . Students’ responses on this item were combined with the group work variety index to create one total additive index called total group work , which was used as the independent variable for this study.
This research sought to gain a broad understanding of group work, so there was great variety in the way the students interacted. To investigate the amount of contribution students made to the group they were a part of, one item was used. This item asked participants to check a box stating what their main role was within the group. This created the data for the variable role in group work . The results from this item allowed the sorting of participants into three categories: high contributors, moderate contributors, and low contributors to group work. These were then put into categorical variables scored as 1 for low, 2 for moderate, and 3 for high. This variable was used as the moderating variable for this study. The subjects in this study were engaged in a variety of group work over the course of the semester. Each class would have had different group combinations and different types of activities. This includes group size and length of time working together. The variable is used to understand if being primarily a contributor of information or primarily a receiver of information is more beneficial. The Breusch–Pagan test and Koenker test were used to test for homoscedasticity. The variables used in this study met the assumptions of linear regression.
Common method variance
An issue with research like that done in the present study relates to common method variance. This is because all items used in this study were taken from a single survey (Porumbescu, 2017 ). For this reason, the relationships discovered by that analysis of the variables the present study investigated may be subject to influences that may systematically affect relationships between variables, leading to erroneous relationships being discovered (Podsakoff et al., 2003 ). The key way to reduce common method bias in this type of research is in the design of the survey and the construction of the items (Jakobsen & Jensen, 2015 ). There are several strategies suggested by MacKenzie and Podsakoff ( 2012 ) used in the present study to mitigate common method bias. These are that items should be simply worded, easy to understand and varied response scales. The scales used to measure germane cognitive load are easy-to-understand Likert type items that have been used in many previous studies without confusion. The measure of amount of group work asks students to simply check boxes of the type of group work they engaged in and how often, which should make it relatively clear and easy for them to complete. The role-taking variable also asks simply about their perceived level of contribution. While common method bias should still be considered, for the aforementioned reasons along with the lack of a strong relationship between role-taking and amount of group work, it is reasonable to believe the results of the present study are not greatly affected. For this reason, Harman single factor method for measuring common method bias was used. This analysis showed that a single factor accounted for 41% of the variance found regarding the variables of interest in the present study. This is below the cut-off of 50% and suggests that there is not systematic common method bias in the present study (Harman, 1976 ).
The means, standard deviations, and Pearson correlation coefficients of the main variables used in this research are shown in Table 1 . The results show that the amount of group work was negatively and significantly correlated with role in group work (β = − 0.097, p < 0.05), though the correlation coefficient was small. Amount of group work was much more strongly and positively correlated with germane load (β = 0.551, p = < 0.01). Finally, there was no statistically significant relationship between role in group work and germane load (β = 0.015, p = > 0.05). The mean for the amount of group work was 4.37, with a standard deviation of 1.71. The mean for germane load was 4.88, with a standard deviation of 1.24. Means and standard deviations were not calculated for role in group work as it was a categorical variable.
Linear regression was used to measure the effect of both role in group and amount of group work on germane load. Overall, the model predicted increased levels of germane load with moderate accuracy (r 2 = 0.3224). This result shows that together both the independent variable and the moderating variable combined positively impacted germane cognitive load. More specifically, each unit increase in the amount of group work led to a 0.65 ( p = < 0.001) increase in germane load.
To test the interaction effects of amount of group work and role in group work on germane load, PROCESS macro (model 1, Hayes, 2013 ) was used, as can be seen in Fig. 1 . To show this, 10,000 bootstrap samples with a 95% confidence interval were used. Furthermore, variables were mean centered to ± 1 standard deviation, showing strong evidence of an interaction that was based on the standardized coefficients that were produced. Role in group work negatively moderated the relationship between amount of group work and germane load, or in other words, as a student’s role changes to contribute more, the strength of the relationship between the amount of group work and germane load moderately decreases.
The moderating effect of group contribution on the relationship between amount of group work and germane load
PROCESS macro was used to center variables and measure the moderated effect of amount of group work on germane load at the level of average role in group work, and at one standard deviation above and below the mean. Therefore, there were low, average, and high groupings of relationships between the amount of group work and germane load. In all three conditions, there was a statistically significant relationship between the amount of group work and germane load. However, as can be seen in Table 2 , in the low contributor role condition, the effect size (0.51) is stronger than in the average contributor role condition, (0.42) and stronger again than in the high contributor role condition (0.33). As shown in Fig. 2 , this creates an effect where the lines draw more closely together, whereby the low contributor role condition has a steeper line than that of the average contributor role condition, and the high contributor role condition is slightly flatter than both. This leads to the lines intersecting where germane load and amount of group work is high.
The present study shows that group work to support online classes will improve higher-order cognitive skills as represented by germane cognitive load. That is, as the amount of group work students engage in increases, so do learners’ levels of cognitive germane load. This shows that the process of group collaboration leads to at least some level of perceived individual learning, which is the ultimate goal of much of online group work (Kalyuga, 2013 ). This may be caused by collaboration leading to greater effort put forth by learners, which may lead to greater learning. The present study gives support to the notion that collaborative learning can help with developing higher cognitive skills in online learning situations in which some learners struggle (Akyol & Garrison, 2008 ; Kirschner et al., 2011 ). The present study goes some way to refuting claims that transaction cost in collaboration may harm learning by showing that greater variety and amount of learner-to-learner interaction lead to higher levels of cognitive development in the form of germane cognitive load. More specifically, the results found in the present study support research that shows that more interaction between learners leads to greater learning (Huang et al., 2019 ). Therefore, as this study shows, learners in groups that meet more often and engage in a greater variety of types of collaboration will benefit in the form of higher levels of germane cognitive load.
Some research claims that the scaffolding offered by the group to weaker members who make less of a contribution means that lower contributors benefit more (Pee et al., 2010 ). The present study showed that learners who make fewer contributions to group work have higher perceived levels of germane cognitive load than those who make a greater contribution to group work. Though the effect found in the present study is small, it is statistically significant. This result is likely caused by two factors. The first is the difficulty high contributors may have in subsuming their own goals and interests to the group’s goals and interests (Järvelä et al., 2010 ). The second factor is the learner-to-learner interaction provided by the group offers low contributors the scaffolding and processing power of the high contributors in the group (Costley & Lange, 2018 ; Pee et al., 2010 ). According to Duran ( 2017 ), those who teach contents to others will have a more complete understanding of those contents.
As each learner will contribute to their own level of knowledge and ability (Johnson & Johnson, 2003 ), those who may be more knowledgeable will give the weaker members of the group the information they require. It may be that the higher contributors are tutoring the students who are making less of a contribution. This may lead to lower gains from group work for the high contributors and greater gains for the low contributors. This fits well within the current theoretical explanation of cognitive load in that the group work allows the sharing of mental models, which leads to greater cognitive development (Kirschner et al., 2018 ). According to Duran ( 2017 ), those who teach contents to others will have a more complete understanding of those contents. As each learner will contribute to their own level of knowledge and ability (Johnson & Johnson, 2003 ), those who may be more knowledgeable will give the weaker members of the group the information they require. This helps explain the moderating effect that was found as part of the present study that provides a deeper understanding of the dynamics that are occuring the context of collaboration in online learning environments.
Theoretical and practical implications
The present study looked at how the amount of group work a learner does and his/her role within the group interact to affect germane load. More specifically, we asked if the members role in the group moderated the effect of more collaboration on germane cognitive load. The theoretical contribution of this paper is that we have shown that as the contribution to the group increased, the relationship between level of group work and germane cognitive load decreased. Although group work had a positive relationship with germane cognitive load, the relationship was weaker in the high contribution group work condition. In other words, doing more group work was more beneficial for the low contributors when compared with the high contributors. There is a kind of transaction here—high level contributors gain from teaching; low level contributors gain from scaffolding. Furthermore, in the present study, that transaction benefits the low contributor more than the high contributor. This research has shown that while group work benefits learners, learners do not have to be high contributors to gain these benefits. In fact, the learners who contribute less to the group achieve greater relative gains than those who contribute substantially to the group. This does not imply that being a high contributor to the group is bad per se, as the high contributors still benefited considerably from the group work; however, low contributors will make even greater gains.
This research helps to fill in our understanding of group work in online situations. The value of this to the field of educational research is that it gives a more well-rounded view of the nature of collaboration online and allows us to understand that the effects of collaboration are not just a factor of the amount of group work, but also related to the behaviors of the individuals within the group. Pedagogically speaking, this research adds to the body of literature by showing the value of varied types of learner-to-learner interactions within an online course that are happening regularly (the direct relationship between amount of group work and germane load). However, this research also shows that collaboration is of value for all learners, regardless of their contribution to group work. From a practical pedagogical point of view, this research allows us to see that learners are primarily gaining an advantage from just being a member of a group, not necessarily by making large contributions to that group. Based on this research, students should be encouraged to study together regardless of their level of knowledge or confidence. The main practical contribution of this study is to show that students who may not be able to contribute greatly to a group can still substantially benefit from the interactions they have with other learners.
Conclusion and limitations
In online learning environments, students will benefit when they are part of learning groups to help support their study towards their classes. One of the reasons this may be effective is that many large online courses lack student-to-student interaction, and these learning groups give students the opportunity to share what they know and what they have learned (Kirschner et al., 2009 ). The present study shows the importance of these groups by revealing the cognitive benefits students will get from studying together. Furthermore, this study shows that those learners who contribute little will also benefit from group work. The main limitation of this study is that it is based on a survey that deals with student perceptions of their levels of group work and germane load. Future research should utilize more varied constructs to create more focused and reliable measurements of the amount of group work learners are doing and their roles within the group. For example, controlled experiments where the learners’ amount of group work are controlled and their contributions are observed and measured may allow a deeper understanding how different types of learners contribute to the group and how those contributions affect the group. Also, further investigation into the specific behaviors of those who classify themselves as high, moderate, or low contributors will allow us to more deeply understand how the specifics of group dynamics impact learning and collaboration. While the present model does show some effect of the collaborative variables on germane cognitive load, this model could be improved by the inclusion of other variables related to student interface with the learning environment usability. Furthermore, investigations into the issues of group formation and how group dynamics change over time will further develop our understanding of learner-to-learner interactions in an online setting. This research has value because it gives us a deeper understanding of the dynamics of learner-to-learner interaction as well as how those interactions impact learning. This area of research is fruitful for researchers as it helps give empirical weight to many of the assumptions of collaborative learning, and provides nuance to our understanding of theory.
Availability of data and materials
The data for this study was available to reviewers on reasonable request.
Akyol, Z., & Garrison, D. R. (2008). The development of a community of inquiry over time in an online course: Understanding the progression and integration of social, cognitive and teaching presence. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 12 (2–3), 3–23.
Google Scholar
Andriessen, J., Baker, M., & Suthers, D. (2003). Arguing to learn. Confronting Cognitions in computer—Supported collaborative learning environments . . Kluwer.
MATH Google Scholar
Chen, C. H., & Yang, Y. C. (2019). Revisiting the effects of a project-based learning on students’ academic achievement: A meta-analysis investigating moderators. Educational Research Review, 26 (1), 71–81.
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Cooke, N. J., Gorman, J. C., Duran, J. L., & Taylor, A. R. (2007). Team cognition in experienced command-and-control teams. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 13 , 146–157.
Costley, J., & Lange, C. (2018). The moderating effects of group work on the relationship between motivation and cognitive load. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning , 19 (1).
DeChurch, L. A., & Mesmer-Magnus, J. R. (2010). The cognitive underpinnings of effective teamwork: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95 (1), 32–53.
Article Google Scholar
Duran, D. (2017). Learning-by-teaching. Evidence and implications as a pedagogical mechanism. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 54 (5), 476–484.
Harman, H. H. (1976). Modern factor analysis . . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis . . The Guilford Press.
Hefter, M. H., & Berthold, K. (2020). Preparing learners to self-explain video examples: Text or video introduction? Computers in Human Behavior, 110 , 106404.
Hernández-Sellés, N., Muñoz-Carril, P. C., & González-Sanmamed, M. (2019). Computer-supported collaborative learning: An analysis of the relationship between interaction, emotional support and online collaborative tools. Computers & Education, 138 , 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.04.012 .
Herrmann, K. J. (2013). The impact of cooperative learning on student engagement: Results from an intervention. Active Learning in Higher Education, 14 (3), 175–187.
Homer, B. D., Plass, J. L., & Blake, L. (2008). The effects of video on cognitive load and social presence in multimedia-learning. Computers in Human Behavior, 24 (3), 786–797.
Huang, C. Q., Han, Z. M., Li, M. X., Jong, M. S. Y., & Tsai, C. C. (2019). Investigating students’ interaction patterns and dynamic learning sentiments in online discussions. Computers & Education, 140 , 103589.
Hughes, C., Costley, J., & Lange, C. (2019). The effects of multimedia video lectures on extraneous load. Distance Education, 40 (1), 54–75.
Jakobsen, M., & Jensen, R. (2015). Common method bias in public management studies. International Public Management Journal , 18 (1), 3–30.
Järvelä, S., Volet, S., & Järvenoja, H. (2010). Research on motivation in collaborative learning: Moving beyond the cognitive–situative divide and combining individual and social processes. Educational Psychologist, 45 (1), 15–27.
Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (2003). Student motivation in cooperative groups. In R. M. Gillies & A. F. Ashman (Eds.), Co-operative learning: The social and intellectual outcomes of learning in groups. (pp. 136–176). Oxfordshire: Routledge.
Johnson, D. W., Johnson, R. T., & Smith, K. A. (2014). Cooperative learning: Improving university instruction by basing practice on validated theory. Journal on Excellence in University Teaching, 25 (4), 1–26.
Kalyuga, S. (2013). Enhancing transfer by learning generalized domain knowledge structures. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 28 (4), 1477–1493.
Kirschner, F., Paas, F., & Kirschner, P. A. (2009). A cognitive load approach to collaborative learning: United brains for complex tasks. Educational Psychology Review, 21 , 31–42.
Kirschner, F., Paas, F., Kirschner, P. A., & Janssen, J. (2011). Differential effects of problem-solving demands on individual and collaborative learning outcomes. Learning and Instruction, 21 (4), 587–599.
Kirschner, P. A., Sweller, J., Kirschner, F., & Zambrano, J. (2018). From cognitive load theory to collaborative cognitive load theory. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 3 (2), 213–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-018-9277-y .
Klepsch, M., & Seufert, T. (2020). Understanding instructional design effects by differentiated measurement of intrinsic, extraneous, and germane cognitive load. Instructional Science, 48 (1), 45–77.
Leppink, J., Paas, F., Van der Vleuten, C. P., Van Gog, T., & Van Merriënboer, J. J. (2013). Development of an instrument for measuring different types of cognitive load. Behavior Research Methods, 45 (4), 1058–1072.
Leppink, J., van Gog, T., Paas, F., & Sweller, J. (2015). Cognitive load theory: Researching and planning teaching to maximise learning. In Researching medical education (pp. 207–231)
MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, P. M. (2012). Common method bias in marketing: Causes, mechanisms, and procedural remedies. Journal of Retailing, 88 (4), 542–555.
Pee, L. G., Kankanhalli, A., & Kim, H. W. (2010). Knowledge sharing in information systems development: A social interdependence perspective. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 11 (10), 550.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88 (5), 879.
Porumbescu, G. (2017). Not all bad news after all? Exploring the relationship between citizens’ use of online mass media for government information and trust in government. International Public Management Journal, 20 (3), 409–441. https://doi.org/10.1080/10967494.2016.1269859 .
Rienties, B., Tempelaar, D., Van den Bossche, P., Gijselaers, W., & Segers, M. (2009). The role of academic motivation in Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning. Computers in Human Behavior, 25 (6), 1195–1206.
Suh, S., & Kim, S. (2013). Study on policy for an entrance quota of cyber universities . . Korea Educational Information and Research Service.
Swanson, E., McCulley, L. V., Osman, D. J., Scammacca Lewis, N., & Solis, M. (2019). The effect of team-based learning on content knowledge: A meta-analysis. Active Learning in Higher Education, 20 (1), 39–50.
Thom, M. (2020). Are group assignments effective pedagogy or a waste of time? A review of the literature and implications for practice. Teaching Public Administration, 38 (3), 257–269.
Tsay, M., & Brady, M. (2012). A case study of cooperative learning and communication pedagogy: Does working in teams make a difference? Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 10 (2), 78–89.
Wosnitza, M., & Volet, S. (2009). A framework for personal content goals in collaborative learning contexts. In Contemporary motivation research: From global to local perspectives (pp. 49–67).
Zhang, L., Kalyuga, S., Lee, C., & Lei, C. (2016). Effectiveness of collaborative learning of computer programming under different learning group formations according to students’ prior knowledge: A cognitive load perspective. Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 27 (2), 171–192.
Zheng, L., Li, X., Zhang, X., & Sun, W. (2019). The effects of group metacognitive scaffolding on group metacognitive behaviors, group performance, and cognitive load in computer-supported collaborative learning. The Internet and Higher Education, 42 , 13–24.
Download references
There is no funding to declare in relation to this paper.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
National Research University Higher School of Economics, Institute of Education, Myasnitskaya Ulitsa, 20, Moscow, 101000, Russia
Jamie Costley
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jamie Costley .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Costley, J. How role-taking in a group-work setting affects the relationship between the amount of collaboration and germane cognitive load. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 18 , 24 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-021-00259-w
Download citation
Received : 09 November 2020
Accepted : 25 March 2021
Published : 30 April 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-021-00259-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Cognitive load
- Collaboration
- Germane cognitive load

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Psychologists have studied small groups for well over 60 years. Much of that research was initially conducted by social psychologists who were interested in how individual behavior was influenced by the group context and in factors that influenced interpersonal processes and group behavior (McGrath, 1964).For example, early work focused on power and social influence, social forces that bond ...
The aim of this article is to add to the current level of knowledge and understandings regarding the essence behind successful group work in higher education. This research is focused on the students' experiences of group work and learning in groups, which is an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work prior to the beginning of ...
The aim of this article is to add to the current level of knowledge and understandings regarding the essence behind successful group work in higher education. This research is focused on the students' experiences of group work and learning in groups, which is an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work prior to the beginning of ...
Research suggests that groups which are assigned by the instructor tend to perform better than self-selected groups (Felder & Brent, 2001). Teaching Students It is difficult for teachers to design and implement group work effectively, and it is diffi- ... in this paper). When a group is not working well together, the students need to learn how
This research investigates how learning groups affect student learning from two perspectives: first, the amount of group work students do, and second, the role that they take within the group. It is not clear from the current research how a student's role in collaborative learning affects his/her development of critical thinking and the construction of knowledge. The present study looks into ...
The research showed that students were more likely to have positive attitudes about group work if they had instructors who discussed group management issues (e.g., group dynamics) and used methods ...
Virtually all of the research papers close with the obligatory acknowledgement that "more research is needed." And, while it is true that there is much we psychologists do not yet know about team effectiveness, there is much that we do. ... Indeed, work groups and teams have been characterized as processors of information (Hinsz, Tindale ...
Introduction. Collaborative group work (CGW) is recognised as a powerful tool in education to enhance student engagement and learning (Stanley and Zhang Citation 2020).In the higher education context, CGW - where students work together in small groups to achieve a common goal - is considered indispensable (Sridharan, Tai, and Boud Citation 2019). ...
This research is focused on the students' experiences of group work and learning in groups, which is an almost non-existing aspect of research on group work prior to the beginning of the 21st ...
CONCLUSION. As we conclude our work on this three-part special issue, we are filled with a mixture of gratitude, satisfaction, and hope. We want to extend our appreciation to those who were historically involved in the Emerging Scholar program within the Association of Specialists in Group Work, as their investment in and exchange of ideas about research in group work were the initial sparks ...